Designed for discovery of novel hits in Immuno-Oncology therapeutic area
45 760 compounds
Immunotherapy has emerged as a transformative approach for cancer treatment being one of the most prospective fields in contemporary drug development. To address growing needs in novel and potent active molecules we designed special library focused on the most important targets: PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoints inhibitors, toll-like receptor family (TLR7 and TLR8, as a key players in antiviral response), IRAK4, ALK5 (one of JNK/P38 effectors and initiator of SMAD association), JAK-STAT pathway inhibitors, STING agonists, IDO inhibitors and the number of kinase targets – BTK, MAPK, VGFR and bRAF.
We have carefully selected 45 760 diverse compounds with the most promising features as potential ligands for known immune-oncology targets. All compounds are stored as dry materials and they can be acquired in diverse custom formats. Using our Immuno-Oncology Library for hit discovery you receive multiple benefits allowing you to save on time and costs in lead generation:
- Hit resupply and hit expansion from dry stock of over 4.7M compounds.
- Straightforward and low-cost analogs synthesis through our REAL Database technology.
- Fully customized hit-to-lead project support with broad capabilities available on-site.
You have also an option to screen the library directly at Enamine. We will be happy to offer you discount on library cost depending on the collaboration scope.
Download SD files
45 760 compounds for cherry-picking
Library design
In Immuno-Oncology Library design a special attention was paid to checkpoint proteins, such as PD-1, CTLA-4, CD152, CD279/74 and PD-L1.
In silico screening of different targets:
Structure-based approach was applied to search potential inhibitors of TLR7 and TLR8 receptors. All reported in PDB proteins structures were analyzed and superimposed for generation of protein structure-based pharmacophores. Thereafter two models have been validated with reference set of active and inactive compounds.
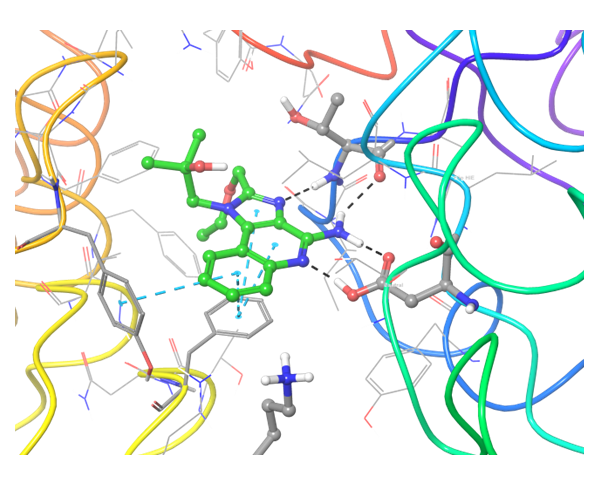
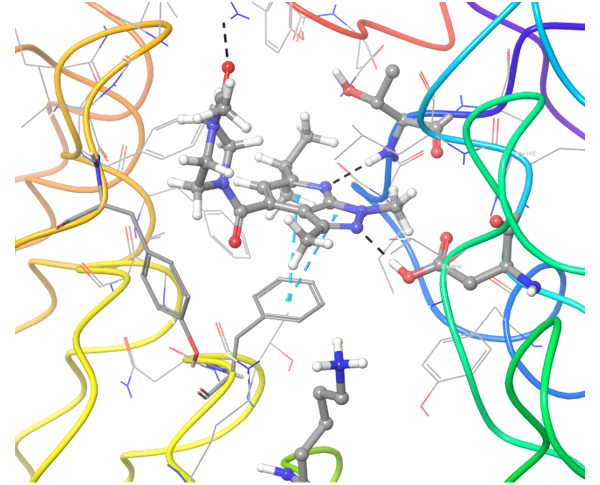
TLR7 and TLR8 in complex with co-crystallized ligands (upper pair). Binding mode of hit Z242112334 found after docking calculations with TLR7 (left) and another hit compound Z1438692506 in the cavity of TLR8 (right).
Two types of transmembrane proteins (IRAK4 and TGF beta R1) with reported kinase activity were studied based on 4U97 and 2WOT structures respectively. The presence of several hydrophobic cores in the ligand structure and its ability to form strong h-bonds with key amino acids in the binding site were requirements for potential inhibitors selection. However, to overlap all possible structures and conformations an alternate combination of hydrophobic cores and h-bonds was used for selection of compounds in these mini libraries. Two subsets of constraints were generated to create the most exhaustive screening model for each kinase.
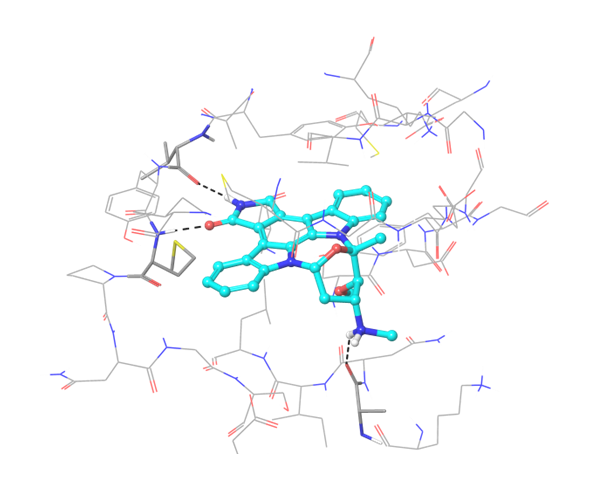
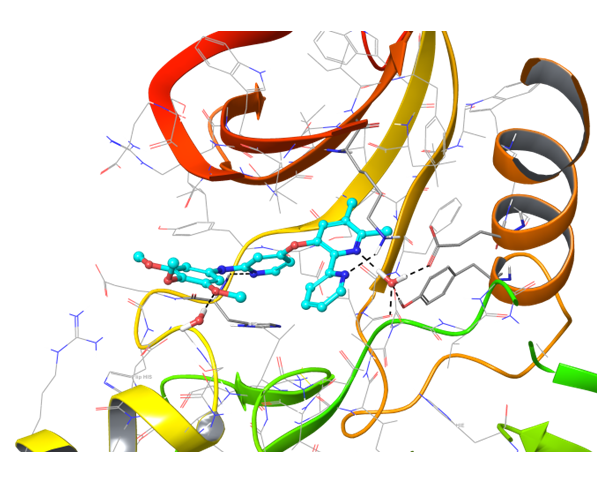
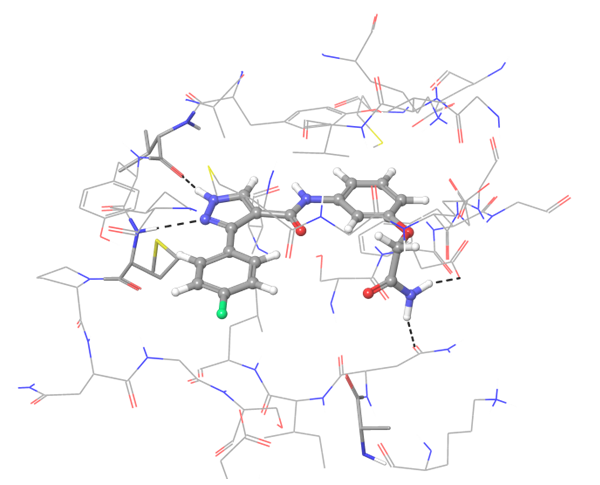
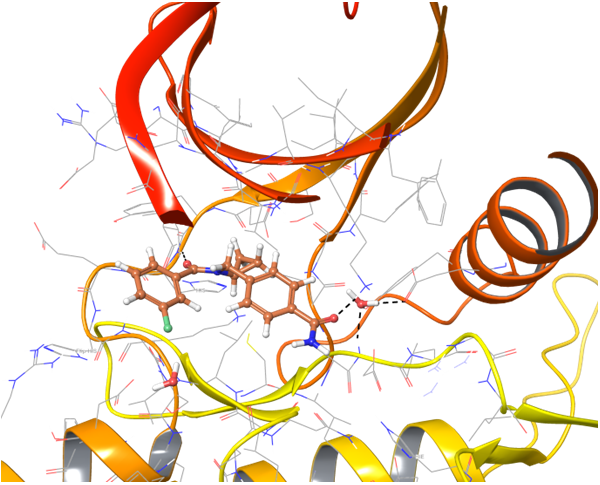
IRAK4 in its crystalized form and in complex with docked Z243559212 are in the left column. TGF beta R1 in original state from RCSB and in complex with Z316882020 are in the right column.
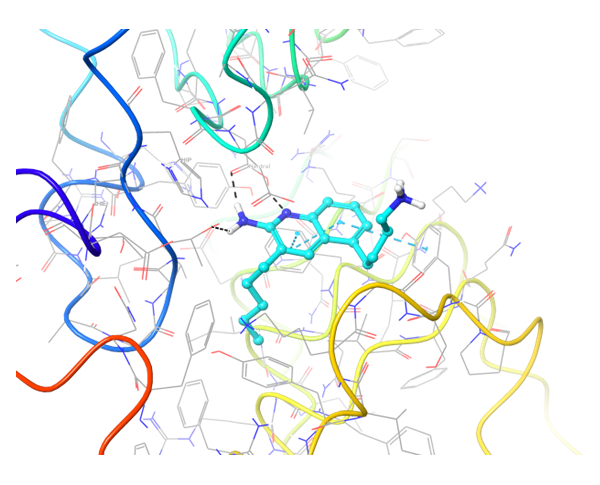
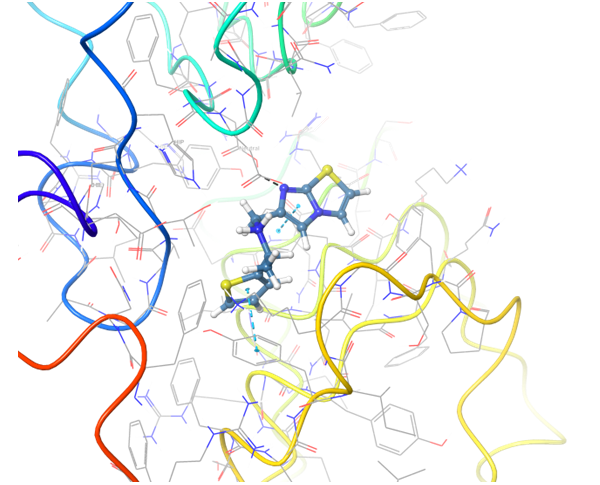
In case of PD-1 and PD-L1 binding, there are few known PD-L1 inhibitors. We applied structural and spatial constraints to find compounds, which can similarly modulate PD-L1 structure. To increase selectivity and at the same time avoid the conformational similarity, two-staged screening was performed, resulting in the selection of the most potent binders.
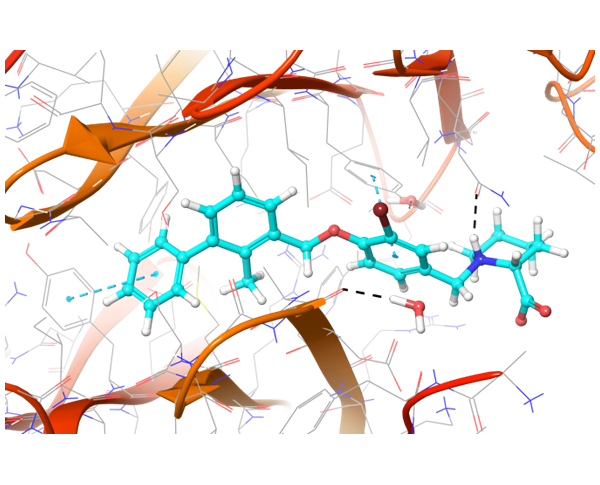
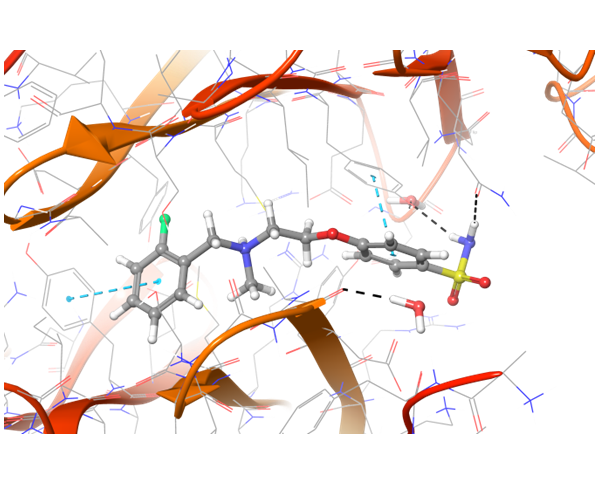
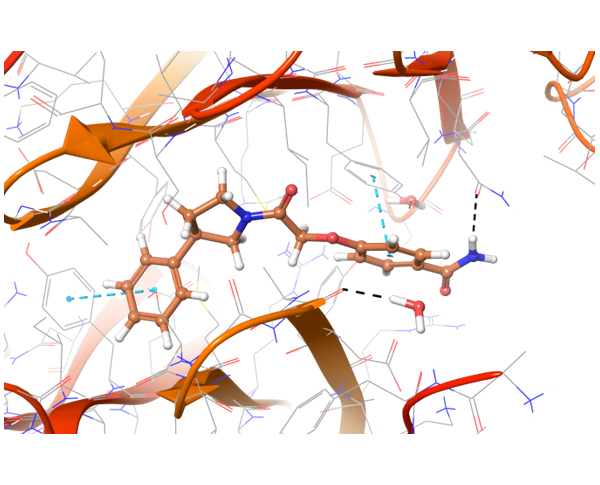
Co-crystallized BMS-8 structure (upper left) with indicated interactions and both Z195611316 and Z942299126 ligands, which have similar structure and binding modes.



