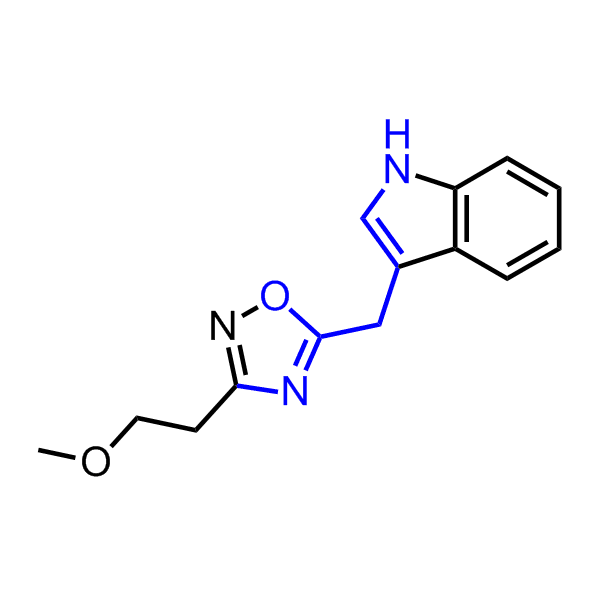
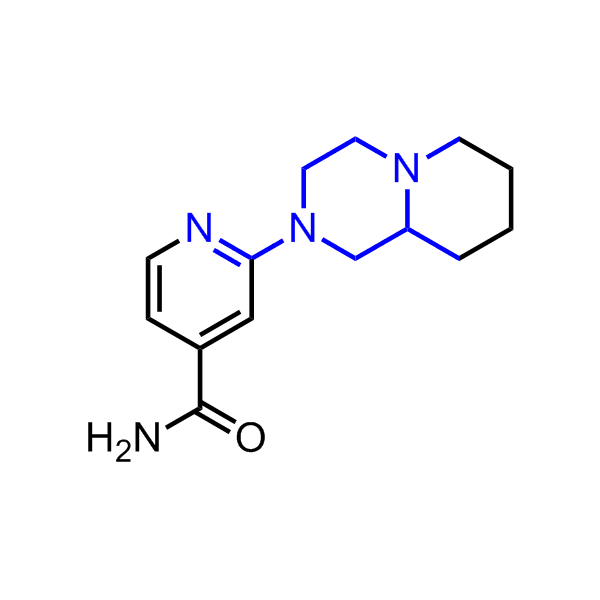
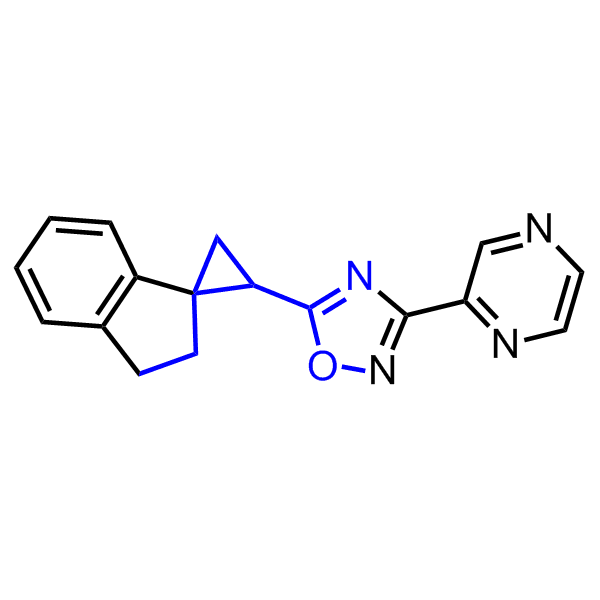
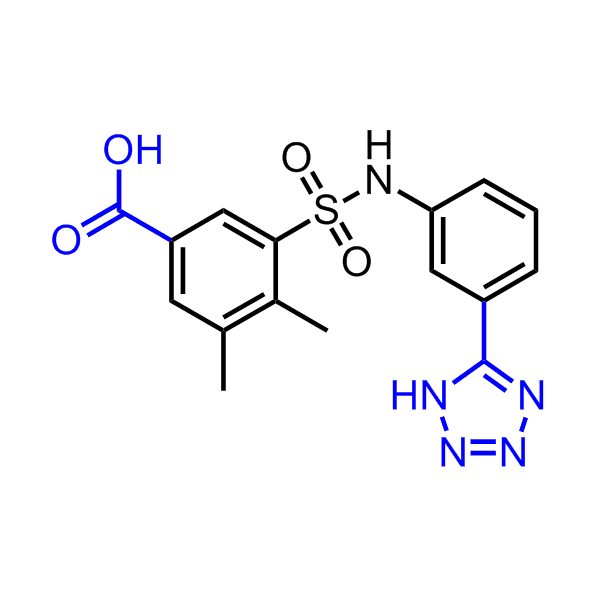
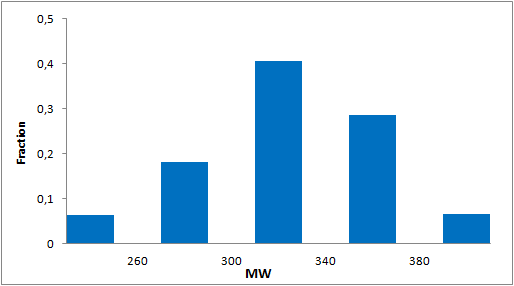
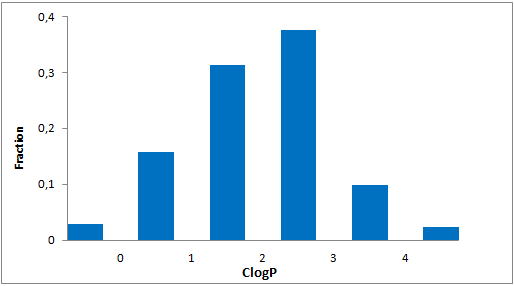
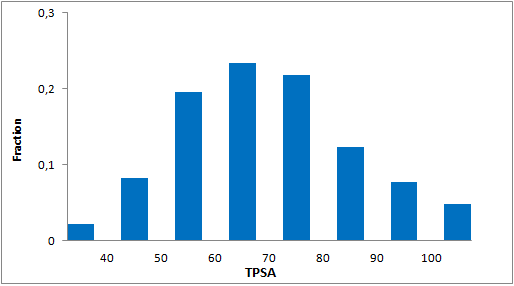
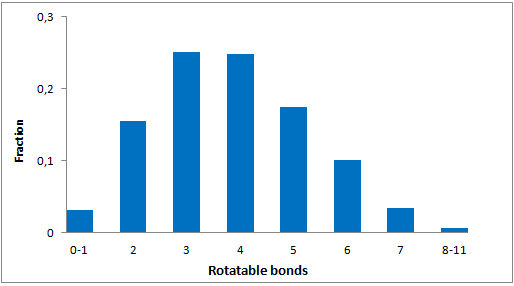
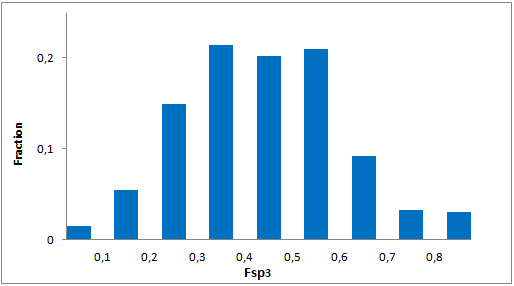
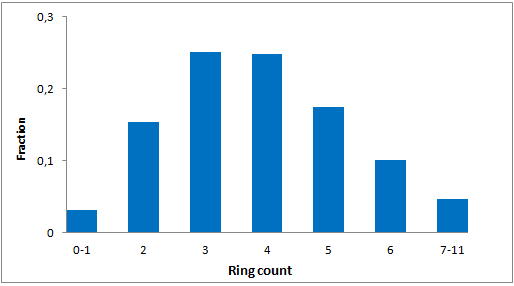
A set of compounds focused on targeting molecular chaperones
2 468 compounds
Protein folding is very important as attractive field in new drug development paradigm. Control of these processes in the cell achieves through action of assembly of enzymes known as molecular chaperones. This set of diverse protein families assists a large variety of processes involving folding, translocation, unfolding, disaggregation and homeostasis of proteins within the cellular environment. In spite of intensive studies, the spectrum of cellular substrates and functions mediated by these different chaperones remains largely undefined. Meanwhile, targeting molecular chaperones is proven to be crucial for the prevention of the many deleterious effects of protein misfolding and aggregation, which might lead in the end in cell death, in neurodegeneration and in other protein misfolding diseases.
Enamine has been following investigation on molecular chaperones for years and developed a library of 2 468 synthetic compounds potentially targeted molecular chaperones. The emphasis has been made on most promising and studied targets: Heat shock proteins (Hsp90, Hsp82, Hsp27), Chaperone activity of bc1 complex-like and histone-chaperone ASF1a complex (ASF1-histone interaction). In addition, the library was enriched with bioisosteric replacement and compounds bearing new chemotypes predominantly with polar scaffolds and cores to increase novelty of the targeted sets.
The library is available in convenient and ready to ship pre-plated formats. Also, the library can be delivered in any other custom formats within a week only.
Typical Formats
Molecular Chaperones Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
MCL-2468-0-Z-10
Compounds
2 468
2 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
MCL-2468-10-Y-10
Compounds
2 468
8 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
MCL-2468-50-Y-10
Compounds
2 468
8 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
MCL-2468-10-Y-10 screening library 2 468 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.7M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD file
Library design
- Ligand based approach: pharmacophore searches, bioisosteric replacement, 3D shape-based screening.
- Protein/target-based: Docking, in silico screening with protein-ligand key interaction feature constraints.
- Strict MedChem filters including PAINS and other industry affiliated structural filters and rules.
The sets of the reported active molecules, collected for the targets mentioned above, were carefully analyzed. Series of 3D pharmacophore models within volume restriction constraints were created and further validated with the set of reference actives and non-active ligands (Figure 1). Enamine’s MedChem stock compound collection (Ro5 compliant and filtered through series of MedChem filters) was then screened against these models. The results were inspected visually, and molecules derived from trivial chemotypes, as well as those poorly matching the pharmacophore models, were removed. The bioisosteric replacement of the core structures and selection of compounds by privileged motifs were also used to enrich the library with new valuable structures and prospective drug/lead-like compounds.
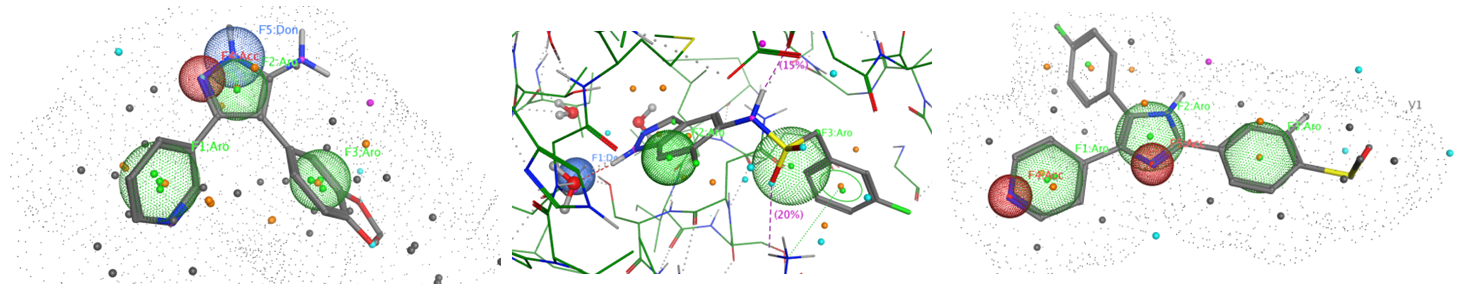
Figure 1. Examples of 3D pharmacophore models. In the cases when protein 3D structure was known superposition of ligand and protein key features was used to create pharmacophore model.
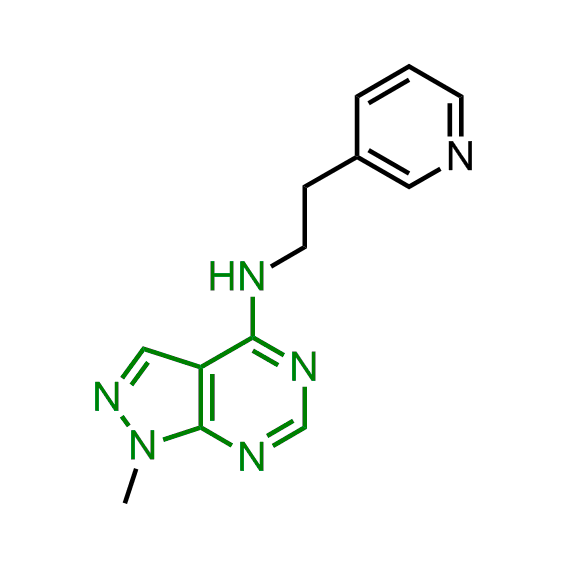
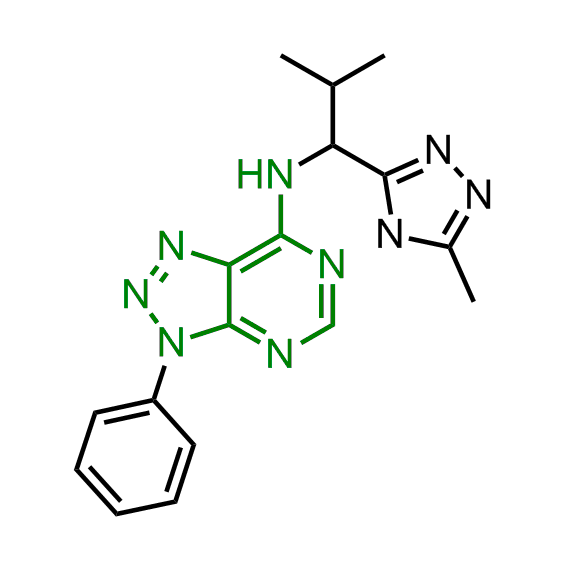
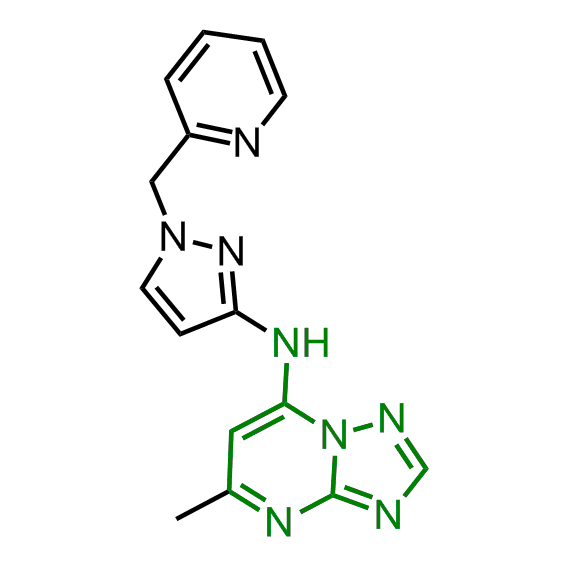
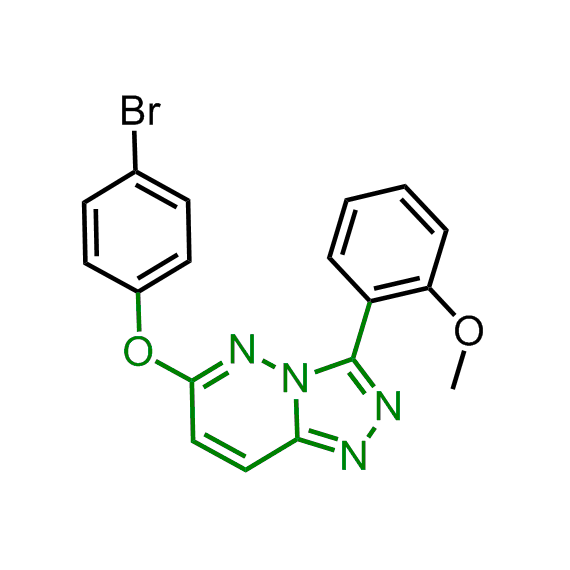
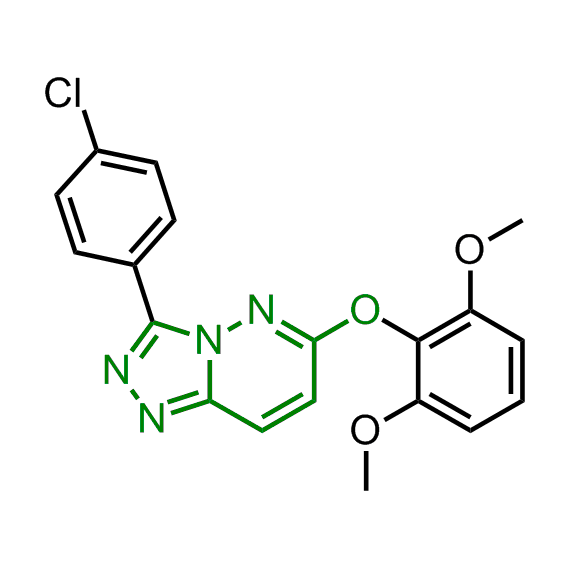
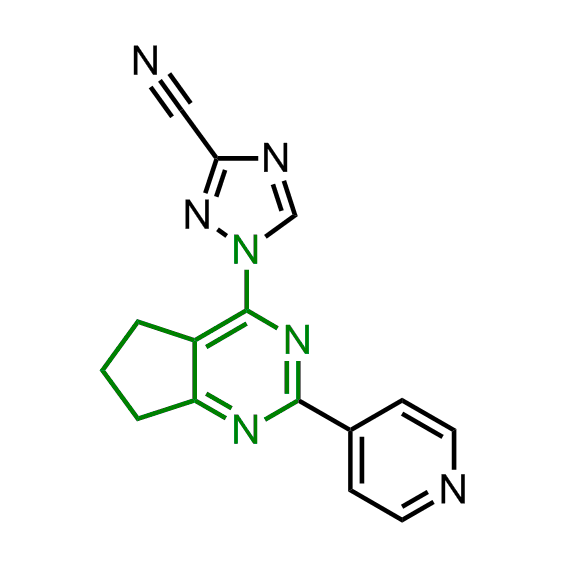
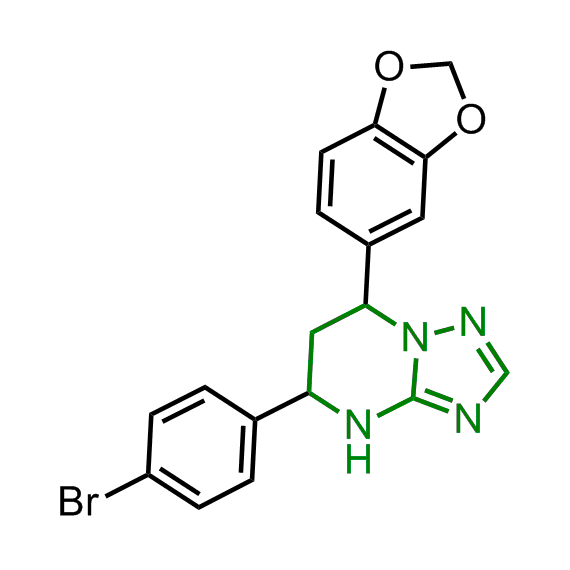
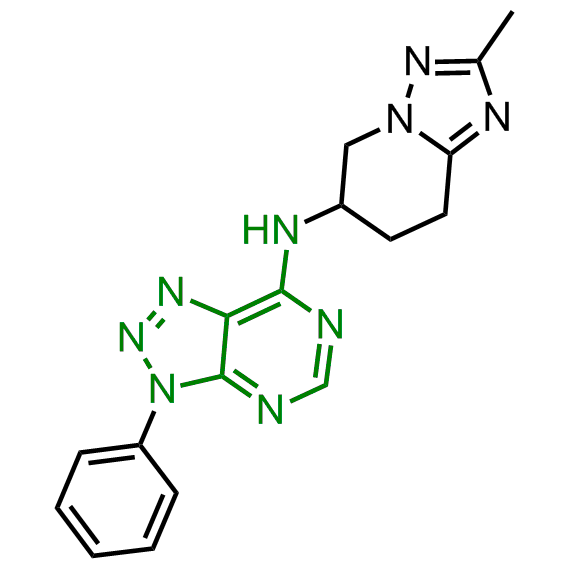
Examples of the molecules in the library
Bioisosteric replacements of the adenosine core of known highly active molecular chaperones ligands
Library of potential tubulins ligands
3 200 compounds
Tubulin targeted library was designed using a combination of different approaches, including molecular docking, substructure and similarity, topological analogs search, molecular parameters restrictions, and specially developed structural filters.
Tubulin library is available in pre-plated format and can be quickly delivered in any customized format.
Typical Formats
Tubulin Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
TBL-3-0-Z-10
Compounds
3 200
3 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
TBL-3-10-Y-10
Compounds
3 200
10 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
TBL-3-50-Y-10
Compounds
3 200
10 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
TBL-3-10-Y-10 screening library 3 200 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.7M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library design
Protein structures recorded recently in PDB were considered and analyzed to be most suitable for in silico screening: 4YJ2, 5C8Y, 5CA1. The main features of protein-ligand interaction in the binding site of all three tubulin structures are very similar and could be superimposed. Hence, the protein docking model was built based on the features of critical amino acid residues in the binding pocket and ligand interactions observed in analyzed protein structures.
The docking models have been validated with a reference set of known actives (110 ligands) and nonactive molecules. Molecular queries and docking constraints were corrected according to the activity of the reference compound set.
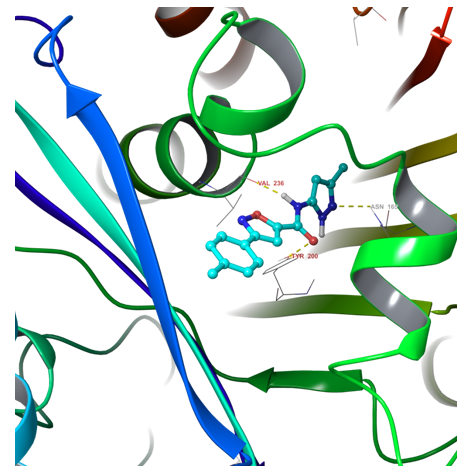
Fig. 1. Example of hit binding confirmation after docking calculation
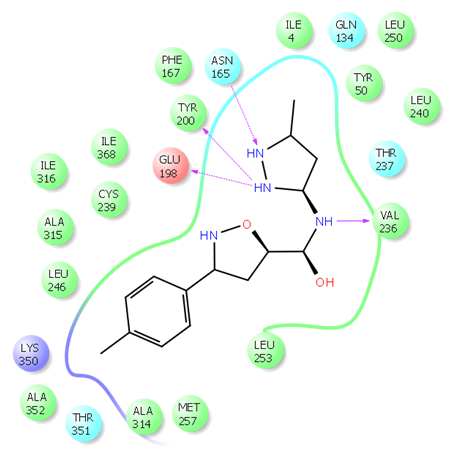
Fig. 2. 2D ligand interaction diagram of hit compound Z666232790 with a high docking score
2D Similarity search & topological analogues search
- The reference compound set was carefully compiled from available literature sources and databases: ChEMBL, BindingDB, and PudChem.
- A Tanimoto similarity range of 95–80% was used for compound selection.
- Topological fields and bioisosteric group replacement were used to search for analogs of the most potent tubulin inhibitors.
Examples of active molecules
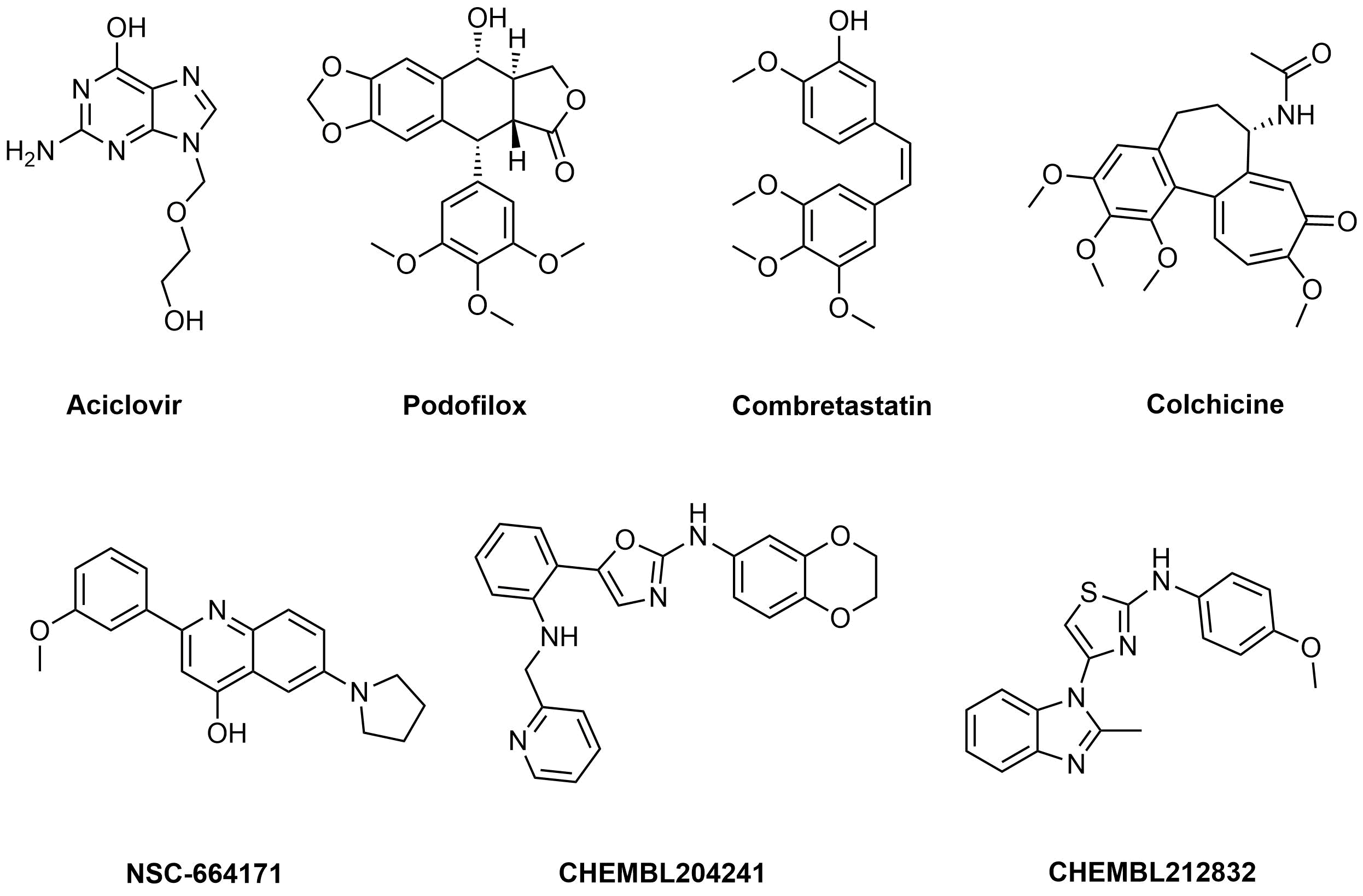
Approximately 900 compounds were selected using this approach.
Examples of molecules in Tubulin Targeted Library
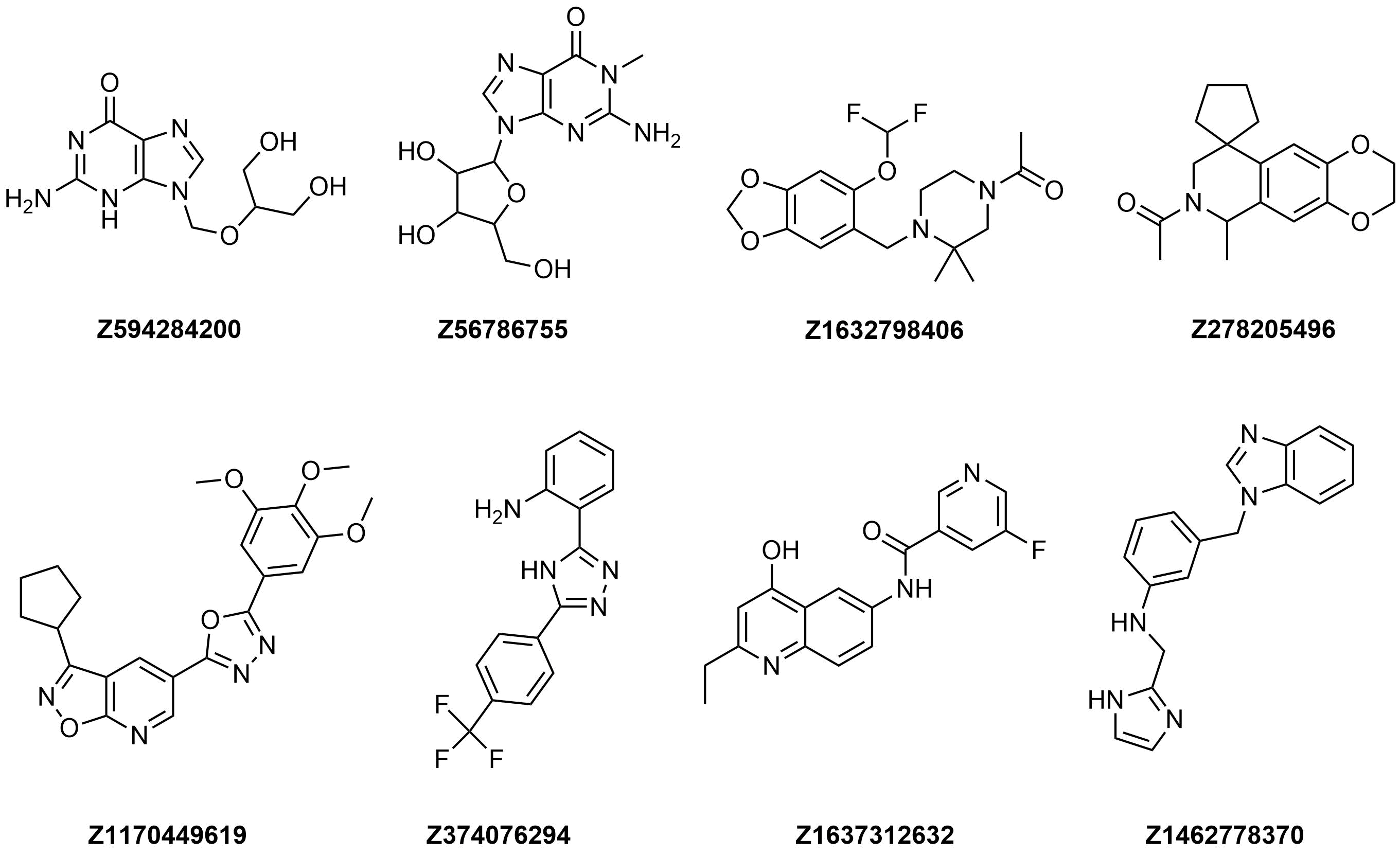
Filters applied to the Library
- In-house developed MedChem filters of unwanted structural fragments were applied to Enamine stock compound Collection as a pre-selection procedure.
- PAINS, Eli Lilly, REOS, and trivial functionalities filters included.
- Full Rule of Five compliance.
Designed for discovery of mild electrophilic inhibitors of the largest enzyme class
12 160 compounds
Serine hydrolases are important class of enzymes which include lipases, esterases, thioesterases, amidases, peptidases and proteases. They belong to one of the largest and most diverse classes of enzymes found in nature and represent ~1% of all proteins in mammalians playing vital roles in such pathophysiological processes as blood clotting, digestion, nervous system signalling, inflammation and cancer.
Despite the fact that pharmaceutical industry avoid developing therapeutics that form covalent bonds with protein targets, several commercialized serine hydrolase inhibitors as well as promising drug-candidates contain electrophilic chemical groups that interact covalently with Serine residue in the active site of their targets.
The library of mild electrophilic compounds has been plated for most convenient and quick access. Using our Serine hydrolase focused library you receive multiple benefits, allowing you to save on time and costs in hit expansion and optimization:
- Hit confirmation support – resupply of dry samples after QC check, samples repurification or resynthesis upon request.
- Analogs from dry stock of over 4.7M compounds or REAL Space of 78.1B make-on-demand molecules.
- Straightforward & low-cost synthesis of follow-up libraries through our REAL Database technology
You have also an option to screen the library directly at Enamine. In this case we will be happy to offer discount on library cost depending on the collaboration scope.
Typical Formats
Covalent Serine Hydrolase Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
CSHL-12-0-Z-10
Compounds
12 160
10 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
CSHL-12-10-Y-10
Compounds
12 160
38 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
CSHL-12-50-Y-10
Compounds
12 160
38 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
CSHL-12-10-Y-10 screening library 12 160 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.7M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library code: CSHL-12160
Version: 10 January 2022
12 160 compounds
Library design
The main criterion of the selection was presence of the electrophilic groups (cyano, epoxide, carbonyl etc.), which can provide the key interaction with serine in the active site of targeted enzyme. Next we estimated the 3D-shape of the molecules and compared them by throughput docking with the volume of the active sites taken from X-ray data of several serine hydrolases. The compounds which did not fit to the active site were withdrawn.
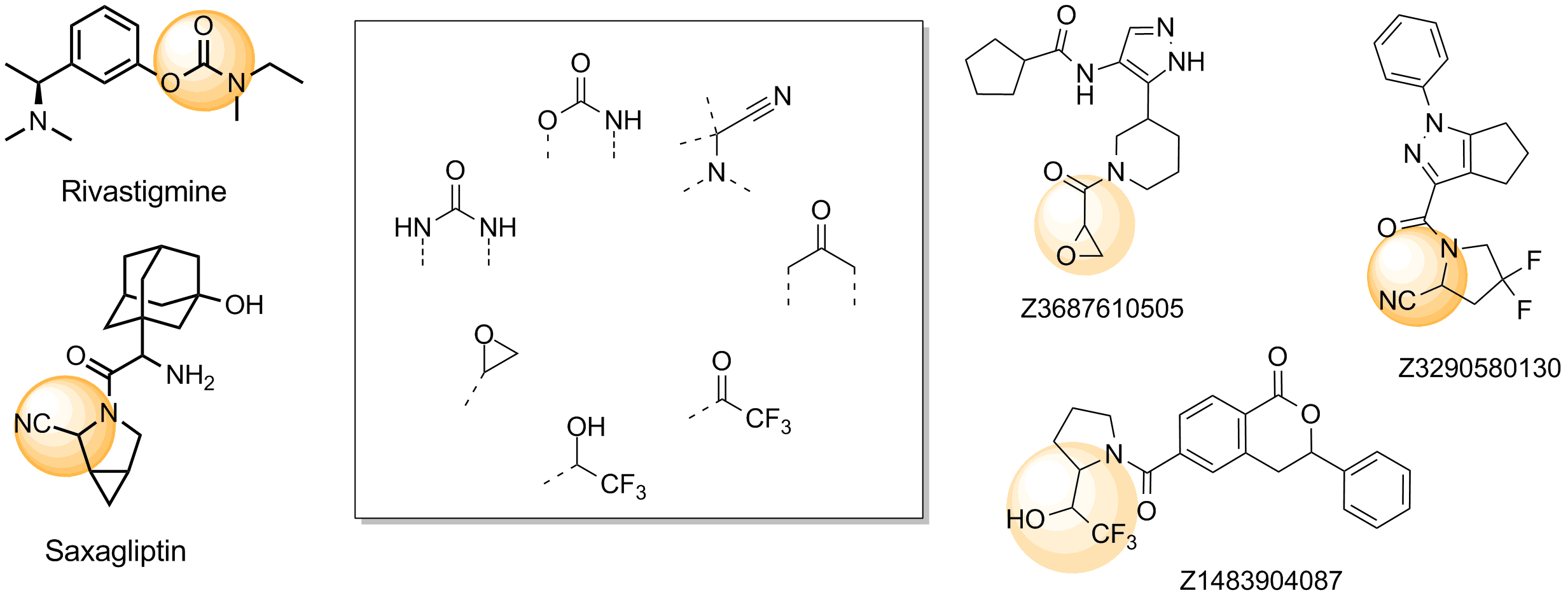
Representative examples of commercialized serine hydrolase covalent inhibitors and examples of functional groups which usually bind in the active site.
In addition, we applied several MedChem structural filters in order to remove unattractive moieties, trivial chemotypes and enhance the library with compounds with the latest scaffolds, sp3-rich frameworks and peptidomimetic structural motifs.
A set of LOXs inhibitors designed using docking and 2D similarity search
1 388 compounds
Lipoxygenases (LOXs) are enzymes that catalyze formation of the corresponding hydroperoxides from polyunsaturated fatty acids (e. g. linoleic or arachidonic). LOXs are widely expressed in immune, epithelial, and tumor cells, and activation of these enzymes induces numerous structural and metabolic changes. Abnormal LOX activity contributes to a number of pathophysiological conditions including inflammation, skin disorders and tumor genesis.
The 1 388 - compound Enamine lipoxygenase library was designed using two different approaches:
- Docking-based in silico screening, which identified compounds derived from novel scaffolds;
- Similarity search using 2D linear fingerprints and 3D pharmacophore features of the reported lipoxygenase inhibitors, which gave molecules with new side chains.
Download SD files
1 388 compounds for cherry-picking
Library design
Molecular docking
Docking models were built from the PDB reported protein structures 3O8Y, 4NRE and 3D3L. Prior to docking, all structures were optimized and reconstructed to correct gaps and missing side chains (Figure 1). Water molecules coordinated to Fe3+ ion were restrained, and their ionization state was assigned. Each docking model contained electrostatic descriptors of the binding site and mandatory positional constraints.
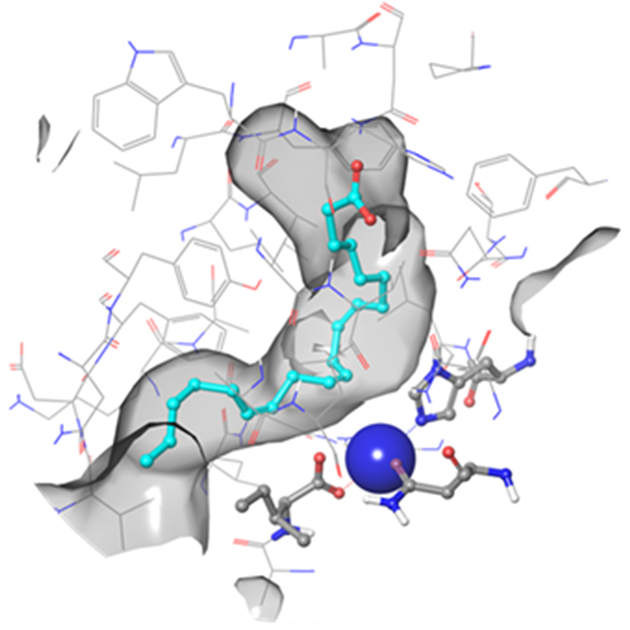
Fig. 1. hLOX-5 binding site in a surface volume representation (channel mode) with a native substrate –arachidonic acid (Fe3+ ion is shown in blue)
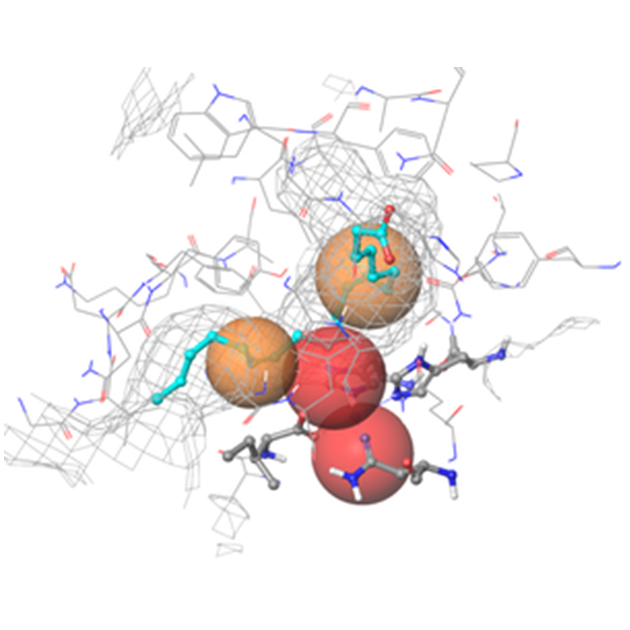
Fig. 2. Binding site of hLOX-15-II (4NRE) in grid representation with the most important pharmacophore features indicated: volume/shape, hydrophobic areas (colored in brown), H-bond acceptors and electron deficient fields (colored in red)
The resulting models were used to screen the MedChem refined subset of ~1.0M molecules of Enamine’s entire stock collection (over 4.7M compounds). Hits were defined as possessing an obligatory alignment for the positional constraints – metal coordination (red) and hydrophobic center (orange) (Figure 2). The docking results were evaluated through comparison of the docking scores and visual inspection of binding poses (presence of H-bonds, degree of exposure to water), which gave 950 compounds (Figure 3).
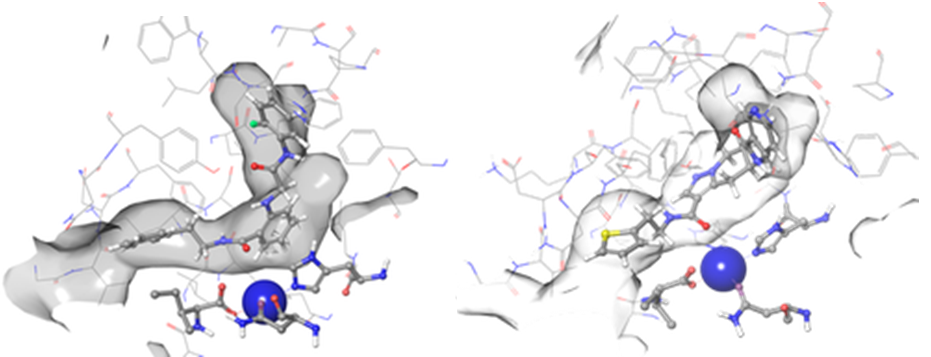
Figure 3. Examples of hit binding poses with high scoring functions identified after docking – Z31004492 (left) and Z1849138647 (right). Both molecules form coordination bonds with Fe3+ ion (shown in blue) and match two hydrophobic features in the binding pockets
Similarity search
- Search of ChEMBL database against the lipoxygenase targets gave a reference set of 322 active compounds for three lipoxygenase types (A5, A12, A15). These compounds were further filtered using potency values cut-off (IC50 ≤ 1μM) and MedChem toxicophore filters.
- 2D similarity search with a 0.85 threshold was done using linear fingerprints and Tanimoto algorithm.
- Nearly 500 compounds were selected from Enamine’s screening collection and added to the LOX library.
Examples of the molecules in the library
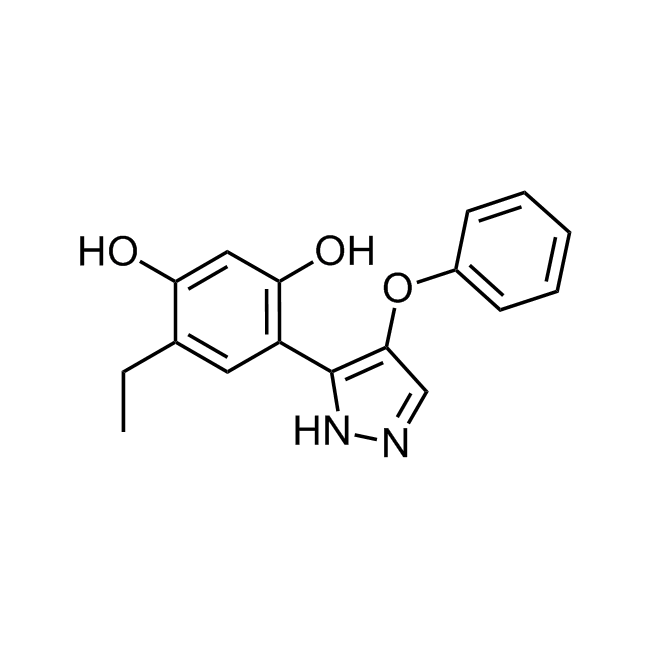
CHEMBL381149 IC50= 920 nM, 15-hLOX
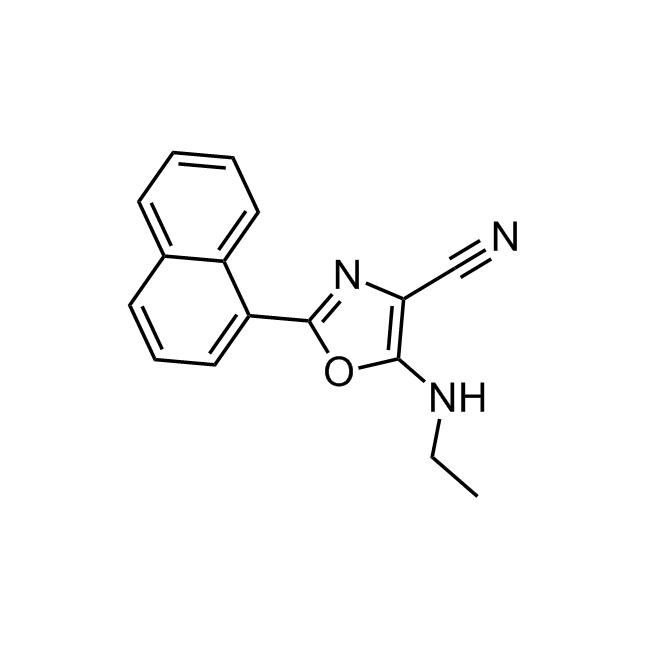
CHEMBL1571456 IC50= 120 nM, 15-hLOX
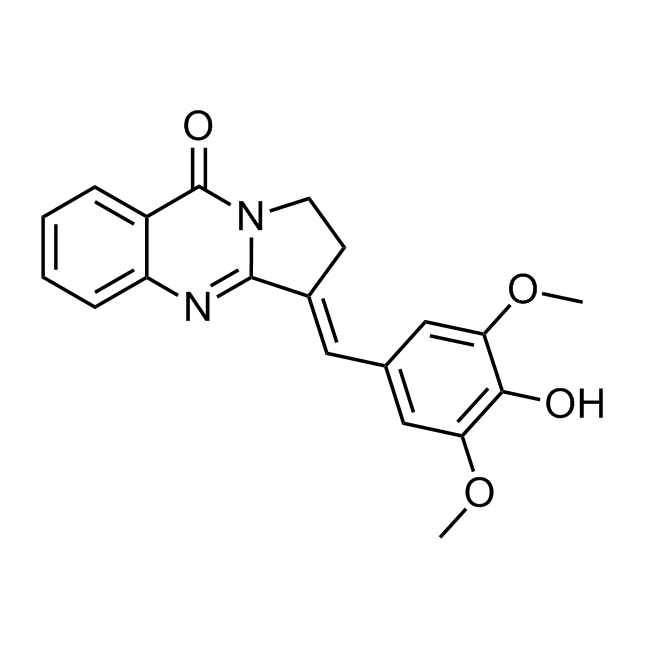
CHEMBL518103 IC50= 40 nM, 5-AhLOX
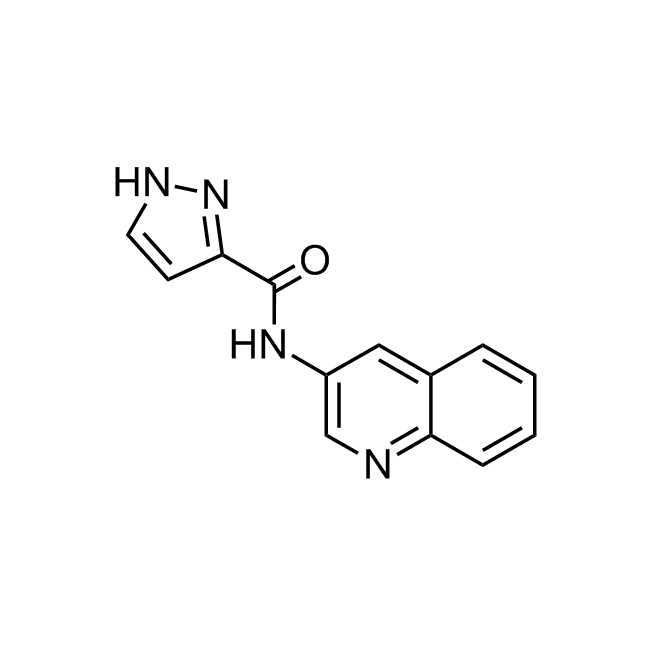
CHEMBL3604141 IC50= 92 nM, 15-AhLOX
Designed for discovery of new regulators of methabolic disorders
13 120 compounds
The kynurenine pathway is a metabolic pathway leading to the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) from the degradation of tryptophan. Disruption in the pathway is associated with wide range of diseases and disorders including infectious diseases (e.g. HIV), neurological disorders (Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington’s disease (HD) and ALS), affective disorders (schizophrenia, depression and anxiety), autoimmune diseases, peripheral conditions and malignancy. The aim of our work was to conduct searches for new potential active compounds for the kynurenine pathway, which, in turn, could be used as convenient and quality starting points for early drug development.
Typical Formats
Kynurenine Pathway Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
KYN-13-0-Z-10
Compounds
13 120
11 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
KYN-13-10-Y-10
Compounds
13 120
41 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
KYN-13-50-Y-10
Compounds
13 120
41 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
KYN-13-10-Y-10 screening library 13 120 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.7M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library code: IDO-4800
Version: 13 August 2024
4 800 compounds at 10 mM in DMSO
Library design
The search of potential actives was performed using all available protein and ligand structural data for the following targets: indoleamine dioxygenase (IDO), tryptophan dioxygenase (TDO), 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase (3-HAO), kynurenine aminotransferases (KATs), kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO).
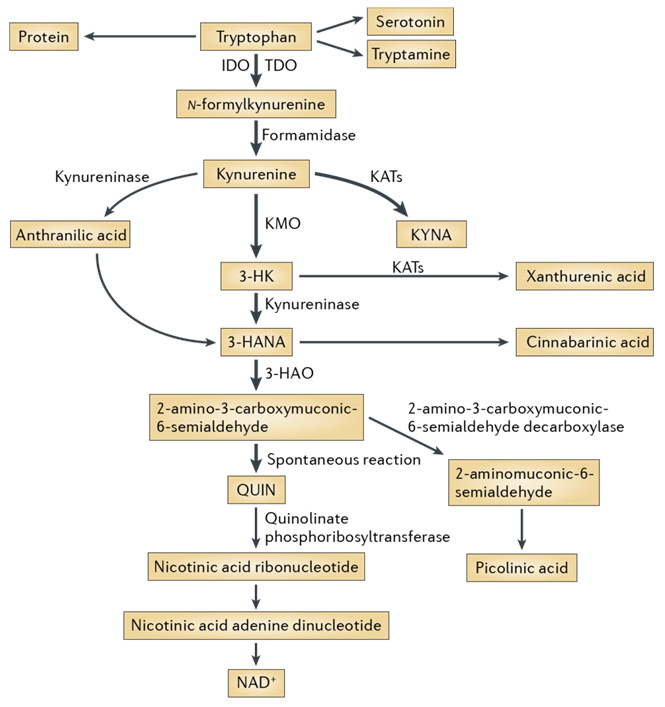
Fig. 1. The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation in mammals.
Screening Models preparation and validation
All available 3D structures of the targets were retrieved from PDB. Alternate superposition and comparison of the protein structures showed high sequence identity in every separate protein target > 90 % with RMSD in a range 0.4 - 0.71 Å2. Considering all representative structures only one has been selected for model preparation taking into account ligand binding parameters (protein- native ligand) and geometric parameters of the binding sites.
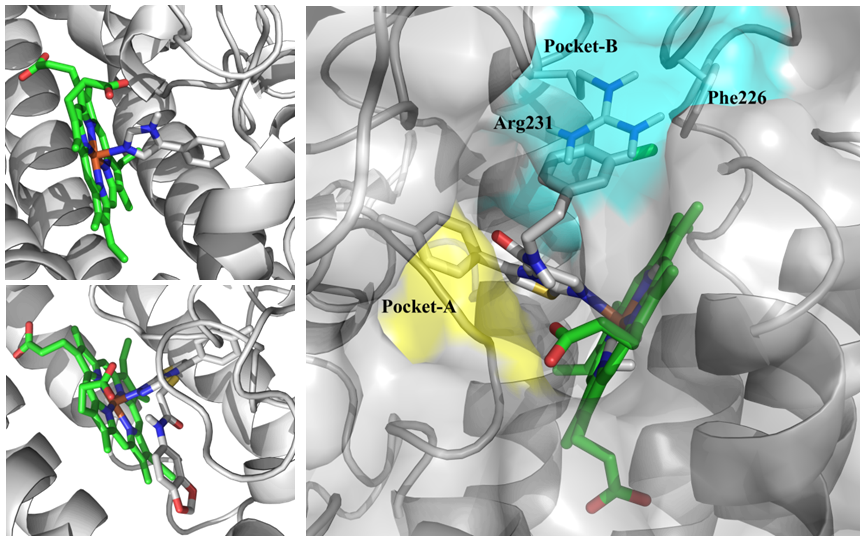
Fig. 2.Binding site of IDO1 (2D0T (top), 4PK5 (bottom) and example two main subpockets (in blue and yellow) used for molecular docking).
Molecular docking & Pharmacophore search
Basing on compounds with known activity and “protein–native ligand” complexes, ligand-based (IDO: 3, TDO: 4, KATs: 3, KMO: 2) and structure-based (IDO: 3, TDO: 6, 3-HAO: 2, KATs: 3, KMO: 4) pharmacophore models were build and validated. Drug-like Enamine database of over 1M compounds were then screened.
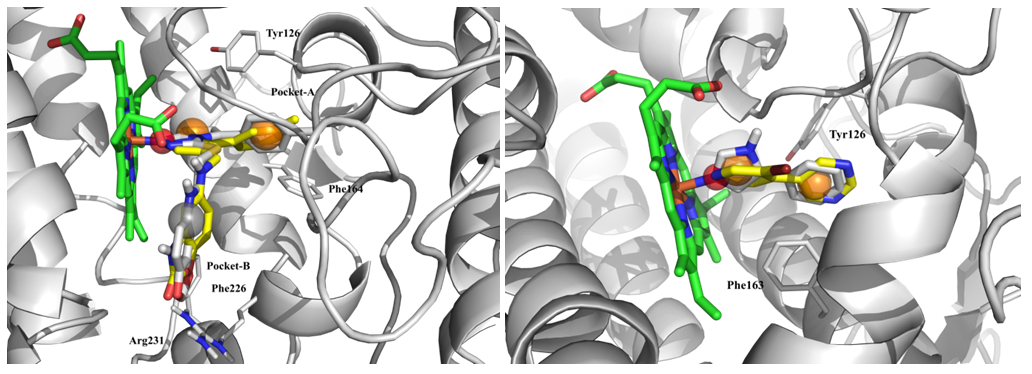
Fig. 3. Results of molecular docking: superposition of native (grey) and hit ligands (yellow) with representation of structure-based pharmacophore features.
Examples of the molecules
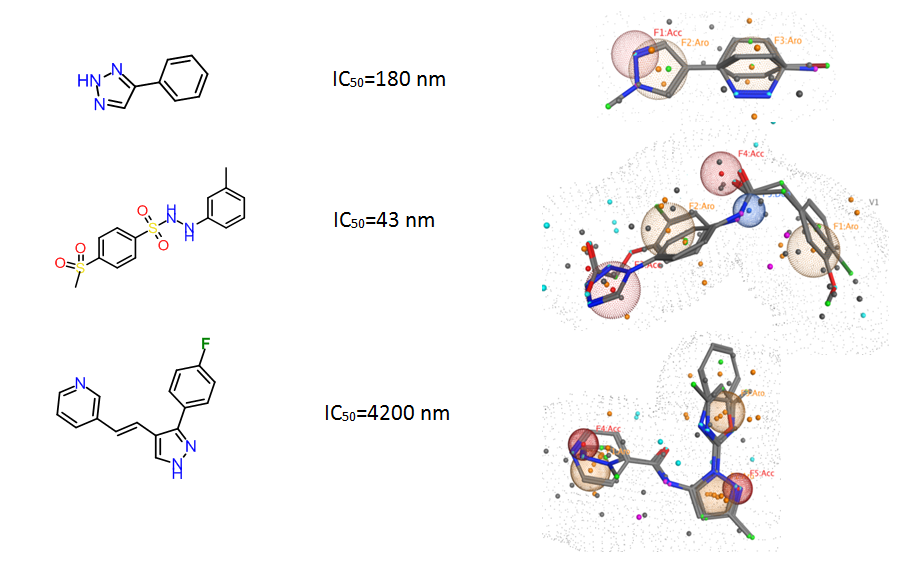
Fig. 4. Ligand-based Pharmacophore models used for in silico screening.
Number of compounds in targeted libraries after molecular docking calculation and pharmacophore searches:
Target Name
IDO
TDO
3-HAO
KATs
KMO
Number of compounds in the library
4 800
5 120
1 000
1 000
3 200
Careful analyzes of proteins and their ligand interactions involved in kynurenine pathway were performed. The iterative in silico searches using all available state-of-the-art methodologies were curried-out to yield unique sets of potentially active molecules. Chemotype control was used to enrich the libraries with structural motifs of true positives and new “patent-free” structural cores.
Developed targeted sets are intended for high-probability initial hit discovery in one step for any particular target.