Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 17, 3584-3591
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201301737
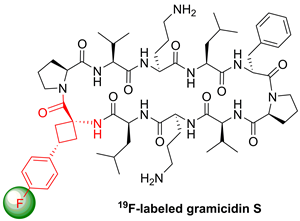
A monofluoro-substituted amino acid was designed to serve as a conformationally restricted label for solid-state 19F NMR distance measurements in membrane-bound peptides. The aromatic cisand transisomers of 1-amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclobutanecarboxylic acid were synthesized in five steps from diethyl 2-(4-fluorophenyl)propanedioate. They were incorporated into the antimicrobial peptide gramicidin S to replace a native DPhenylalanine residue. Because the Cα-tetrasubstituted amino acid cannot racemize, it showed full compatibility with solid-phase peptide synthesis protocols. According to circular dichroism analysis and molecular modeling, the 19F-labeled analogues of the known helix-inducing amino acid (1-aminocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid) do not disrupt the peptide conformation when substituted for Phe, neither in a β-turn nor in an α-helix.