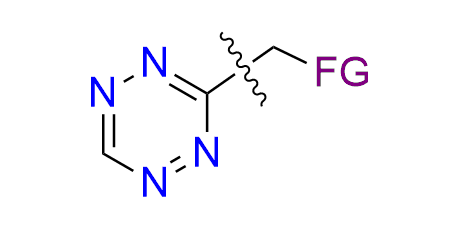
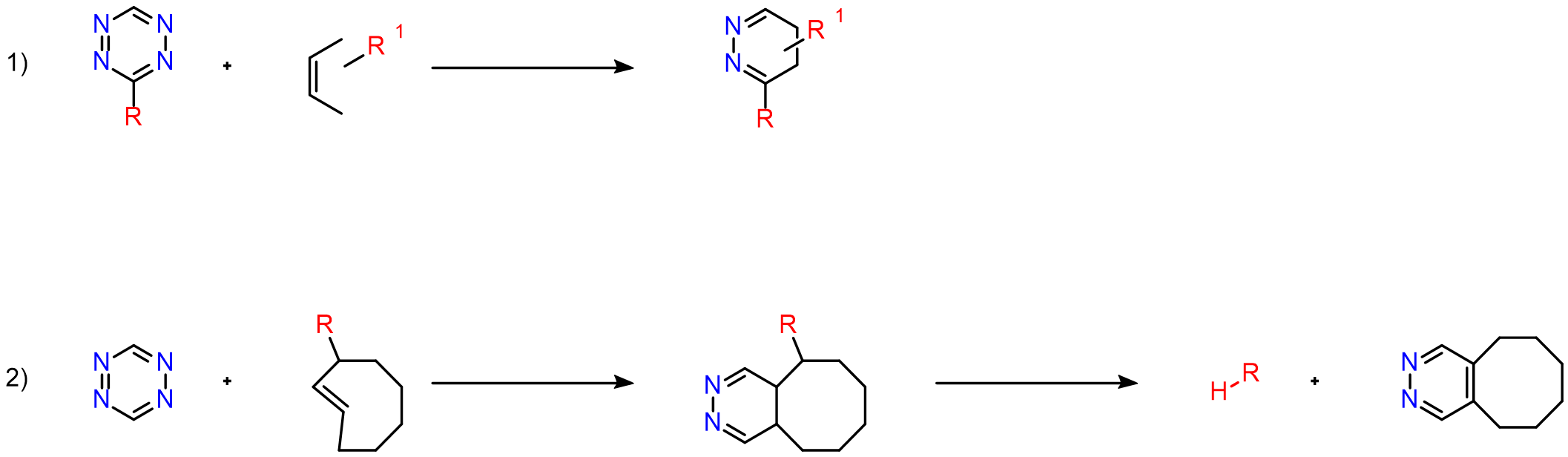
A well-known bioorthogonal reaction is the Inverse Electron Demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) cycloaddition between 1,2,4,5-tetrazines (electron-deficient dienes) and strained alkenes (such as norbornenes, trans-cyclooctenes, and cyclopropenes). This reaction is exceptionally fast, does not require a catalyst, and proceeds cleanly in complex biological systems without perturbing the biological milieu. The two major applications of tetrazine-based cycloadditions include: bioconjugation and click-to-release chemistry
Another important application of tetrazines in chemical biology is their ability to quench fluorescence. When a tetrazine is attached to a fluorophore, it quenches the fluorescence; however, after the cycloaddition reaction, the fluorescence is restored.
Enamine offers a wide range of functionalized tetrazines, all available from stock.
Download SD files
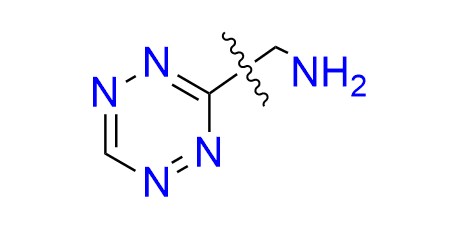
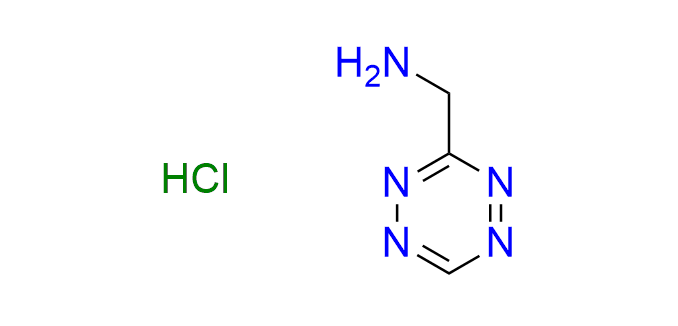
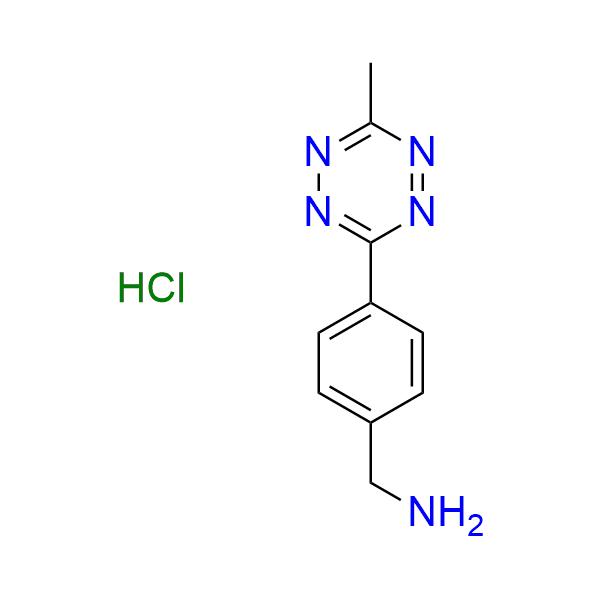
1-(1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)methanamine hydrochloride
CAS 2252340-10-4 (hydrochloride), 1414369-55-3 (base), Cat. No EN300-45381399
The simplest tetrazine derivative featuring a primary amine functionality.
- J. C. Sarris, T. Hansen, M. A. R. de Geus, E. Maurits, W. Doelman, H. S. Overkleeft, J. D. C. Codée, D. V. Filippov and S. I. van Kasteren, Chem. Eur. J., 2018, 24, 18075. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803839
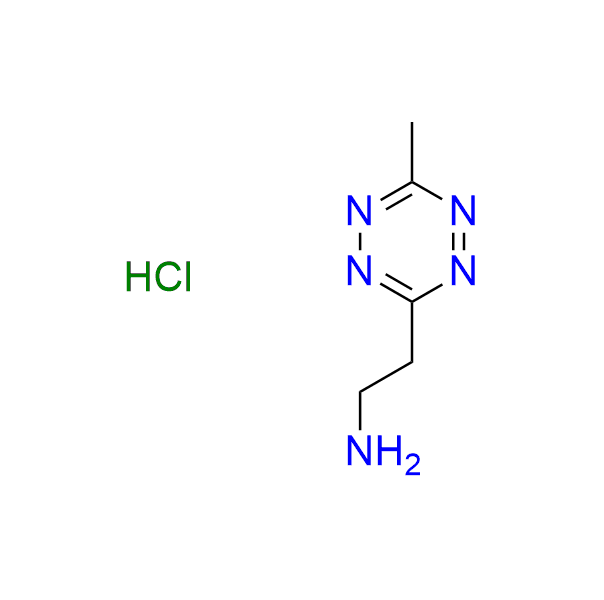
2-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)ethan-1-amine hydrochloride
CAS 2252340-03-5 (hydrochloride), 2171095-25-1 (base), Cat. No EN300-47338928
The compound is useful both as a pH-independent component in click-to-release chemistry and as a compact tetrazine bearing an amine group for ligation reactions.
- J. C. Sarris, T. Hansen, M. A. R. de Geus, E. Maurits, W. Doelman, H. S. Overkleeft, J. D. C. Codée, D. V. Filippov and S. I. van Kasteren, Chem. Eur. J., 2018, 24, 18075. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803839
- Shi, J. Li, X. He, S. Zhou, H. Sun and H. Wu, Org. Lett., 2022, 24, 3368–3372. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c01118
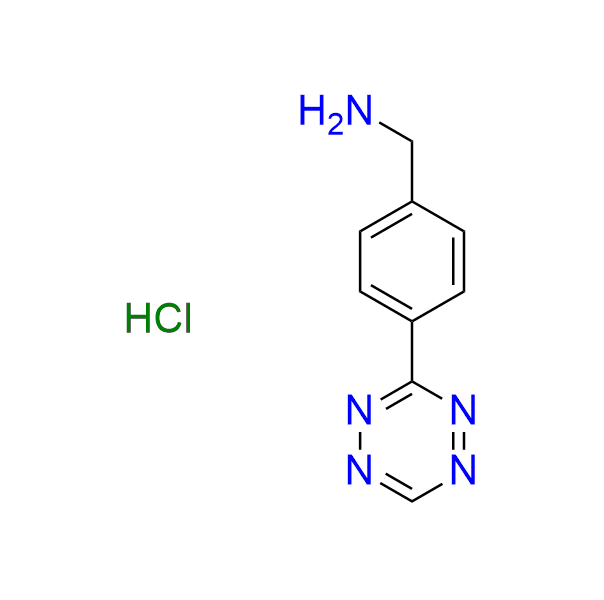
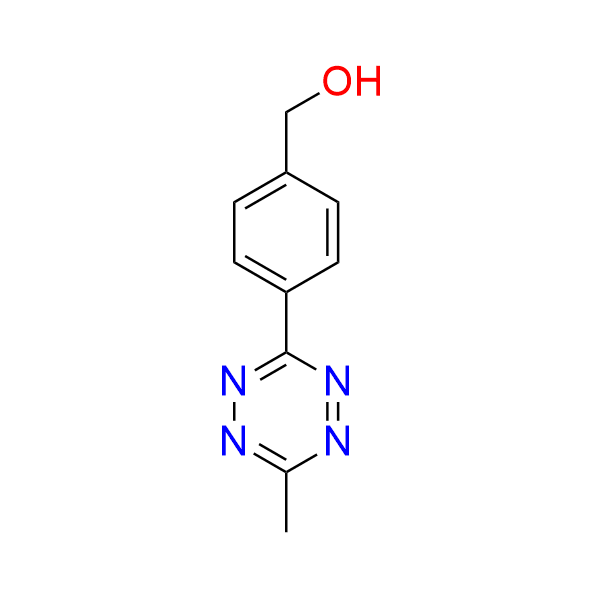
1-[4-(1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]methanamine hydrochloride
CAS 1416711-59-5 (hydrochloride), 1092689-33-2 (base), Cat. No EN300-189526
A well-known tetrazine used in IEDDA ligations, featuring an amino moiety.
- Brudno, R. M. Desai, B. J. Kwee, N. S. Joshi, M. Aizenberg and D. J. Mooney, ChemMedChem, 2015, 10, 617–620. DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201402527
- S. Erdmann, H. Takakura, A. D. Thompson, F. Rivera-Molina, E. S. Allgeyer, J. Bewersdorf, D. Toomre and A. Schepartz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 10242–10246. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201403349
- Uttamapinant, J. D. Howe, K. Lang, V. Beránek, L. Davis, M. Mahesh, N. P. Barry and J. W. Chin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 4602–4605. DOI: 10.1021/ja512838z
1-[4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]methanamine hydrochloride
CAS 1596117-29-1 (hydrochloride), 1345955-28-3 (base), Cat. No EN300-25385661
This well-known tetrazine, bearing an amine handle, is employed in both IEDDA ligations and click-to-release chemistry.
- Sen, D. Gahtory, J. Escorihuela, J. Firet, S. P. Pujari and H. Zuilhof, Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23, 13015. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201703103
- Si, H. Zhu, J. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Pan and J. Zhang, Bioorg. Chem., 2023, 135, 106497. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106497
- A. J. C. Sarris, T. Hansen, M. A. R. de Geus, E. Maurits, W. Doelman, H. S. Overkleeft, J. D. C. Codée, D. V. Filippov and S. I. van Kasteren, Chem. Eur. J., 2018, 24, 18075. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803839
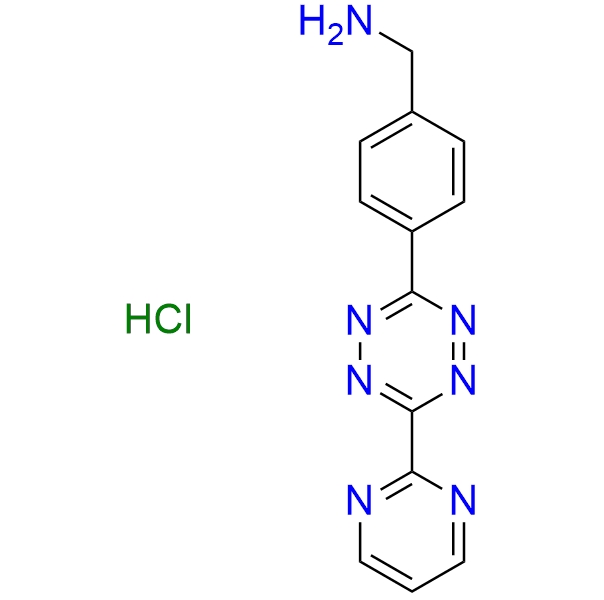
1-{4-[6-(pyrimidin-2-yl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl]phenyl}methanamine hydrochloride
CAS 2252340-09-1 (hydrochloride), 1345955-30-7 (base), Cat. No EN300-47337814
This tetrazine exhibits enhanced reactivity in IEDDA reactions due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the pyrimidine ring. It is used in ligation reactions as well as a pH-independent partner in click-to-release methodology.
- J. C. Sarris, T. Hansen, M. A. R. de Geus, E. Maurits, W. Doelman, H. S. Overkleeft, J. D. C. Codée, D. V. Filippov and S. I. van Kasteren, Chem. Eur. J., 2018, 24, 18075. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201803839
- I. Willems, N. Li, B. I. Florea, M. Ruben, G. A. van der Marel and H. S. Overkleeft, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 4431–4434. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201200923
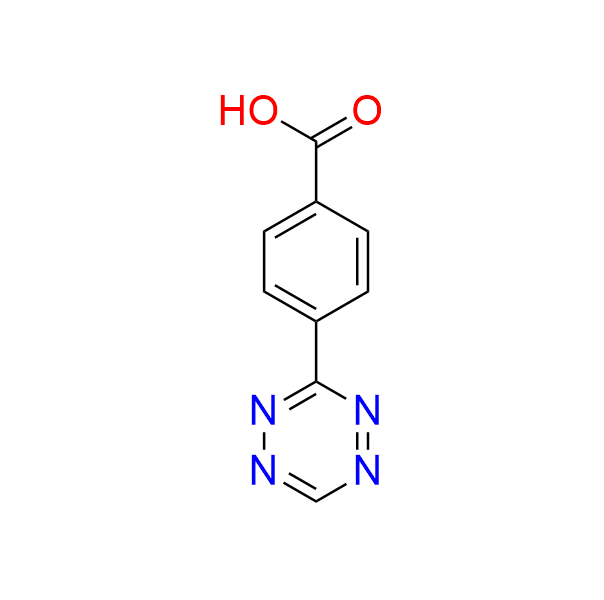
4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)benzoic acid
CAS 1345866-65-0, Cat. No EN300-25368796
A well-known, simple tetrazine with a carboxyl handle, used in both ligation reactions and click-to-release drug delivery.
- R. Edelmann, C. Bredack, S. Belli, P. Mohr, M.-P. Imhoff, F. Reggiani, E. A. Kusznir, A. C. Rufer, D. P. Holt, H. Valentine, D. F. Wong, R. F. Dannals, M. Honer and L. C. Gobbi, Bioconjugate Chem., 2023, 34, 1882–1893. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00385
- Friederich, C. Xu, P. Raunft, H. L. S. Fuchs and M. Brönstrup, Chem. Commun., 2023, 59, 7451–7454. DOI: 10.1039/D3CC01334K
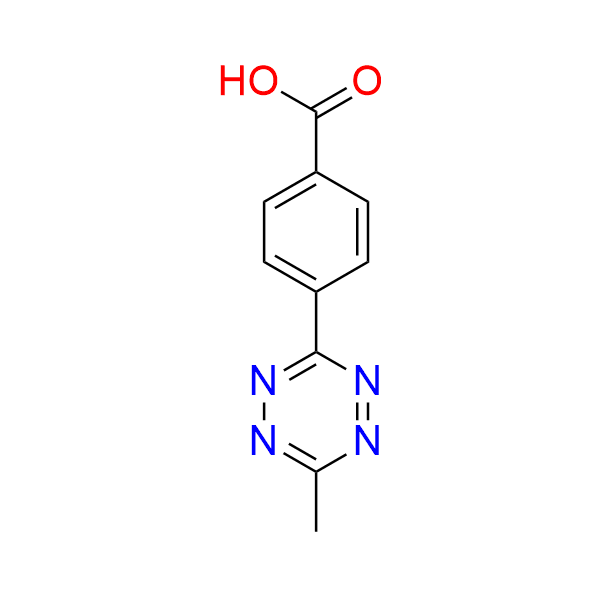
4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)benzoic acid
CAS 1345866-66-1, Cat. No EN300-5505483
This well-known, simple tetrazine with a carboxyl handle is commonly used in bioorthogonal ligation reactions.
- Linden and O. Vázquez, Chem. Eur. J., 2020, 26, 10014. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202001718
- R. Edelmann, C. Bredack, S. Belli, P. Mohr, M.-P. Imhoff, F. Reggiani, E. A. Kusznir, A. C. Rufer, D. P. Holt, H. Valentine, D. F. Wong, R. F. Dannals, M. Honer and L. C. Gobbi, Bioconjugate Chem., 2023, 34, 1882–1893. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00385
- E. Z. Klier, A. M. M. Gest, J. G. Martin, R. Roo, M. X. Navarro, L. Lesiak, P. E. Deal, N. Dadina, J. Tyson, A. Schepartz and E. W. Miller, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 12138–12146. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c02664
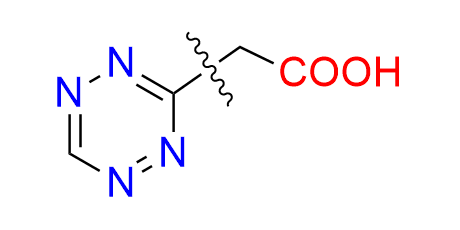
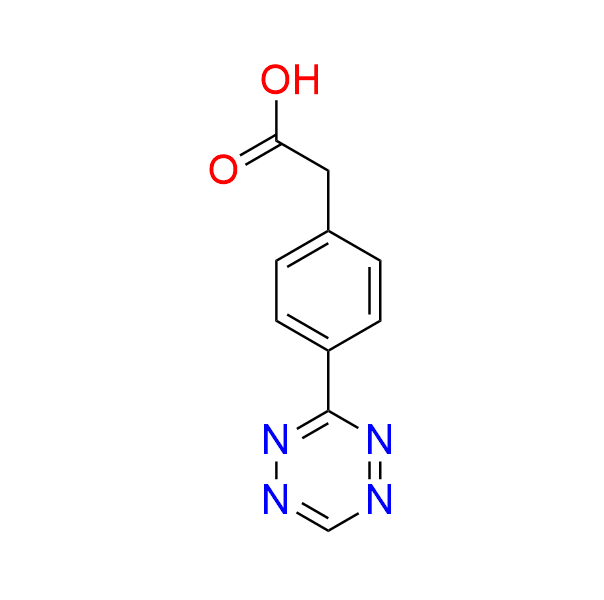
2-[4-(1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]acetic acid
CAS 1380500-92-4, Cat. No EN300-5503971
This carboxyl-containing tetrazine is widely used in bioorthogonal ligations, particularly in proteomics and antibody-drug conjugation.
- M. Zeglis, F. Emmetiere, N. Pillarsetty, R. Weissleder, J. S. Lewis and T. Reiner, ChemistryOpen, 2014, 3, 48–53. DOI: 10.1002/open.201402000
- Fang, S. Chakraborty, E. M. Dieter, Z. E. Potter, C. K. Lombard and D. J. Maly, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 11912–11922. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b02963
- B. M. Poulie, E. Sporer, L. Hvass, J. T. Jørgensen, P. J. Kempen, S. I. Lopes van den Broek, V. Shalgunov, A. Kjaer, A. I. Jensen and M. M. Herth, Chem. Eur. J., 2022, 28, e202201847. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202201847
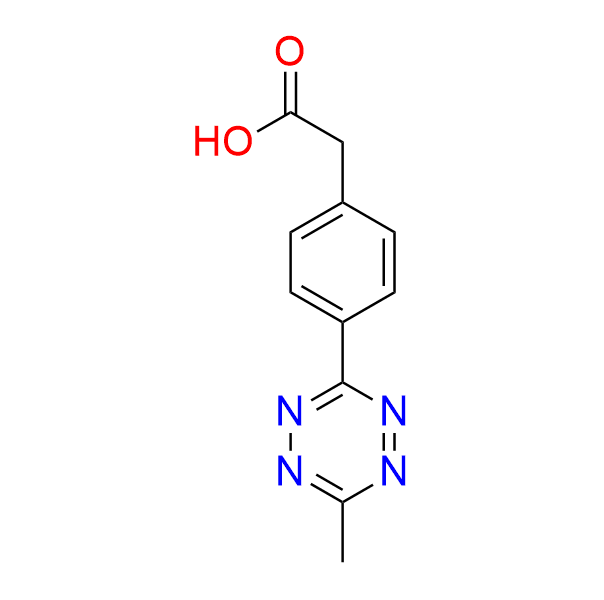
2-[4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]acetic acid
CAS 1380500-88-8, Cat. No EN300-233665
This carboxyl-containing tetrazine is employed in prodrug activation and proteomics applications.
- J. M. Song, A. Menon, D. C. Mitchell, O. T. Johnson and A. L. Garner, ACS Comb. Sci., 2017, 19, 763–769. DOI: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00128
- M. M. A. Mitry, M. L. Dallas, S. Y. Boateng, F. Greco and H. M. I. Osborn, Bioorg. Chem., 2024, 147, 107304. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107304
- Y. Ma, Y. Zhou, J. Long, Q. Sun, Z. Luo, W. Wang, T. Hou, L. Yin, L. Zhao, J. Peng and Y. Ding, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202318372. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202318372
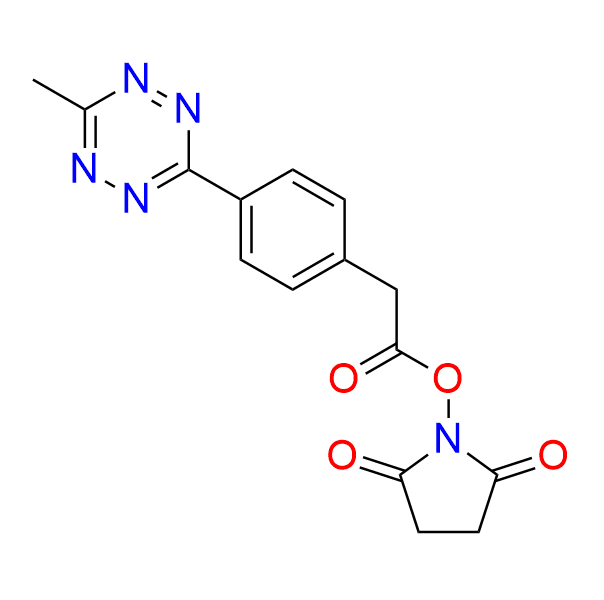
2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl 2-[4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]acetate
CAS 1644644-96-1, Cat. No EN300-7406911
A ready-to-use tetrazine containing an acylation reagent, used in prodrug activation and proteomics.
- M. Song, A. Menon, D. C. Mitchell, O. T. Johnson and A. L. Garner, ACS Comb. Sci., 2017, 19, 763–769. DOI: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00128
- M. A. Mitry, M. L. Dallas, S. Y. Boateng, F. Greco and H. M. I. Osborn, Bioorg. Chem., 2024, 147, 107304. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107304
- Y. Ma, Y. Zhou, J. Long, Q. Sun, Z. Luo, W. Wang, T. Hou, L. Yin, L. Zhao, J. Peng and Y. Ding, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202318372. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202318372
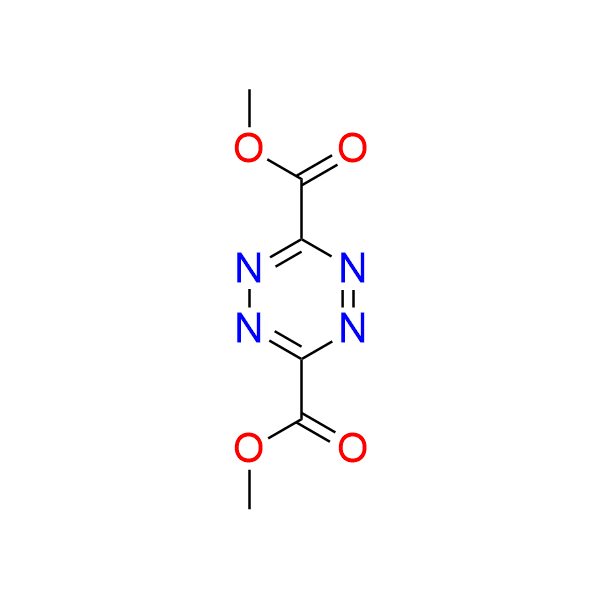
3,6-dimethyl 1,2,4,5-tetrazine-3,6-dicarboxylate
CAS 2166-14-5, Cat. No EN300-211397
A highly reactive tetrazine in IEDDA chemistry. Although not suitable for bioorthogonal transformations due to its high reactivity, the compound possesses immense synthetic potential as a building block in [4+2] cycloadditions.
- H. Marzabadi, S. P. Kelty and A. Altamura, Carbohydr. Res., 2022, 519, 108623. DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2022.108623
- D. Helm, J. E. Moore, A. Plant and J. P. A. Harrity, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 3889–3892. DOI: 10.1002/anie.200500288
- Sauer, P. Bäuerlein, W. Ebenbeck, C. Gousetis, H. Sichert, T. Troll, F. Utz and U. Wallfahrer, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2001, 2001, 2629–2638. DOI: 10.1002/1099-0690(200107)2001:14<2629::AID-EJOC2629>3.0.CO;2-2
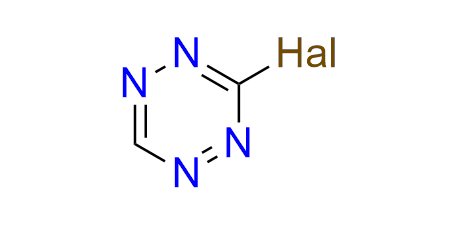
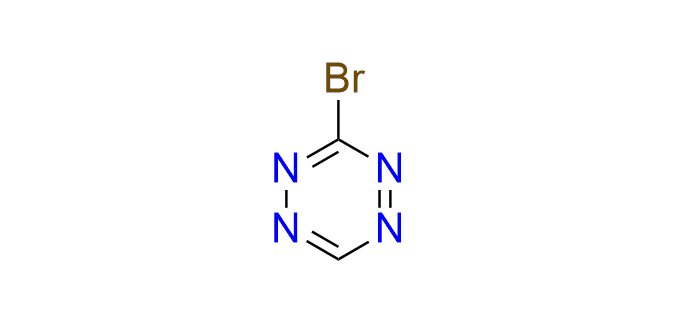
3-bromo-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 2396594-00-4, Cat. No EN300-27145343
A versatile small building block for the incorporation of a tetrazine fragment via arylation and cross-coupling reactions. 3-Bromotetrazine readily arylates O- and N-nucleophiles and also reacts with a variety of boronic acids under Suzuki–Miyaura coupling conditions. The products of these reactions include tetrazine-containing amino acids, fluorogenic probes, and compounds for click-to-release bioorthogonal transformations.
- D. Schnell, L. V. Hoff, A. Panchagnula, M. H. H. Wurzenberger, T. M. Klapötke, S. Sieber, A. Linden and K. Gademann, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 3042–3047. DOI: 10.1039/C9SC06169J
- Ros, M. Bellido, X. Verdaguer, L. Ribas de Pouplana and A. Riera, Bioconjugate Chem., 2020, 31, 933–938. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00052
- V. Hoff, S. D. Schnell, A. Tomio, A. Linden and K. Gademann, Org. Lett., 2021, 23, 5689–5692. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01813
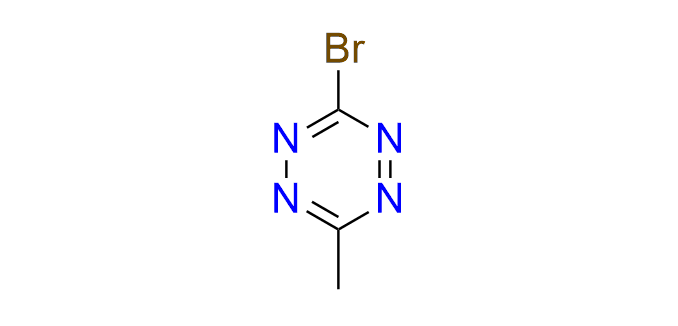
3‑bromo‑6‑methyl‑1,2,4,5‑tetrazine
CAS 67131‑33‑3, Cat. No EN300‑7499546
A small building block for the incorporation of a tetrazine fragment via cross‑coupling reactions, including Suzuki, Sonogashira, and Stille couplings. The resulting products include tetrazine‑containing amino acids and fluorogenic tetrazine probes.
- V. Hoff, S. D. Schnell, A. Tomio, A. Linden and K. Gademann, Org. Lett., 2021, 23, 5689–5692. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01813
- Ros, A. Prades, D. Forson, J. Smyth, X. Verdaguer, L. Ribas de Pouplana and A. Riera, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 11086–11089. DOI: 10.1039/D0CC03482G
- Kim, H. Son and S. B. Park, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202310665. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202310665
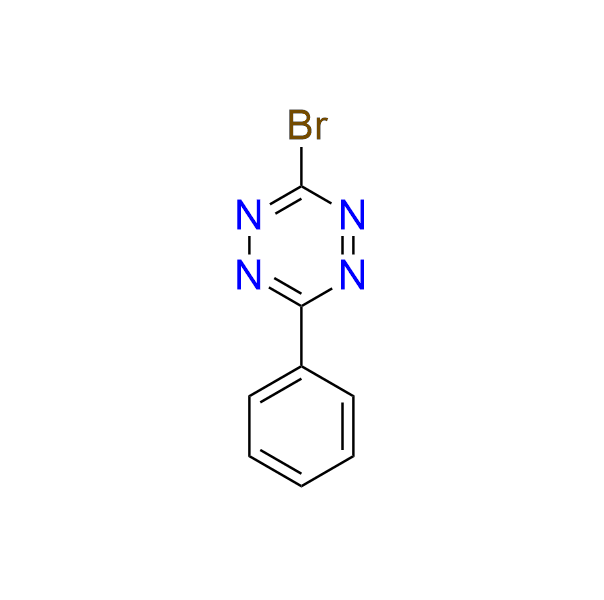
3-bromo-6-phenyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 35011‑53‑1, Cat. No EN300‑34651
The compound can serve as a precursor to various 3-substituted tetrazines via cross-coupling reactions. It has also been employed in the construction of fluorescent amino acid derivatives.
- Ros, M. Bellido, J. A. Matarin, A. Gallen, M. Martínez, L. Rodríguez, X. Verdaguer, L. Ribas de Pouplana and A. Riera, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 14321–14327. DOI: 10.1039/D2RA02531K
- Ros, A. Prades, D. Forson, J. Smyth, X. Verdaguer, L. Ribas de Pouplana and A. Riera, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 11086–11089. DOI: 10.1039/D0CC03482G
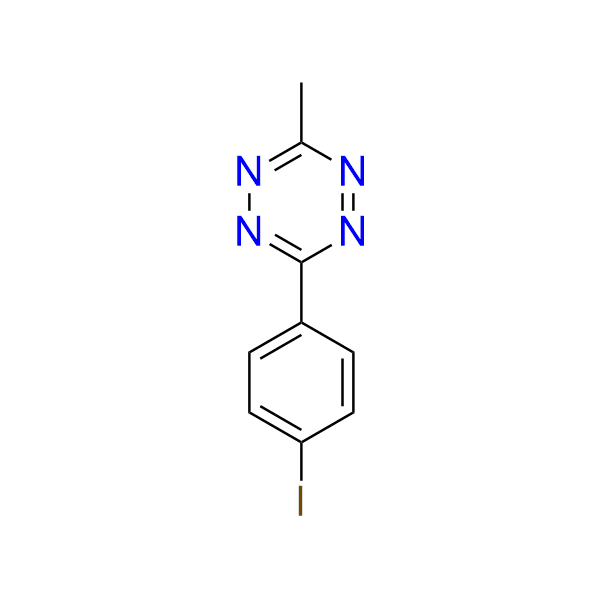
3-(4-iodophenyl)-6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 56108‑04‑4, Cat. No EN300‑1692436
The compound is used in the construction of fluorescent probes via Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, including Sonogashira and Stille couplings.
- Wieczorek, T. Buckup and R. Wombacher, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 4177–4185. DOI: 10.1039/C4OB00245H
- Lee, W. Cho, J. Sung, E. Kim and S. B. Park, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 974–983. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b10433
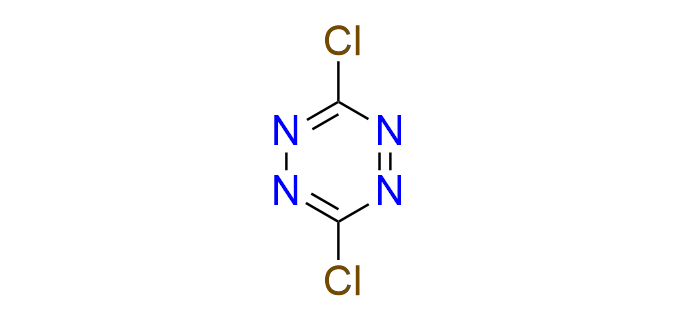
dichloro-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 106131‑61‑7, Cat. No EN300‑1726354
Dichlorotetrazine is a versatile arylation agent, with both chlorine atoms capable of undergoing successive substitution. This property enables the construction of a wide range of disubstituted tetrazine-containing compounds. Cross-coupling reactions are possible under Suzuki–Miyaura conditions. Additionally, dichlorotetrazine is a well-established building block in organic synthesis and materials science.
- Canovas, M. Moreau, C. Bernhard, A. Oudot, M. Guillemin, F. Denat and V. Goncalves, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 10646. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201806053
- M. Bender, T. C. Chopko, T. M. Bridges and C. W. Lindsley, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 5693–5696. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b02868
- Santos, D. S. Rivero, Y. Pérez-Pérez, E. Martín-Encinas, J. Pasán, A. H. Daranas and R. Carrillo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 18783. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202106230
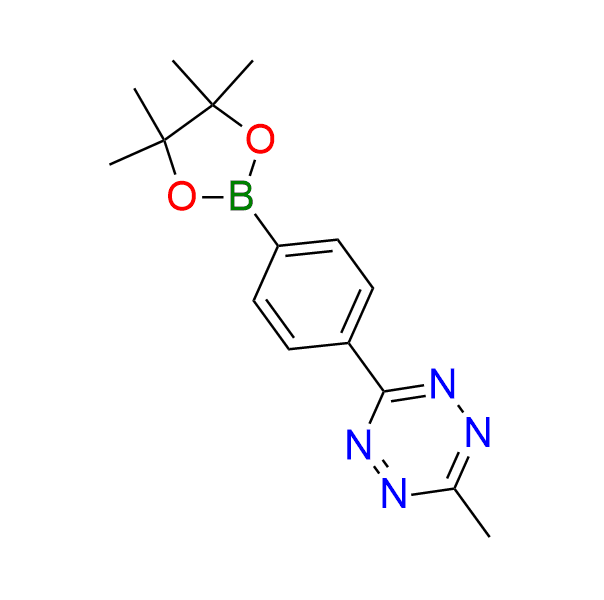
3-methyl-6-[4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl]-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 1939022‑20‑4, Cat. No EN300‑45587846
This boronic acid ester has been successfully used for the construction of tetrazine-based fluorogenic probes via Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. The resulting probes exhibit low-wavelength excitability and a high fluorescence quantum yield. IEDDA methodology has been employed for probe activation through tetrazine-to-pyridazine conversion.
- Kozma, G. Estrada Girona, G. Paci, E. A. Lemke and P. Kele, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 6696–6699. DOI: 10.1039/C7CC02212C
- Teng, R. Zhang, B. Yang, H. Yang, X. Li, D. Yin, X. Feng and Y. Tian, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2022, 10, 8642–8649. DOI: 10.1039/D2TB01893D
- Knorr, E. Kozma, A. Herner, E. A. Lemke and P. Kele, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 8972. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201600590
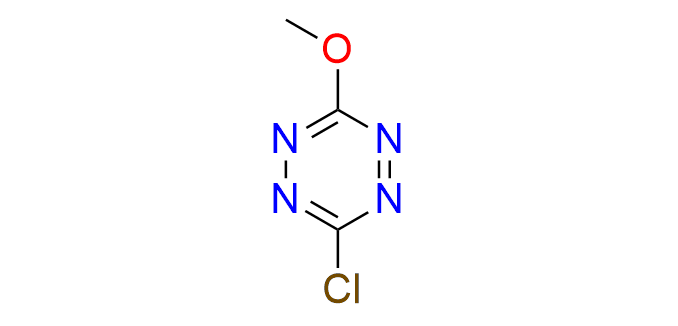
3-chloro-6-methoxy-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 614756‑34‑2, Cat. No EN300‑7627635
This compound is used in the construction of tetrazine-based fluorogenic probes.
- Audebert, F. Miomandre, G. Clavier, M.-C. Vernières, S. Badré and R. Méallet-Renault, Chem. Eur. J., 2005, 11, 5667–5673. DOI: 10.1002/chem.200401252
- Wu and D. F. O’Shea, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 10804–10807. DOI: 10.1039/C7CC06545K
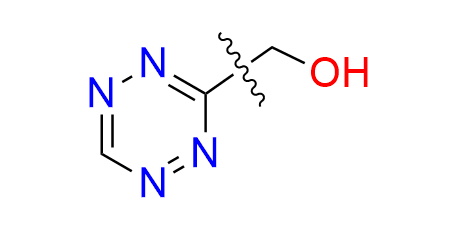
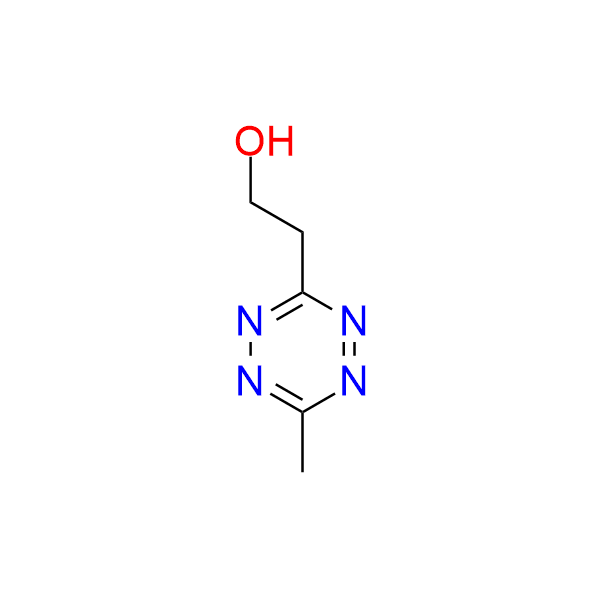
2-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)ethan-1-ol
CAS 1225146‑57‑5, Cat. No EN300‑7500987
A small and simple tetrazine bearing a hydroxyl moiety. The compound can be used in IEDDA ligation and also finds application in the synthesis of alkenyl tetrazines, which are employed as fluorogenic probes.
- V. Mayer, A. Murnauer, M.-K. von Wrisberg, M.-L. Jokisch and K. Lang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 15876. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201908209
- Wu, J. Yang, J. Šečkutė and N. K. Devaraj, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5805–5809. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201400135
[4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]methanol
CAS 1380500‑87‑7, Cat. No EN300‑7499596
This alcohol has been used in the construction of a bioorthogonal theranostic scaffold that enables click-to-release prodrug delivery accompanied by fluorescence emission.
- Pang, S. Feng, B. Huang, J. Zhou, L. Zhan and Y.-Q. Long, J. Med. Chem., 2025, 68, 3824–3836. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02965
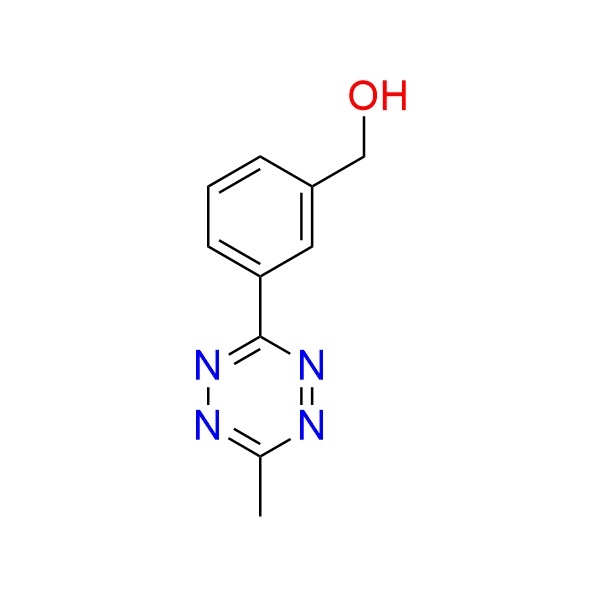
[3-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenyl]methanol
CAS 2382712‑97‑0, Cat. No EN300‑45587416
This alcohol has been used in the synthesis of tetrazine-containing amino acids.
- S. V. Mayer, A. Murnauer, M.-K. von Wrisberg, M.-L. Jokisch and K. Lang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 15876. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201908209
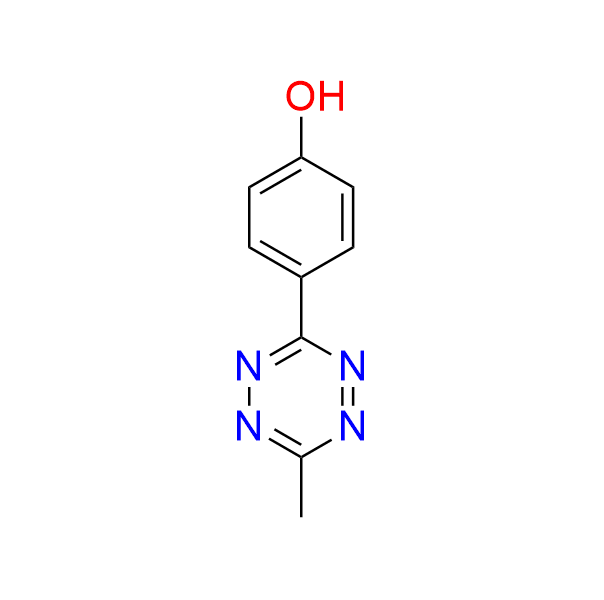
4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)phenol
CAS 58884‑35‑8, Cat. No EN300‑2698863
A simple tetrazine bearing a phenolic moiety. It exhibits modest reactivity in the IEDDA reaction.
- M. R. Edelmann, C. Bredack, S. Belli, P. Mohr, M.-P. Imhoff, F. Reggiani, E. A. Kusznir, A. C. Rufer, D. P. Holt, H. Valentine, D. F. Wong, R. F. Dannals, M. Honer and L. C. Gobbi, Bioconjugate Chem., 2023, 34, 1882–1893. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00385
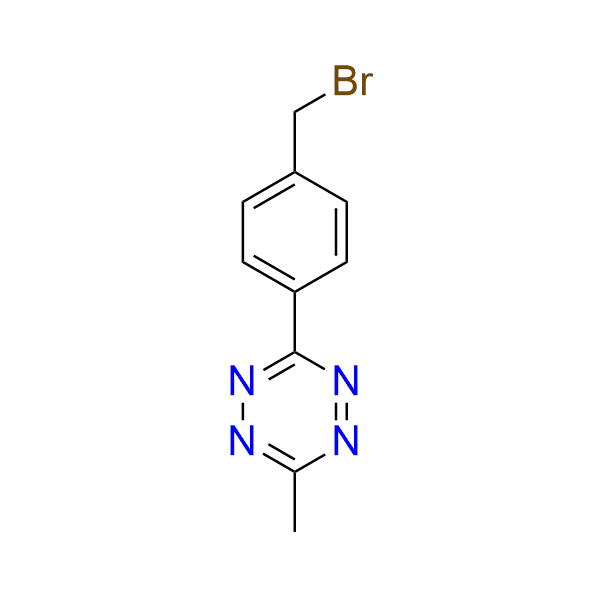
3-[4-(bromomethyl)phenyl]-6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 3017266‑45‑1, Cat. No EN300‑46767537
A tetrazine-containing alkylating agent. This compound has been used in the construction of DOTA-based lanthanide complexes, which can be utilized with peptide-based delivery systems to penetrate the blood–brain barrier.
- Woolley, Y. Wu, L. Xiong, H.-F. Chau, J. Zhang, G.-L. Law, K.-L. Wong and N. J. Long, Chem. Sci., 2025, 16, 3588–3597. DOI: 10.1039/D4SC02335H
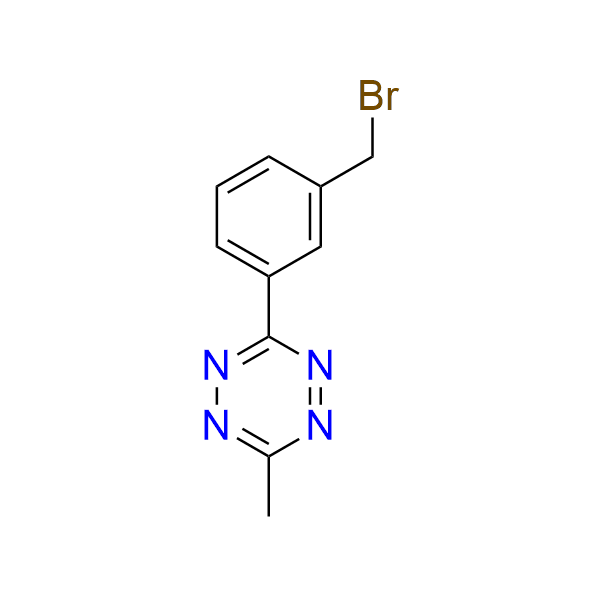
3-[3-(bromomethyl)phenyl]-6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 3017193‑98‑2, Cat. No EN300‑46614924
A tetrazine-containing alkylating agent.
- J. Zhao, H. Guo, Z. Wu and J.-H. Jiang, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 13393–13396. DOI: 10.1039/D2CC05628C
- J. Zhao, Z. Wu and J.-H. Jiang, in Live-Cell RNA Imaging, ed. S. Si, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 2875, Springer, New York, NY, 2025, pp. 165–175. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4248-1_14
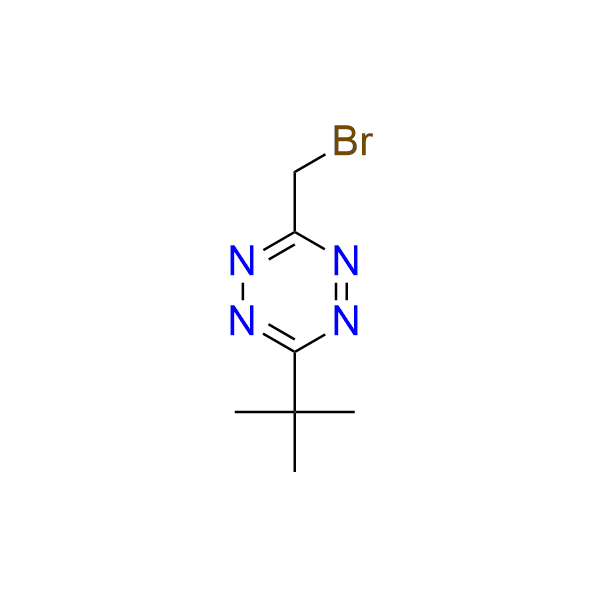
3-(bromomethyl)-6-tert-butyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 2678593‑04‑7, Cat. No EN300‑37098638
This is an unusual tetrazine that displays low reactivity in IEDDA reactions due to the steric hindrance of the bulky tert-butyl substituent. Nevertheless, it has two notable applications:
- Bioorthogonal activation of fluorophores via an isonitrile–tetrazine click-to-release reaction.
- Use as a bioorthogonally removable protecting group, cleavable by isonitriles.
- Zhang, H. Xu, J. Li, D. Su, W. Mao, G. Shen, L. Li and H. Wu, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 573. DOI: 10.1039/D1CC05774J
- Tu, D. Svatunek, S. Parvez, H. J. Eckvahl, M. Xu, R. T. Peterson, K. N. Houk and R. M. Franzini, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 169–179. DOI: 10.1039/C9SC04649F
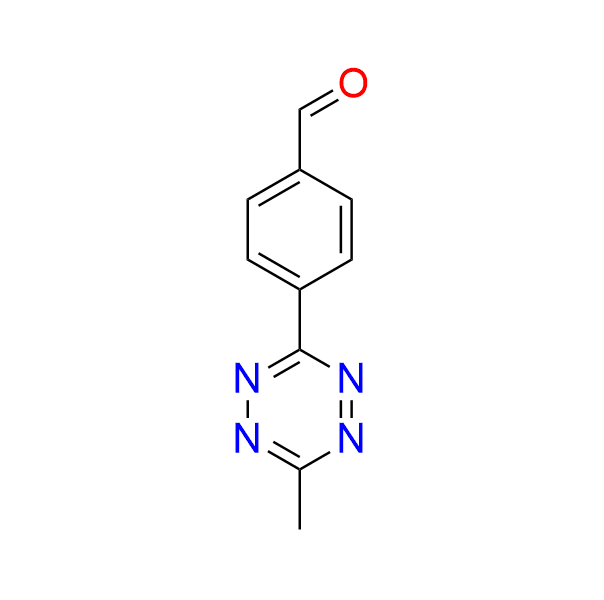
4-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)benzaldehyde
CAS 2196202‑78‑3, Cat. No EN300‑7499591
This tetrazine, bearing an aldehyde functionality, has been used in the construction of fluorogenic probes. Its mechanism relies on fluorescence quenching by the tetrazine moiety in the initial probe. Upon undergoing an IEDDA reaction, the tetrazine is converted to a pyridazine or dihydropyridazine, resulting in the loss of its quenching ability and restoration of the probe’s fluorescence.
- Wieczorek, P. Werther, J. Euchner and R. Wombacher, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 1506–1510. DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201301375
- Werther, J. S. Möhler and R. Wombacher, Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23, 18216. DOI: 10.1002/chem.201703607
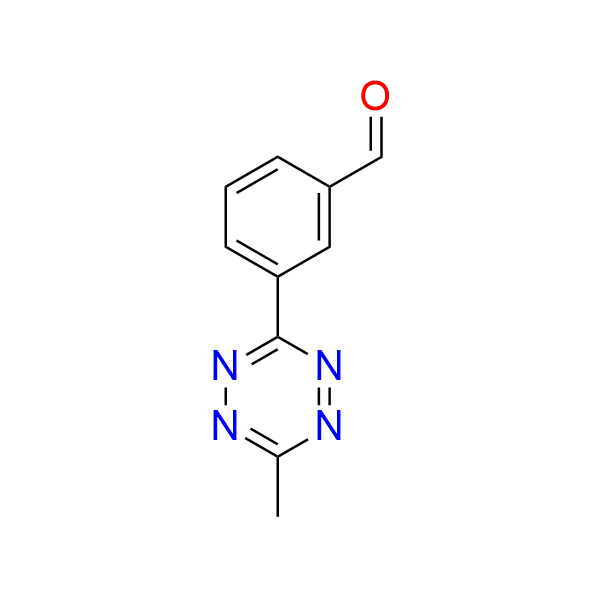
3-(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)benzaldehyde
CAS 2382712‑95‑8, Cat. No EN300‑7499590
This aldehyde-functionalized tetrazine has been used in the development of fluorogenic probes and bioorthogonally activatable photoredox catalysts. The mechanism relies on the intrinsic fluorescence quenching ability of the tetrazine moiety in the initial probe or catalyst. Upon undergoing an IEDDA reaction, the tetrazine is converted into a pyridazine or dihydropyridazine, which no longer exhibits quenching properties. This transformation restores the photochemical activity of the molecule.
- Linden, L. Zhang, F. Pieck, U. Linne, D. Kosenkov, R. Tonner and O. Vázquez, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 12868. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201907093
- Kim, Y. Xu, J. H. Lim, J. Y. Lee, M. Li, J. M. Fox, M. Vendrell and J. S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 701–712. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c13131
- Wieczorek, P. Werther, J. Euchner and R. Wombacher, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 1506–1510. DOI: 10.1039/C6SC03879D
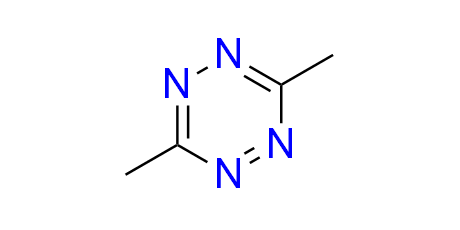
dimethyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 1558-23-2, Cat. No EN300-7316309
This small tetrazine serves two primary purposes: as a model substrate for the inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) reaction, and as a trigger for click-to-release mechanisms from trans-cyclooctenes.
- M. Versteegen, R. Rossin, W. ten Hoeve, H. M. Janssen and M. S. Robillard, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 14112–14116. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201305969
- C. T. Carlson, H. Mikula and R. Weissleder, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 3603–3612. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b11217
- M. Versteegen, W. ten Hoeve, R. Rossin, M. A. R. de Geus, H. M. Janssen and M. S. Robillard, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 10494. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201800402
3-phenyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 36022-11-4, Cat. No EN300-179268
A simple phenyl-substituted tetrazine is commonly used as a model substrate for mechanistic studies and for evaluating the reactivity of IEDDA-compatible dienophiles. Additionally, it serves as a valuable building block for the synthesis of pyridazines.
- Svatunek, M. Wilkovitsch, L. Hartmann, K. N. Houk and H. Mikula, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 8171–8177. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c01056
- Eising, A. H. J. Engwerda, X. Riedijk, F. M. Bickelhaupt and K. M. Bonger, Bioconjugate Chem., 2018, 29, 3054–3059. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00439
3-methyl-6-phenyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 38634-12-7, Cat. No EN300-25692525
This simple phenyl-substituted tetrazine is widely used as a model substrate for mechanistic investigations and for evaluating the reactivity of IEDDA-compatible dienophiles. It also serves as a valuable building block for the synthesis of pyridazines.
- Svatunek, M. Wilkovitsch, L. Hartmann, K. N. Houk and H. Mikula, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 8171–8177. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c01056
- Svatunek, Top. Curr. Chem. (Z), 2024, 382, 17. DOI: 10.1007/s41061-024-00461-0
diphenyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 6830-78-0, Cat. No EN300-7400818
A simple diphenyl-tetrazine is commonly employed as a model substrate for mechanistic investigations and for assessing the reactivity of IEDDA-compatible dienophiles. It also serves as a valuable building block for the synthesis of pyridazines.
- Wei, K. Fu, Z. Yu, Z. Zhan, D. Chang and L. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 14299–14307. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c18057
- Svatunek, Top. Curr. Chem. (Z), 2024, 382, 17. DOI: 10.1007/s41061-024-00461-0
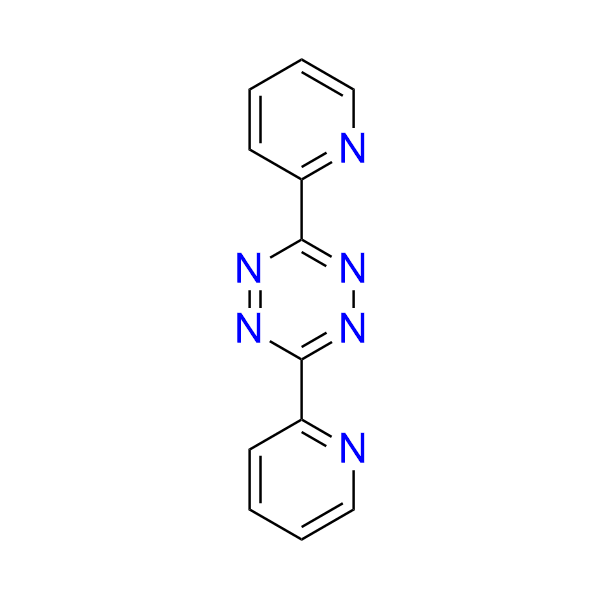
bis(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine
CAS 1671-87-0, Cat. No EN300-1485623
Dipyridyl-substituted tetrazine is a well-known, highly reactive substrate in the inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) reaction. It exhibits a broad range of applications, including click-to-release chemistry, coordination-assisted cycloadditions with vinyl boronic acids, mechanistic studies, and use as both a model substrate and a dienophile acceptor in organic synthesis.
- M. Versteegen, R. Rossin, W. ten Hoeve, H. M. Janssen and M. S. Robillard, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 14112–14116. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201305969
- Eising, A. H. J. Engwerda, X. Riedijk, F. M. Bickelhaupt and K. M. Bonger, Bioconjugate Chem., 2018, 29, 3054–3059. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00439
- Eising, B.-T. Xin, F. Kleinpenning, J. J. A. Heming, B. I. Florea, H. S. Overkleeft and K. M. Bonger, ChemBioChem, 2018, 19, 1648. DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201800275
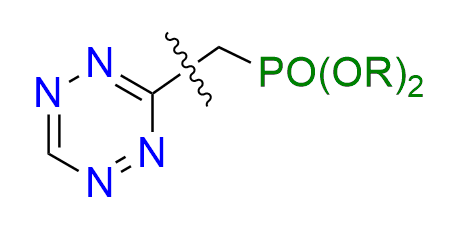
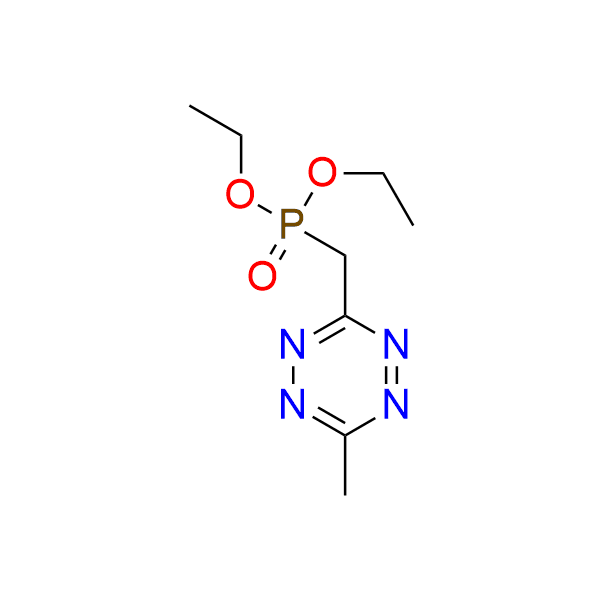
diethyl [(6-methyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-yl)methyl]phosphonate
CAS 2067322-26-1, Cat. No EN300-52272694
A tetrazine bearing a phosphonate moiety is a valuable precursor for the preparation of fluorogenic probes. A biocompatible Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons (HWE) reaction involving tetrazine-based phosphonates has been developed to enable efficient and selective functionalization under mild conditions.
- Wang, H. Yang, J. Li, Q. Kong, S. Zhou, H. Sun, L. Pan, Q. Gong, P. Feng and H. Wu, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2024, 35, 109226. DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109226
- Mao, J. Tang, L. Dai, X. He, J. Li, L. Cai, P. Liao, R. Jiang, J. Zhou and H. Wu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 2393. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202011544