Designed for efficient hit finding against a number of immune disorders, including RA
1 280 compounds
The library was designed to be a universal tool to search potential JAK-STAT pathway modulators. Protein structure-based analysis and scaffold-hopping approach were used to create an optimal in silico screening models. Additionally, ligand-based approach has been applied to enrich the library with topological analogs and similar compounds to reported actives.
Resulted library is as a generic starting point for ligand search, regardless of particular SH2 domain of interest, with high probability of initial hit discovery. The library was validated with in vitro screening against SRC SH2 domain resulting in 3.5 % of identified hits.
Download SD files
Library design
All available structures of SH2 domain binding sites were analyzed and clustered based on their spatial molecular shape. After the alignment analysis and clustering structures with most different conformations were selected for virtual screening. Enamine MedChem filtered in-stock subset (~1 M compounds) with additional selection of compounds carrying peptidomimetic motifs was used for molecular docking calculations.
Multiple sequence alignment was applied to 120 SH2 domains contained within 110 proteins. Over 200 protein structures were extracted from Protein Data Bank (PDB): 66 NMR-based structures and 153 derived from X-ray crystallography experiments. As variation of the binding site conformation may significantly influence its binding properties, all files were split into individual structures, resulting in total structure count of 1633.
Key pharmacophore interaction points: pTyr binding pocket, carbonyl O in the binding site center, hydrophobic sub-pocket.
Solvent accessible molecular surface within 12 Å from the binding site center was used for calculation of shape-based numeric descriptors. 3D structures were clustered based on 3D shape similarity. 8 spatially diverse structures were selected for docking.
Table 1. Summary of protein 3D structures clustering results and structures selected for docking.
1
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
1o49, chain A
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Homo Sapiens SRC SH2
Structures in cluster
223
2
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
2fci, chain A, model 6
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Bos Taurus PLCG1 SH2-2
Structures in cluster
48
3
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
2ge9, chain A, model 15
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Homo Sapiens BTK SH2
Structures in cluster
72
4
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
3in7, chain A
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Homo Sapiens GRB2 SH2
Structures in cluster
183
5
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
2jyq, chain A, model 9
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Homo Sapiens GRB2 SH2
Structures in cluster
114
6
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
2k7a, chain B, model 5
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Mus Musculus ITK SH2
Structures in cluster
218
7
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
2kk6, chain A, model 14
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Homo Sapiens FER SH2
Structures in cluster
149
8
Centroid structure (PDB id, chain, NMR model)
1uus, chain A
Centroid structure: organism, gene, domain
Dictyostelium Discoideum DSTA SH2
Structures in cluster
129
Virtual screening against Stat3beta:
- Collaborator: Gyeong Baeg, NYMC
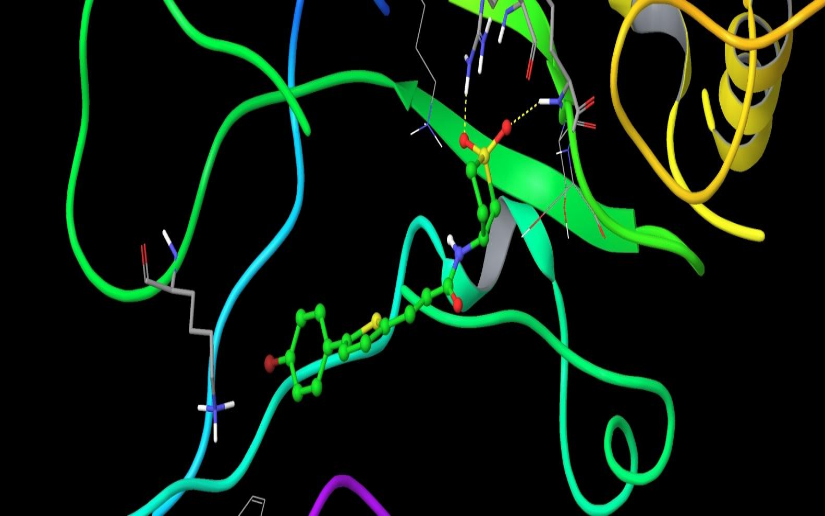
Chemical compounds are significantly smaller in size than the natural peptide interacting with this target. Therefore, when creating the library, we tried to fill all potential sub-pockets available near the phosphotyrosine binding site. The entire available surface of the protein was conditionally broken down into 5 models and proceeding from this was carried out post-docking analysis. As an example, the first two models:
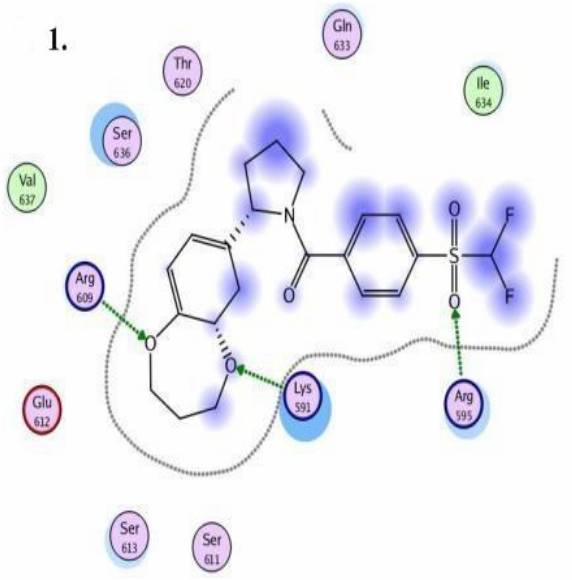
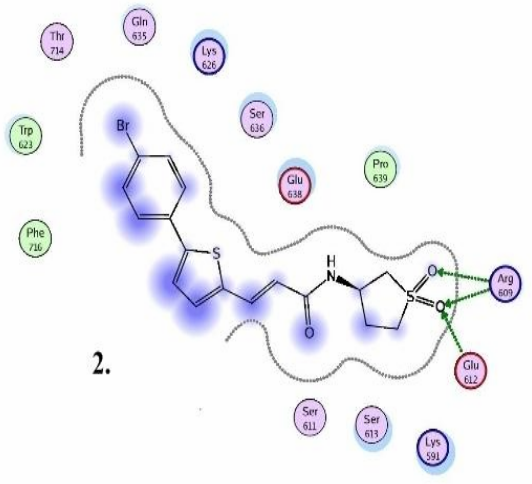
STAT3 models: Schematic representation of ligand binding pocket



