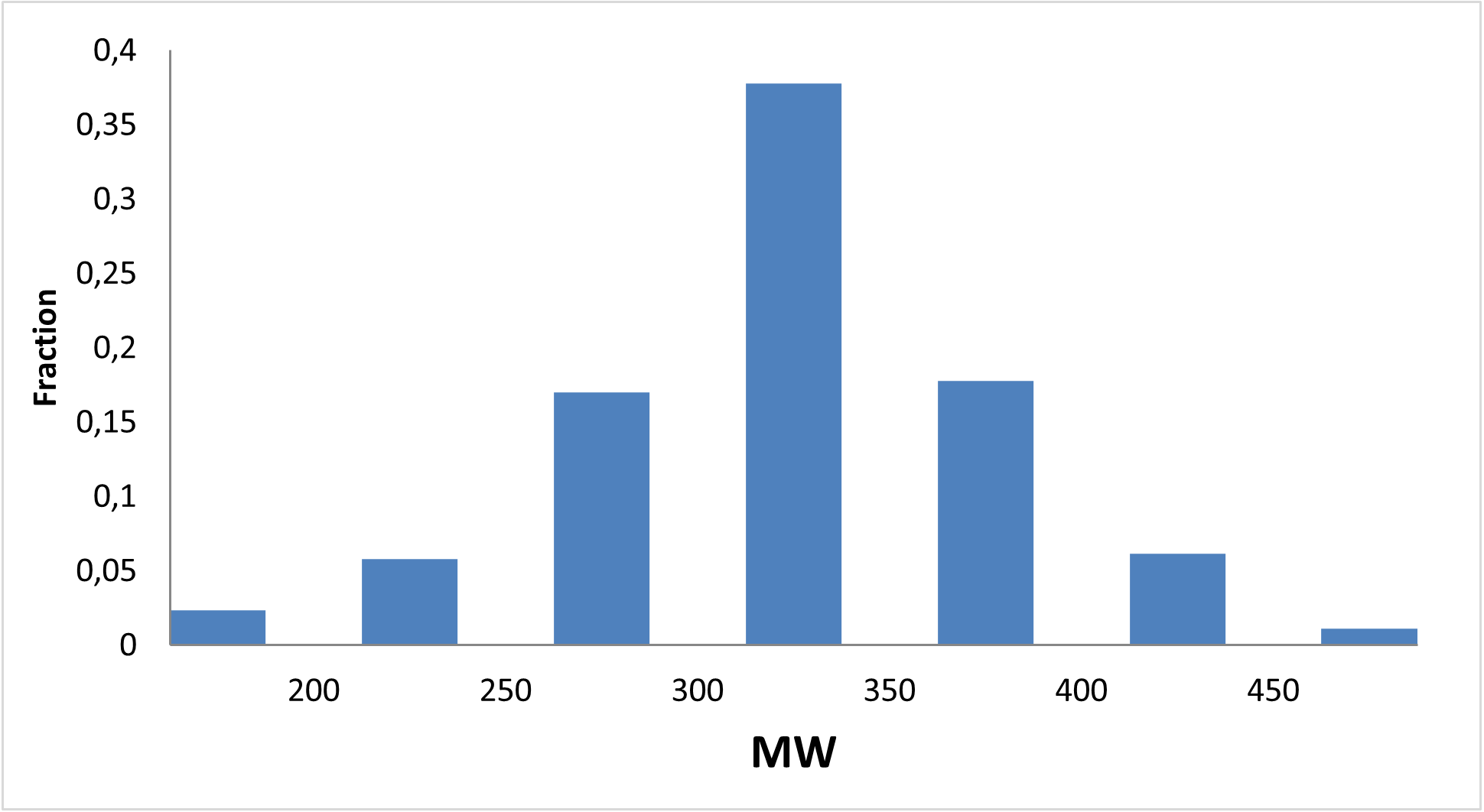
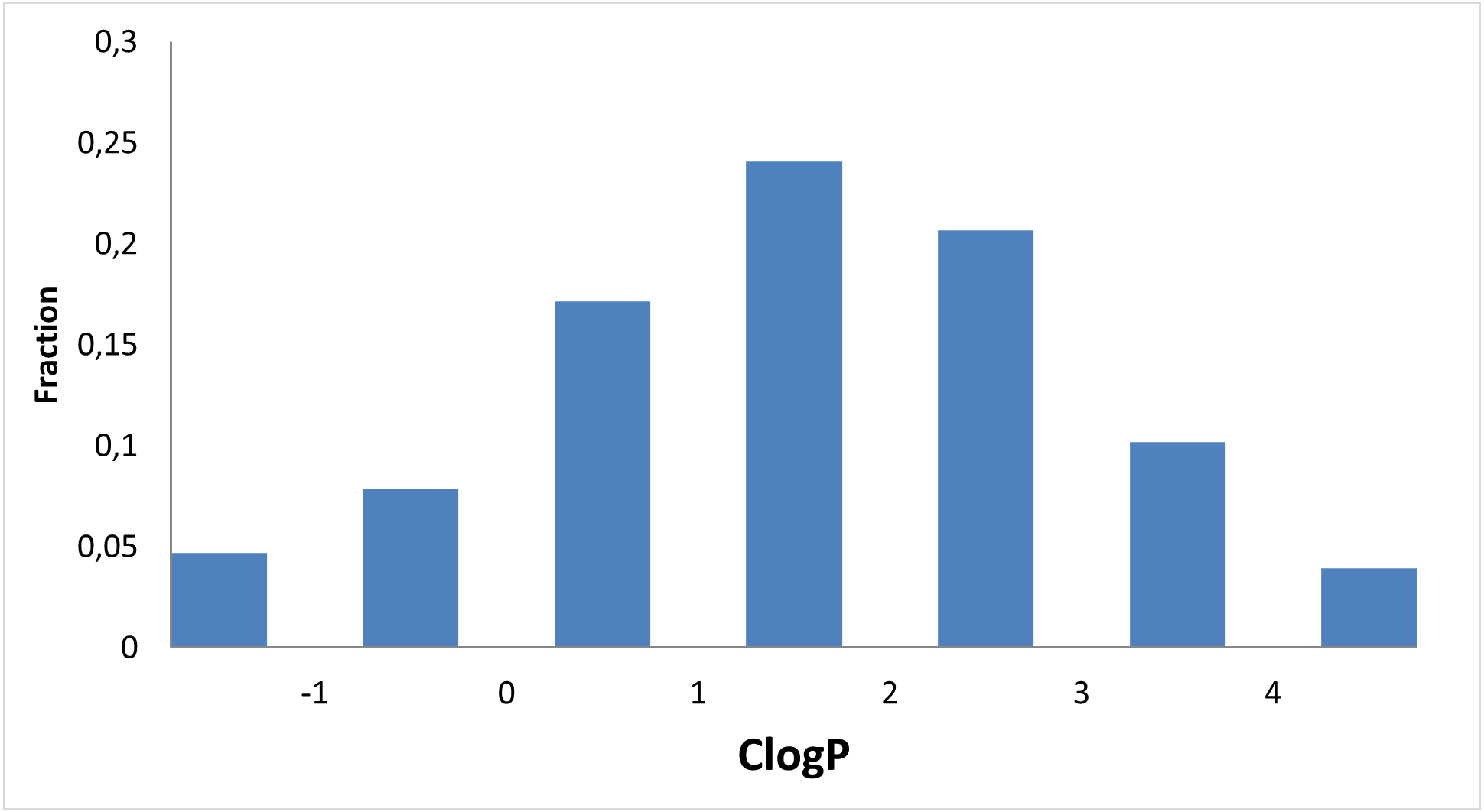
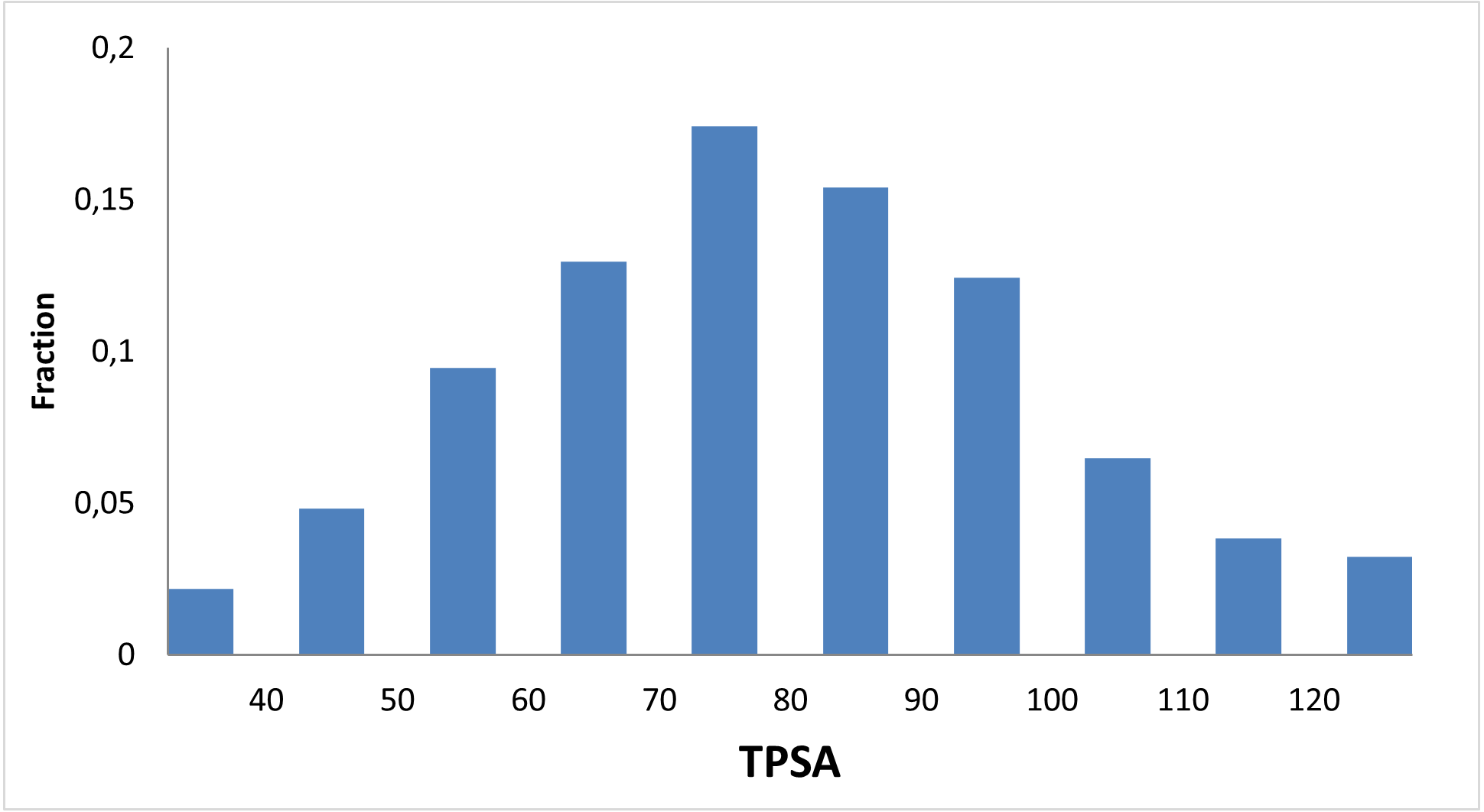
Designed for discovery of new regulators of methabolic disorders
13 120 compounds
The kynurenine pathway is a metabolic pathway leading to the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) from the degradation of tryptophan. Disruption in the pathway is associated with wide range of diseases and disorders including infectious diseases (e.g. HIV), neurological disorders (Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington’s disease (HD) and ALS), affective disorders (schizophrenia, depression and anxiety), autoimmune diseases, peripheral conditions and malignancy. The aim of our work was to conduct searches for new potential active compounds for the kynurenine pathway, which, in turn, could be used as convenient and quality starting points for early drug development.
Typical Formats
Kynurenine Pathway Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
KYN-13-0-Z-10
Compounds
13 120
11 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
KYN-13-10-Y-10
Compounds
13 120
41 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
KYN-13-50-Y-10
Compounds
13 120
41 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
KYN-13-10-Y-10 screening library 13 120 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.4M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library code: IDO-4800
Version: 13 August 2024
4 800 compounds at 10 mM in DMSO
Library design
The search of potential actives was performed using all available protein and ligand structural data for the following targets: indoleamine dioxygenase (IDO), tryptophan dioxygenase (TDO), 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase (3-HAO), kynurenine aminotransferases (KATs), kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO).
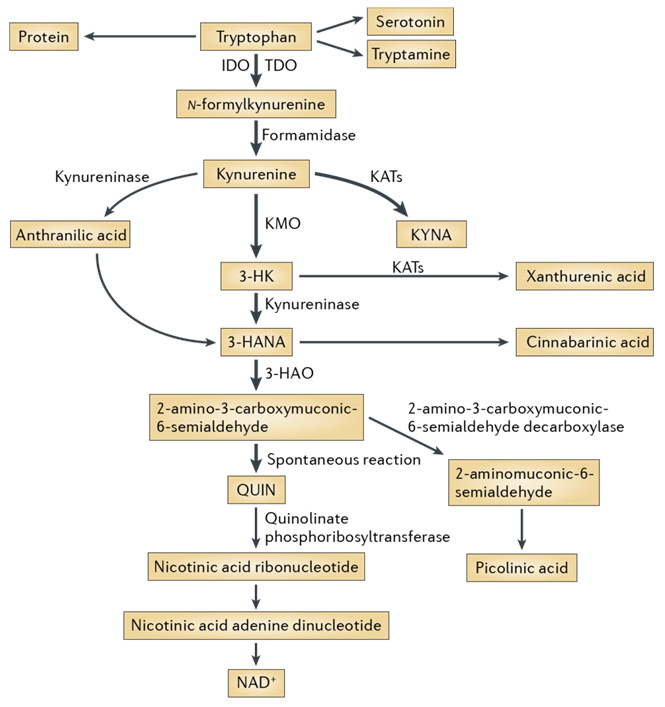
Fig. 1. The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation in mammals.
Screening Models preparation and validation
All available 3D structures of the targets were retrieved from PDB. Alternate superposition and comparison of the protein structures showed high sequence identity in every separate protein target > 90 % with RMSD in a range 0.4 - 0.71 Å2. Considering all representative structures only one has been selected for model preparation taking into account ligand binding parameters (protein- native ligand) and geometric parameters of the binding sites.
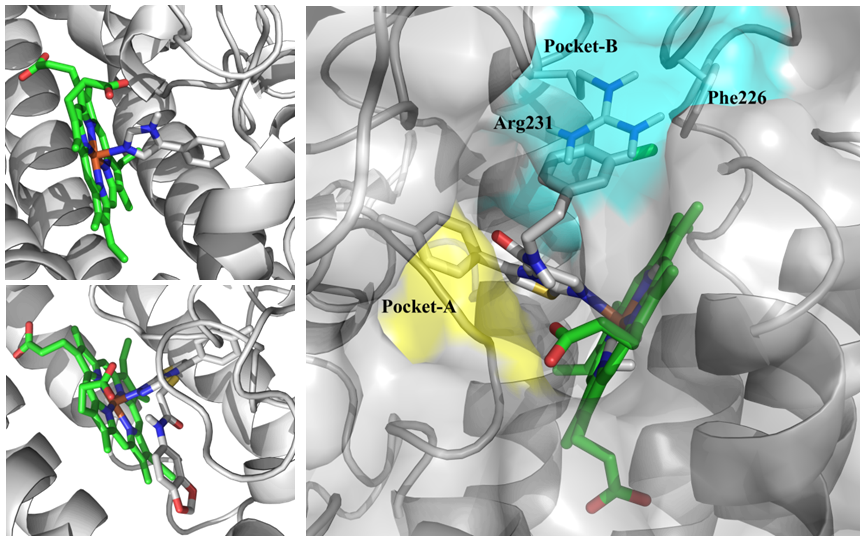
Fig. 2.Binding site of IDO1 (2D0T (top), 4PK5 (bottom) and example two main subpockets (in blue and yellow) used for molecular docking).
Molecular docking & Pharmacophore search
Basing on compounds with known activity and “protein–native ligand” complexes, ligand-based (IDO: 3, TDO: 4, KATs: 3, KMO: 2) and structure-based (IDO: 3, TDO: 6, 3-HAO: 2, KATs: 3, KMO: 4) pharmacophore models were build and validated. Drug-like Enamine database of over 1M compounds were then screened.
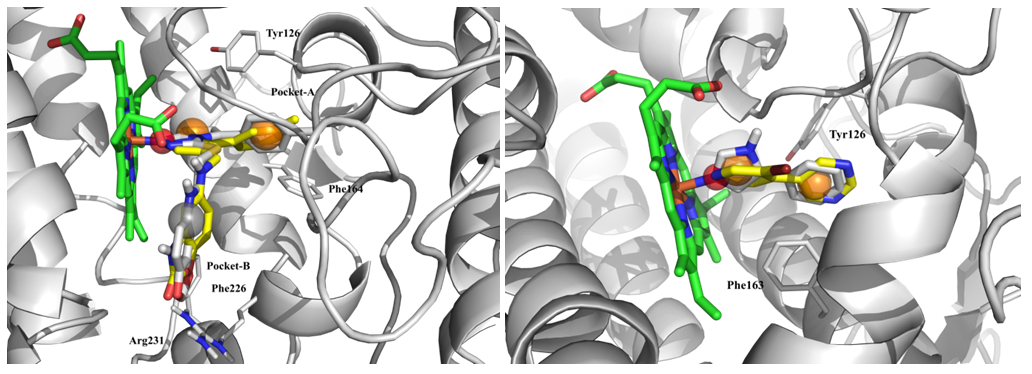
Fig. 3. Results of molecular docking: superposition of native (grey) and hit ligands (yellow) with representation of structure-based pharmacophore features.
Examples of the molecules
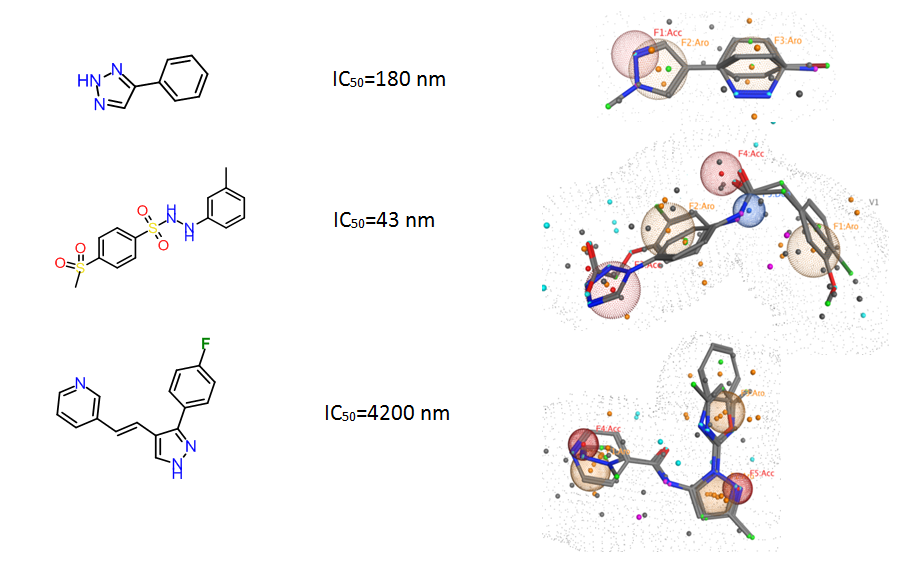
Fig. 4. Ligand-based Pharmacophore models used for in silico screening.
Number of compounds in targeted libraries after molecular docking calculation and pharmacophore searches:
Target Name
IDO
TDO
3-HAO
KATs
KMO
Number of compounds in the library
4 800
5 120
1 000
1 000
3 200
Careful analyzes of proteins and their ligand interactions involved in kynurenine pathway were performed. The iterative in silico searches using all available state-of-the-art methodologies were curried-out to yield unique sets of potentially active molecules. Chemotype control was used to enrich the libraries with structural motifs of true positives and new “patent-free” structural cores.
Developed targeted sets are intended for high-probability initial hit discovery in one step for any particular target.
Carefully selected molecules via docking and visual evaluation
4 800 compounds
Development of efficient kinase inhibitors has been a long-standing challenge in drug development. The structural and mechanistic characterization of kinase inhibitor provides new strategies to develop specific kinase inhibitors by targeting a binding pocket adjacent or not adjacent to the ATP binding pocket.
Allosteric kinase inhibition is among the most promising and sensitive deactivation mechanism of kinase activity. Four type of possible allosteric kinase pockets were determined by now:
- Myristoyl pocket;
- Inhibitor binding mode that occupies part of binding pocket adjacent to the ATP-site;
- PIF-pocket (regulatory site targeted);
- Pocket type I1/2 relatively allosteric regulators of kinases.
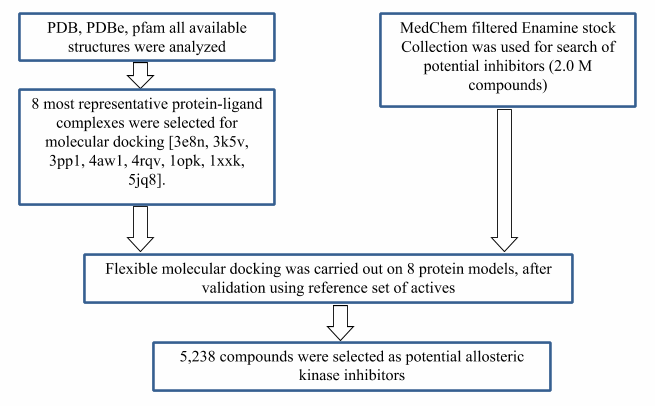
All available PDB structures with kinase allosteric inhibitors were analyzed. Most representative structures were used for molecular docking calculation. General algorithm of library design represented on the scheme below:
Typical Formats
Allosteric Kinase Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
ALK-4-0-Z-10
Compounds
4 800
4 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
ALK-4-10-Y-10
Compounds
4 800
15 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
ALK-4-50-Y-10
Compounds
4 800
15 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, 1,2 and 23,24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
ALK-4-10-Y-10 screening library 4 800 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.4M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD file
Library code: ALK-4
Version: 17 February 2022
4 800 compounds
sublibrary of KNS-64
Examples of the molecules
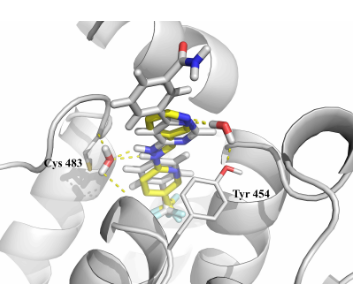
Fig. 1. Example of molecular docking result into the Myristoyl pocket (4aw1 PDB entry). Native ligand represented in grey sticks, docked ligand – in yellow.
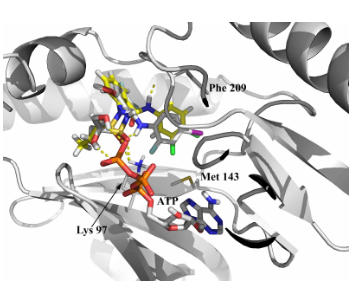
Fig. 2. Example of molecular docking into the ATP-kinase subpocket (3e8n PDB entry). Docking calculations were performed with CoA features.
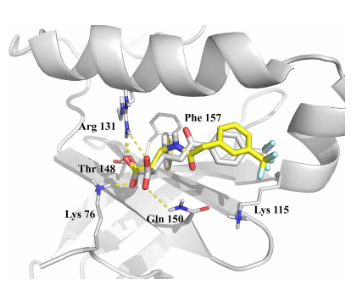
Fig. 3. Example of molecular docking into the PIF pocket (4aw1 PDB entry).
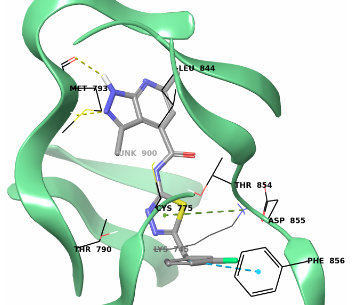
Fig. 4. Example of molecular docking into the PIF I1/2 binding site (4aw1). Hit binding mode.
Special diversity library created for Phenotypic Screens
5 760 compounds
Phenotypic screening has proven its efficacy in drug discovery and become more and more popular approach in search of new actives. Recently researchers have concluded that sharp focused approaches such as target-based screening are useful but may also limit the breadth of new findings.
Development of new phenotypic screening techniques within implementation of specially designed compound libraries makes this approach a powerful tool in repurposing, finding of new mechanism of action, investigation of signaling pathways and discovery of new biological targets. For successful screening campaign special attention must be paid to the source of chemical entities and their annotation. This requires access to richer, diverse and cross-linked biological data associated to chemical compounds. In order to meet all requirements, we designed special compound library intended for phenotypic screens.
The Library has been pre-plated for most convenient access and prompt delivery in various customized formats. Most popular library formats available for immediate supply are summarized in the table below:
Typical Formats
Phenotypic Screening Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
PSL-5760-0-Z-10
Compounds
5 760
5 plates
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
PSL-5760-10-Y-10
Compounds
5 760
18 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
PSL-5760-50-Y-10
Compounds
5 760
18 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, 1,2 and 23,24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
PSL-5760-10-Y-10 screening library 5 760 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.4M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library Design
To create multipurpose phenotypic library we investigated an optimal balance between diversity of biological activities versus structural diversity of small molecules. The library includes 900+ approved drugs and most similar compounds with identified mechanism of action (T>85%, linear fingerprints). In addition, PSL is enriched with 2000+ of annotated potent inhibitors and their biosimilars, covering a broad diversity of biological targets. Compounds from PSL are cell-permeable and possess pharmacology-compliant physicochemical properties.
- Approved drugs and most similar compounds with identified mechanism of action, over 2 000 molecules, that were found from Enamine Collection (T>87%, linear fingerprints).
- Potent inhibitors or highly similar compounds to diversified protein targets, about 5 000 molecules.
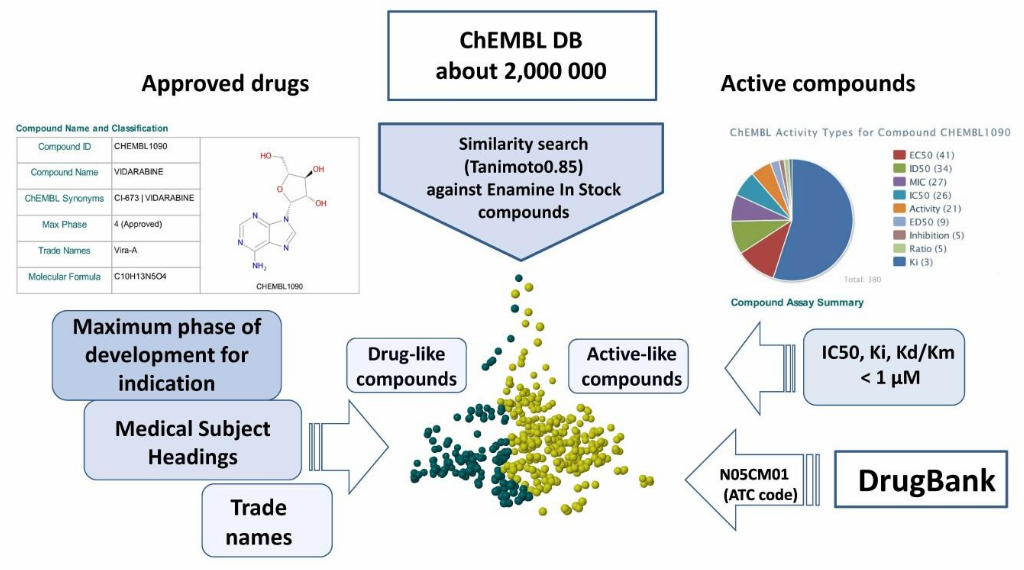
Supporting biological data/documentation:
- Provides easy access and analyze information from in-fields.
- Covers different aspects: polypharmacology, number of targets and description.
- Numbers and names of associated diseases are indicated for majority of compounds.
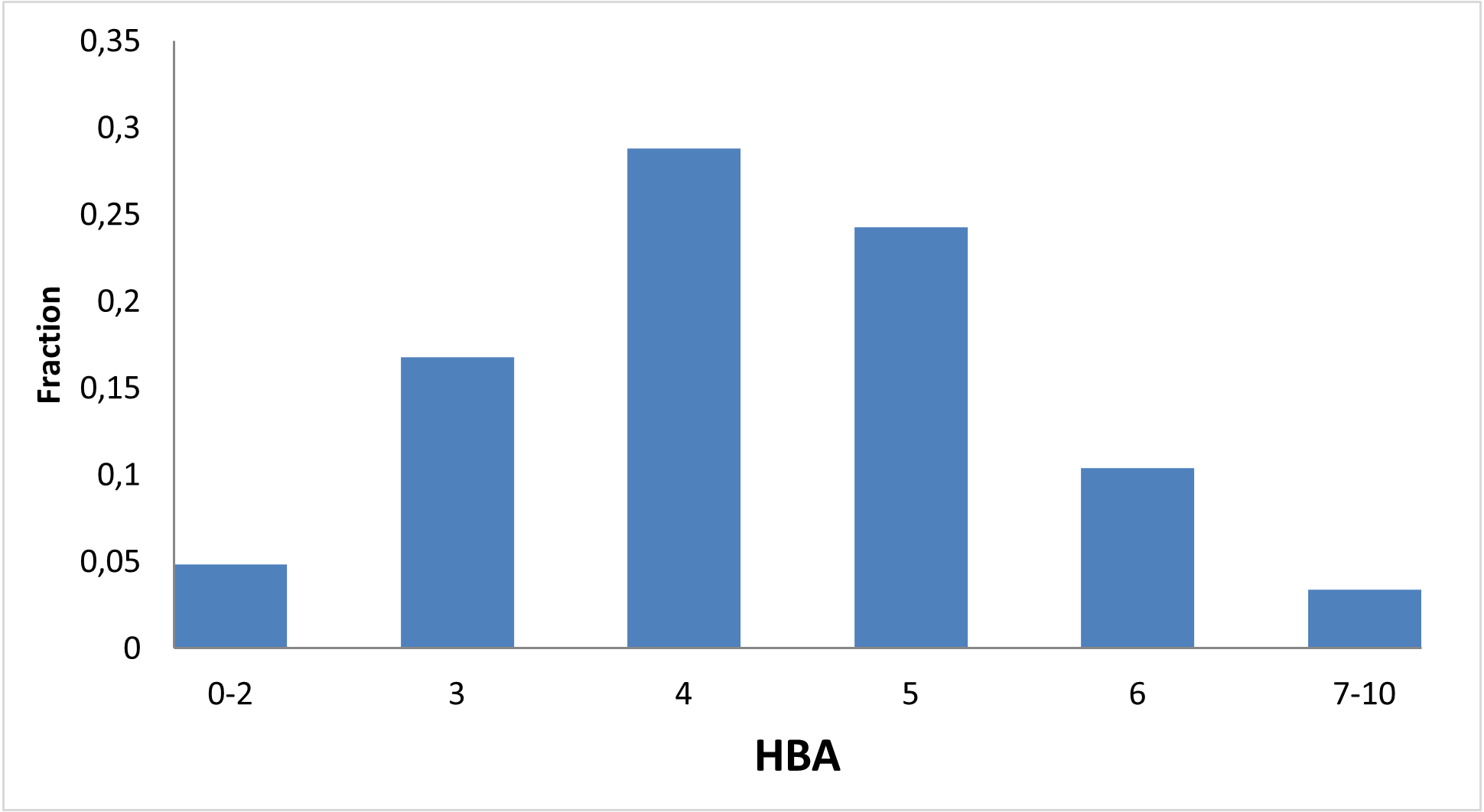
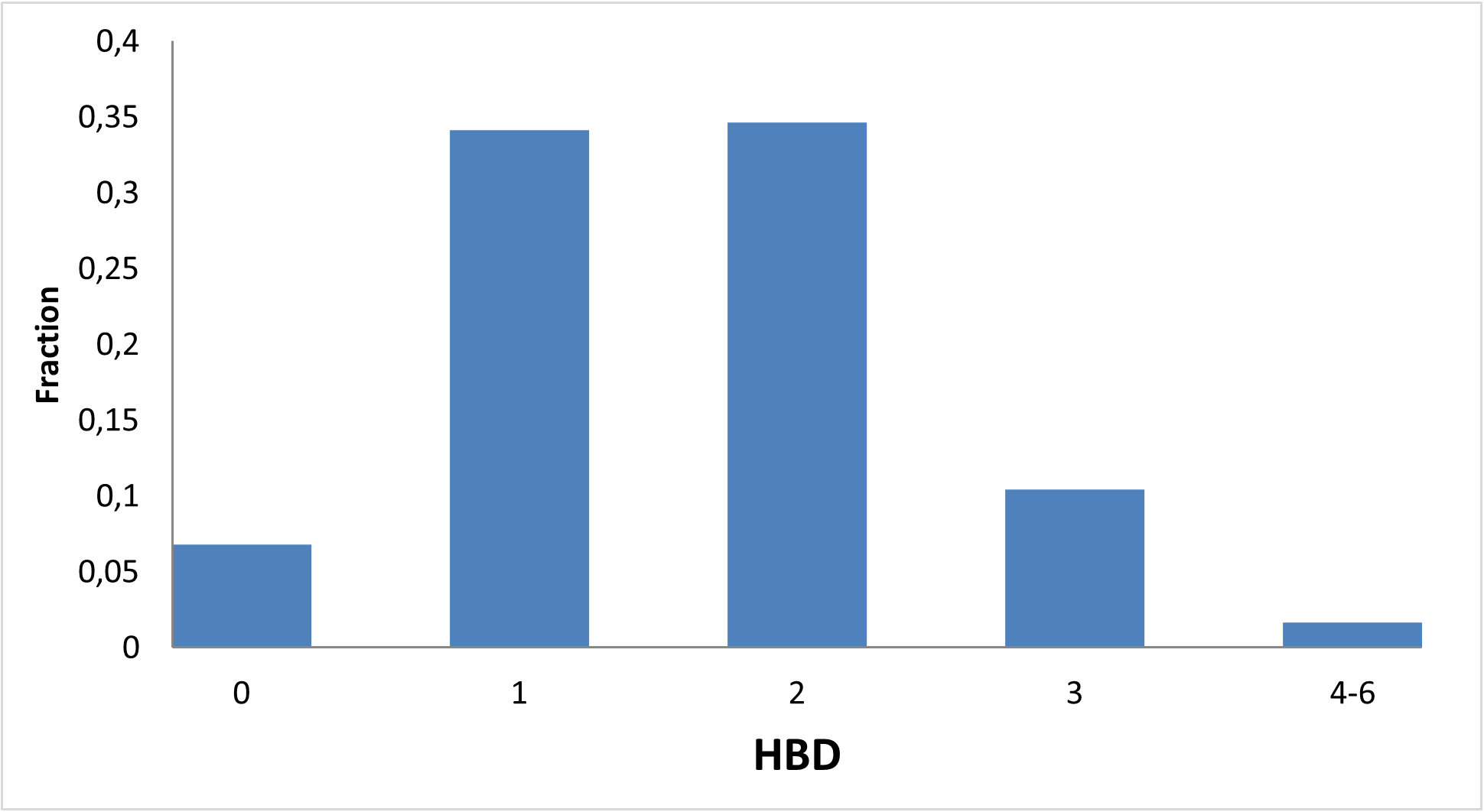
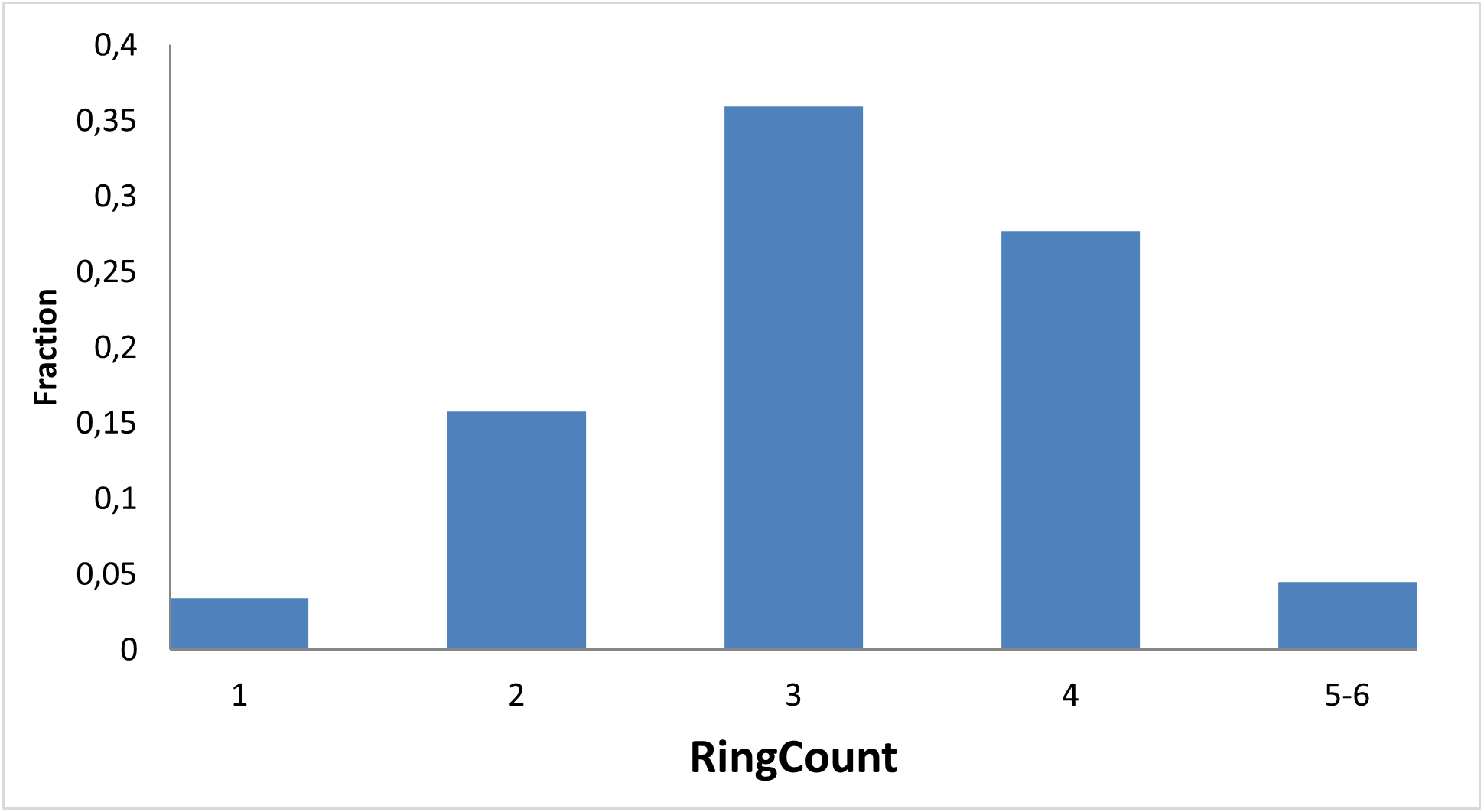
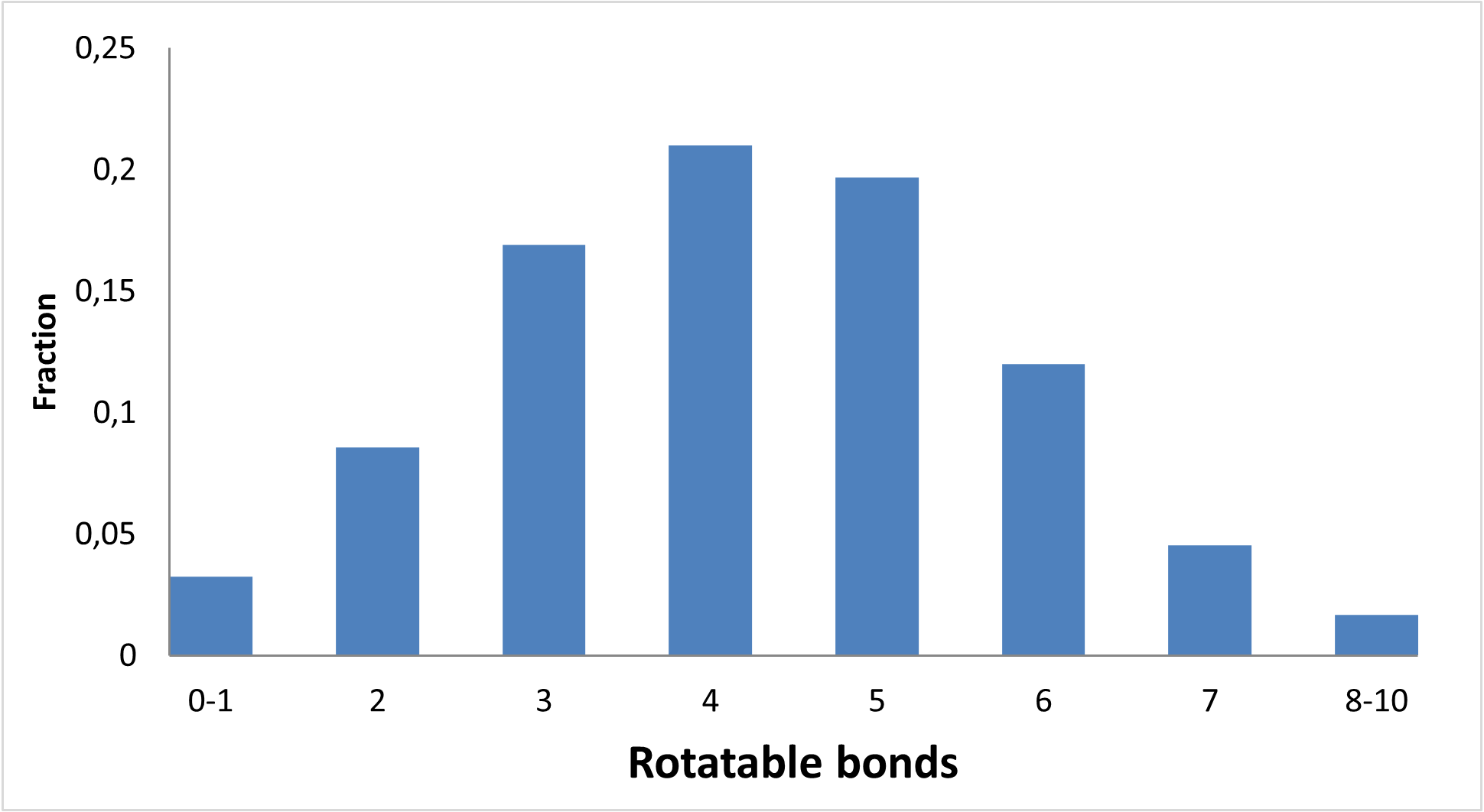
Figure below demonstrates chemical space distribution using 2D prop parameters (ClogP, fraction of Rotatable bonds, donor/acceptor count, etc.), normalized PMI vectors and distribution between classes of the most potent targets, total number of targets per compound and first level of Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification.
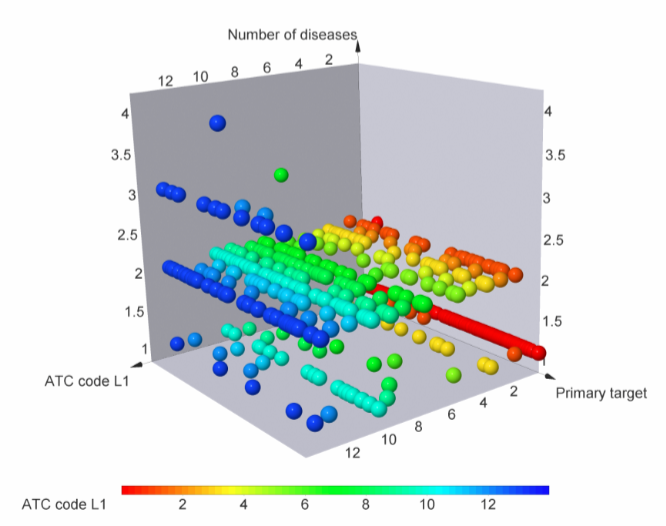
Our Phenotypic Library can be applied for screening against different protein classes and diseases, affecting adjacent tissues or individual body systems.
Designed to promote the discovery of new-generation medicine
28 000 compounds
RNA-focused drug discovery has dramatically changed over the last decade and has become the most exciting frontier in developing new-generation pharmaceuticals for better healthcare. This new stage of RNA investigation, also called “RNAissance” owes to recent advances in genetic engineering and genome sequencing. This gives us high anticipation for discovering efficient medications against difficult-to-treat and incurable diseases, along with new antibacterials and antivirals.
RNA is a versatile biomolecule capable of transferring information, adopting distinct three-dimensional shapes, and responding to ambient conditions. These biological structures can carry out a wide range of functions, from translating genetic information into the molecular machines and structures of the cell to regulating the activity of genes during development, cellular differentiation, changing environments, and more.
We focused on investigating three main types of interactions of small molecules with RNA secondary structures and 3D fold of tRNAs, and mRNAs (avoiding direct targeting of RNA helix and intercalation) with virtual screening of available structures of G-quadruplex and Riboswitches.
The library has been plated for the most convenient and quick access. Using our RNA library you receive multiple benefits, allowing you to save on time and costs in hit exploration and optimization:
- Hit confirmation support: Analogs search and hit samples resupply from dry stock with strict QC
- Straightforward & affordable synthesis of hit follow-up libraries by parallel chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry support enhanced with on-site broad ADME/T panel
Typical Formats
RNA Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
RNA-28-5-Y-10
Compounds
28 000
88 plates
Amount
5 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well acoustic LDV microplates, 320 compounds per plate, 1, 2 & 23, 24 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
RNAS-10400-10-Y-10
Compounds
10 400
33 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, echo qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
RNAR-14800-20-Y-10
Compounds
14 800
47 plates
Amount
20 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates Greiner #781280, 320 compounds per plate, first two and last two columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
RNAG4-2800-50-X-10
Compounds
2 800
35 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner #650160, 80 compounds per plate, 1 & 12 columns empty
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library design
G-quadruplexes are high-order, four-stranded structures formed by repeated guanine tracts in the genome. Despite the significant prevalence of DNA G-quadruplexes over RNA, RNA quadruplexes remain crucial in various biological processes such as epigenetic regulation, telomere maintenance, mitochondrial RNA expression, and many others. We analyzed all reported RNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) structures and created 6 docking models based on RNA aptamers and modeling of h-MYC G4s.
Riboswitches are bacterial regulatory segments of mRNA and consist of a metabolite-binding aptamer and an expression platform. They are essential for different processes: expression of viral genes, gene-regulating function, production control of the proteins encoded by the mRNA, catalyze reactions, bind to other RNA or regulatory macromolecules, and many more. Given their absence in mammalian cells, riboswitches are very attractive targets for the discovery of new antibacterials. Over 20 docking models have been created and used for in silico screening of the following riboswitches: 2-deoxyguanosine, c-di-AMP, c-di-GMP, class I PreQ1, FMN, glmS ribozyme with G40A mutation, Glutamine II, Glycine, Guanine, L-glutamine, Lysine, metY SAM V, preQ1 Class II, PreQ1, PRPP, s-adenosylhomocysteine, SMK box (SAM-III), THF, thi-Box, thi-M, ZTP riboswitch.
RNA splicing regulation is probably the most attractive in eukaryotic drug discovery. Modulation of RNA splicing would be one of the most effective ways for cancer treatment and genetic disorders. We focused on the targeting of regulatory and precursor mRNAs and kinases, which activity required for RNA splicing: serine and arginine-rich splicing factor protein kinases SRPKs and CDC2-like kinases CLKs.
The structure-based approach (molecular docking) has been used as a main technique for library construction. All available PDB structures of RNA G4s, riboswitches, mRNAs and SRPK and CLK kinase swere analyzed. Unique "protein-ligand" complexes were selected for further analysis and docking model constructions. The following PDB structures were used for G4s: 6C63, 6e81, 6E81, 6E8S, 7oa3, 8EYV; and Riboswitches: 2hom, 2miy, 3b4b, 3d0u, 3e5e, 3irw, 3npn, 3p49, 3q50, 3ski, 4lvy, 4nya, 4nyb, 4nyd, 4qk8, 4rzd, 5c45, 5ddq, 6ck4, 6fz0, 6p2h, 6qn3, 6uc8, 6uc9, 6wzs.
Pharmacophore models are represented below using the following color scheme: red spheres - H-bond acceptors, blue – Hb donors, orange – aromatic groups, and grey spheres represent any other atom types, purple – mixed acceptor/donor groups. RNA nucleobases are highlighted in green, the native is yellow, and an example of a docked ligand is shown in grey.
Examples of molecular docking simulation, and used pharmacophore models, G-quadruplex
Example 1 (PDB ID 5bjp, RNA aptamer)
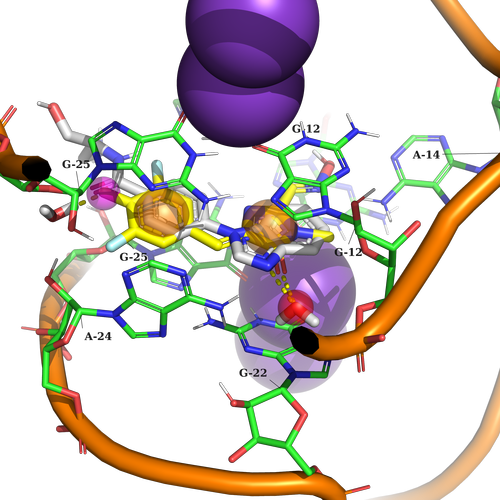
Example 1. The potential ligand should contain two aromatic features to create stacking interaction with G25, A24, G12, and G22. Additionally, it should be capable of forming hydrogen bond interactions with two HOH (water) molecules.
Example 2 (PDB ID 6c63)
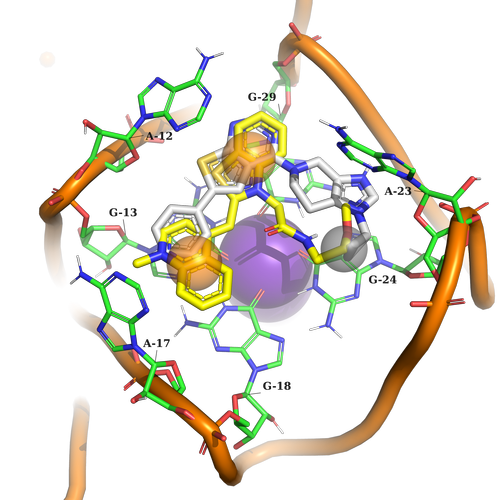
Example 2. The ligand must contain two aromatic parts for stacking interaction with G13, G18, A12, and G29. At another part of the pocket, it should just fill in the sub-pocket formed by A23 and G24.
Examples of molecular docking simulation, and used pharmacophore models, riboswitches
Example 1 (PDB ID 3e5e, SAM Riboswitch)
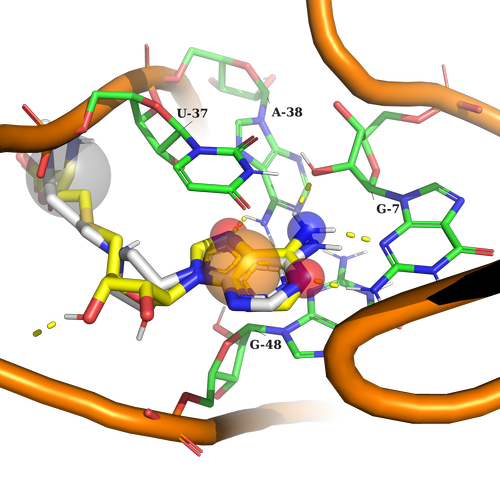
Example 1. According to the used pharmacophore model ligand should contain an aromatic part to interact by stacking interactions with U37, and G48, Any atom part just to fill in the sub-pocket behind U37, and 3 donors of h-bond interaction (two acceptors, and one donor) to interact with G7, A38. It is important to note here, that the ligand should contain at least 2 of 3 h-bond interaction features used in the pharmacophore model.
Example 2 (PDB ID 3d0u, Lysine Riboswitch)
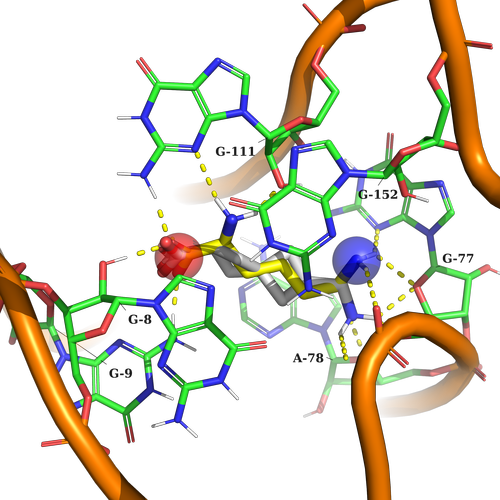
Example 2. In this case, the ligand should contain a string acceptor to imitate the COOH lysine group, and on the other part of the pocket NH3 group to crate caton-p interaction with surrounding nucleotides.
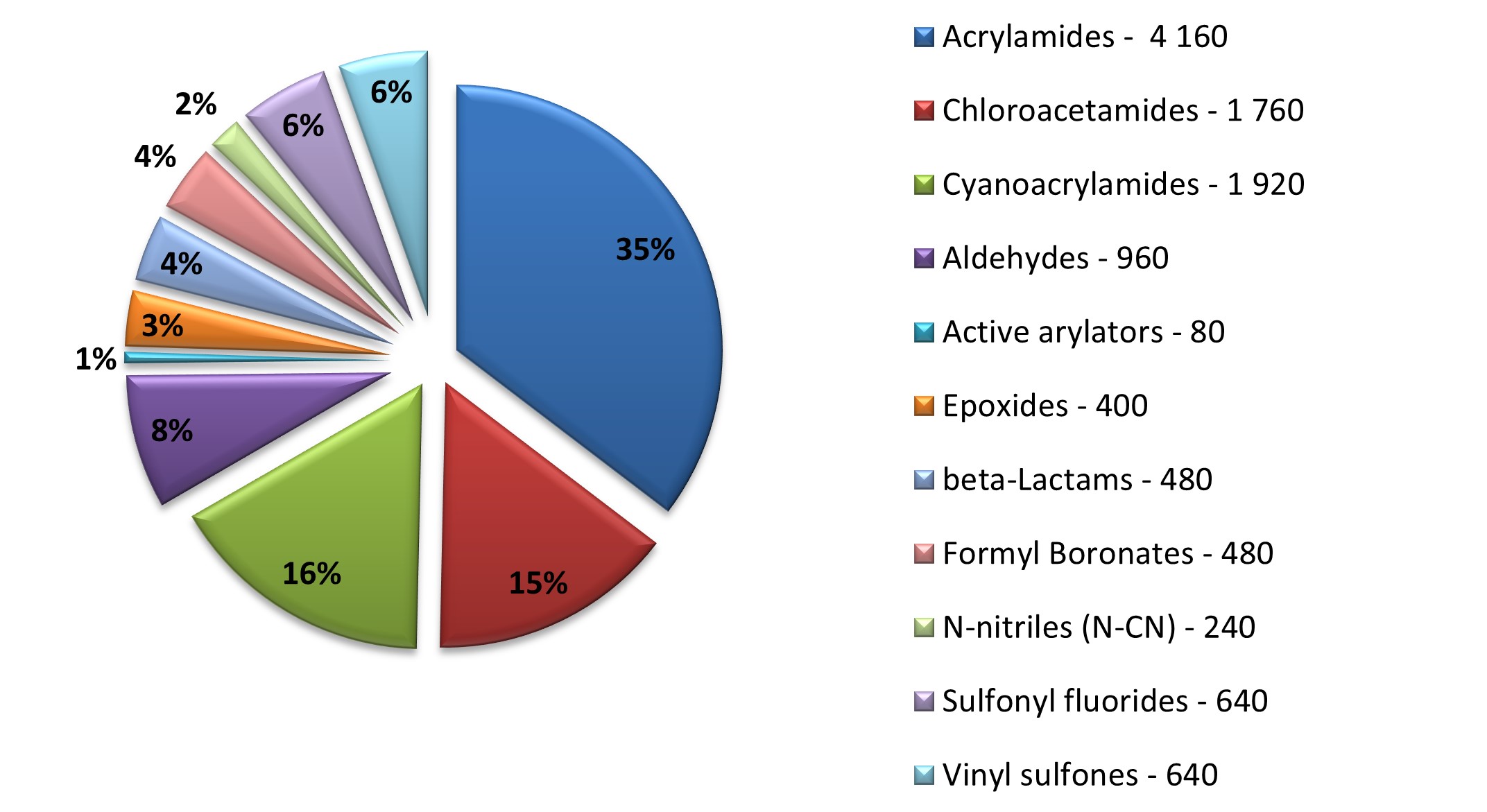
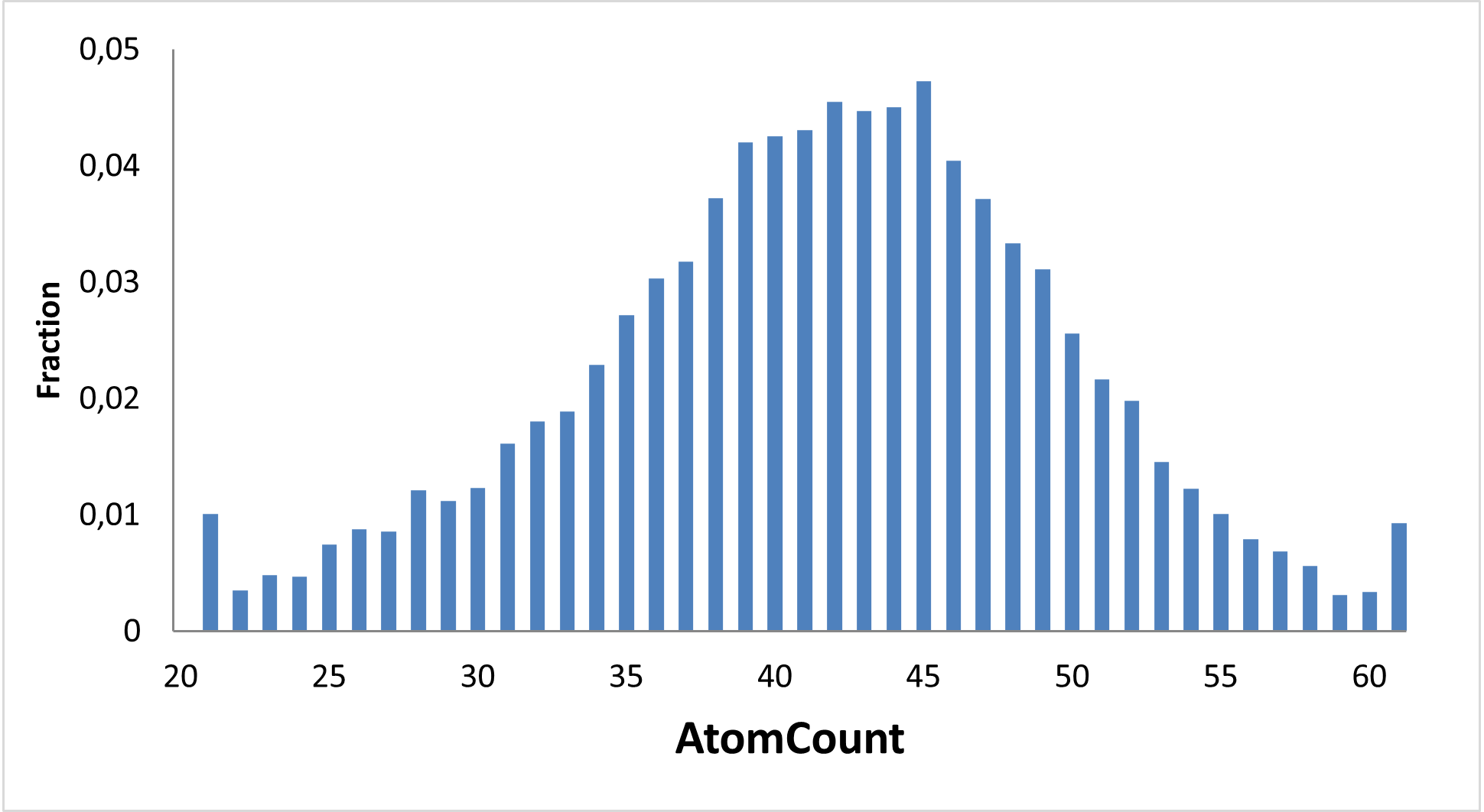
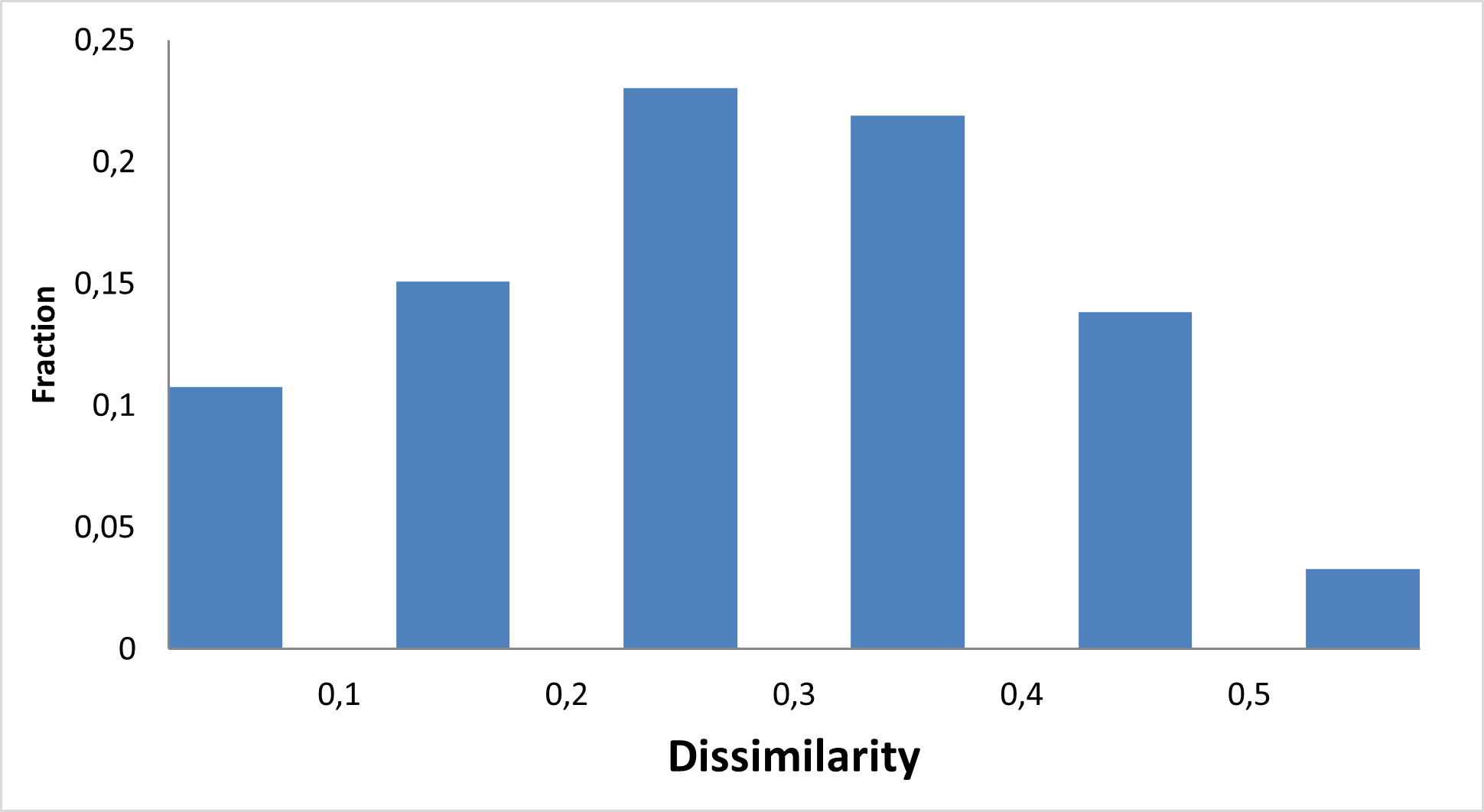
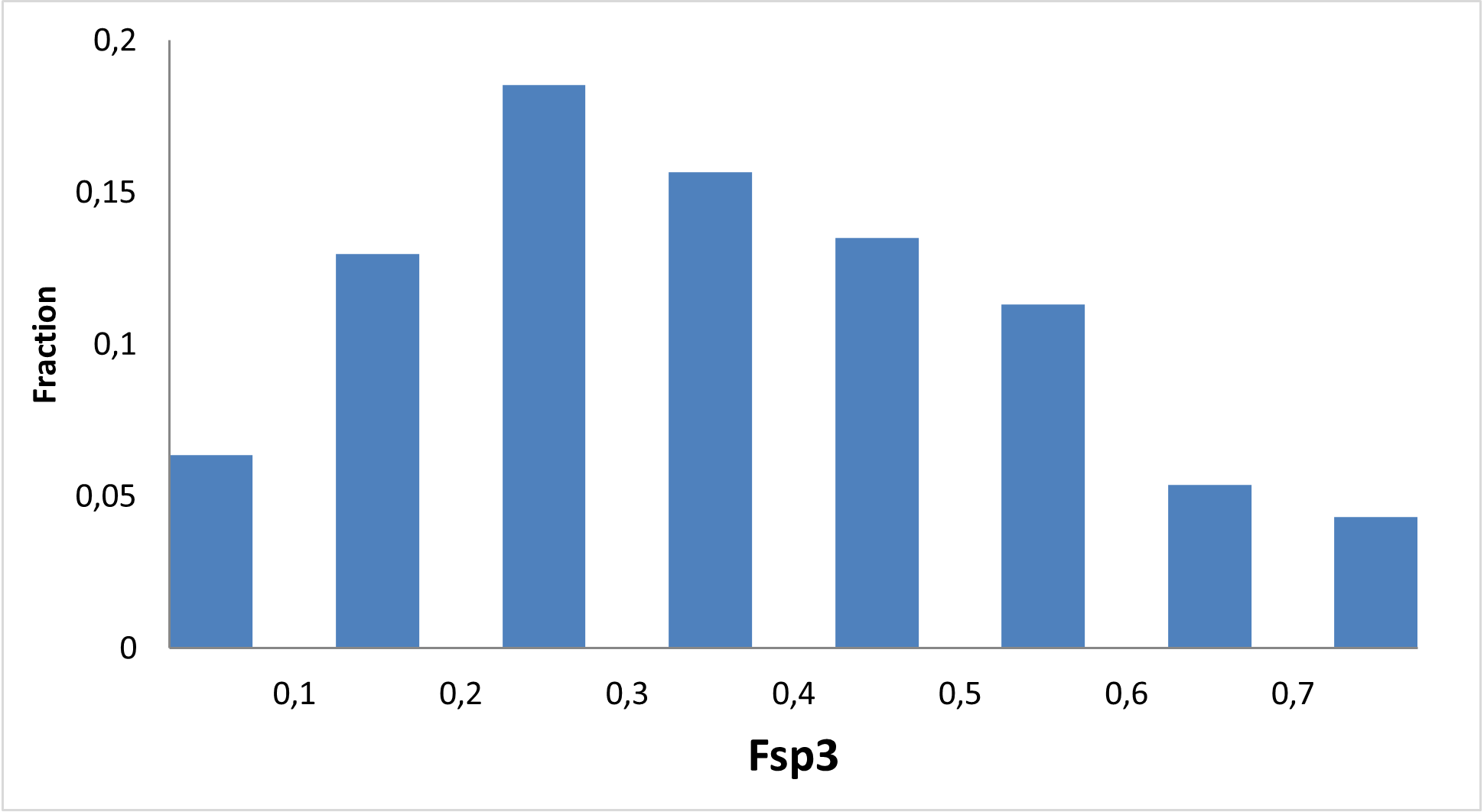
Diverse covalent library with most demanded warhead types
11 760 compounds
Covalent probes play an essential role in the discovery of new technologies, investigation of new proteins, and assessment of their drugability. We at Enamine have been working since 2016 on synthesis on covalent compounds and development of new covalent warheads.
Enamine focused on the elaboration of parallel synthesis approaches to synthesize a series of new valuable covalent compounds with well-working and not overreactive warheads. All our efforts resulted in the production of the largest commercially available Collection of Covalent Compounds. Most interesting and popular covalent classes were assembled into a diverse Library, aimed to represent Enamine’s Covalent Collection.
The Library is available in pre-plated format at 10 mM concentration in DMSO. Each covalent binder type is plated in separate plates.
Typical Formats
Covalent Screening Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
Covalent Screening Library
CSL-11-10-Y-10
Compounds
11 760
37 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Representative Set
CSRS-320-20-Y-10
Compounds
320
1 plate
Amount
20 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well Echo Qualified LDV plates, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Acrylamides
CSAC-4160-20-Y-10
Compounds
4 160
13 plates
Amount
20 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates, Greiner #765021, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Cyanacrylamides
CSCN-1920-10-Y-10
Compounds
1 920
6 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well echo LDV plates, #LP-200, 1,2 and 23,24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Chloroacetamides
CSCL-1200-25-Y-10
Compounds
1 200
4 plates
Amount
25 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates, Greiner #784201, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Vinyl Sulfones
CSVS-640-50-X-10
Compounds
640
2 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, 2D-barcoded Matrix microtubes #4271, 1 and 12 columns empty, 80 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
Formyl Boronates
FBA-480-15-Y-10
Compounds
480
2 plates
Amount
15 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well echo plates, Labcyte #PP-0200, 1,2 and 23,24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Key features
- Careful choice of warheads: only experimentally confirmed, well-validated, and reported in the number of papers. No overreactive binders.
- All compounds in the library feature a certain chemotype, “recognition pattern”, to avoid promiscuous bindings.
- Compounds plated by classes for ease of reactivity analysis and residue-focusing screening campaigns.
Examples of molecules in the library
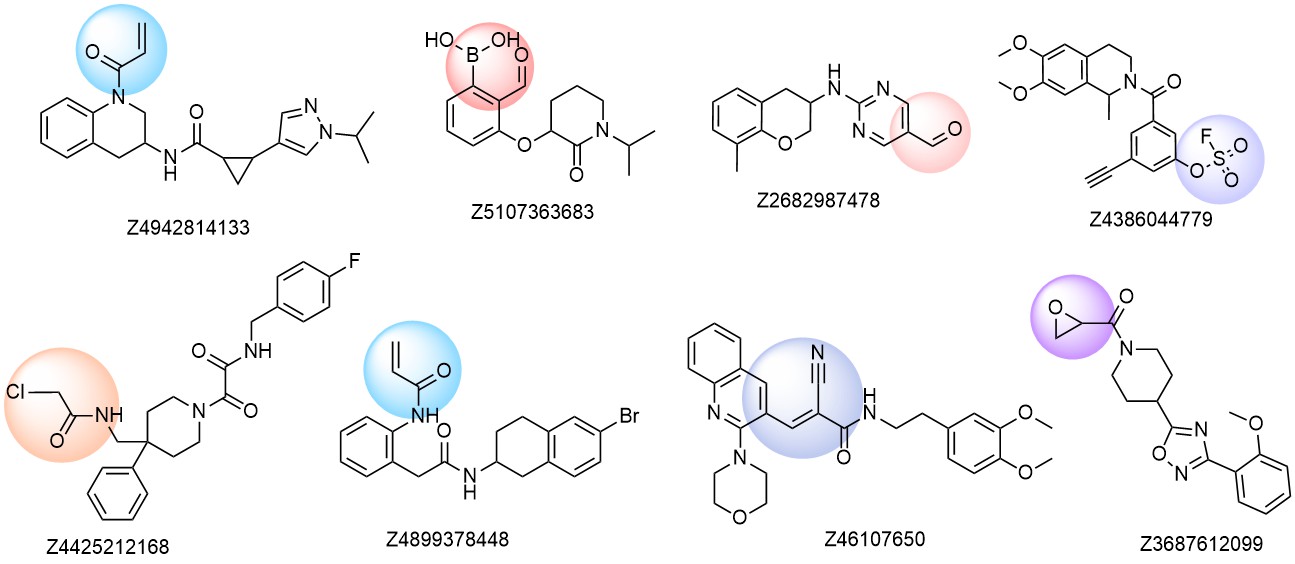
Distribution by covalent warheads