J. Fluorine Chem. , 2013, 152 136-143
DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2013.03.002
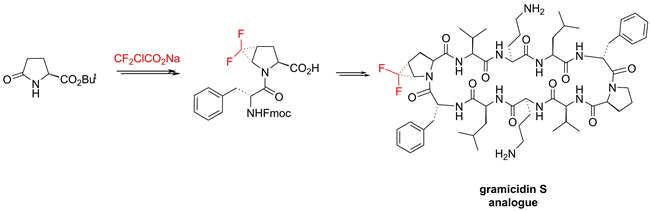
Trans-4,5-Difluoromethano-proline was incorporated into the cyclic antimicrobial peptide gramicidin S in place of a native proline residue. Introduction of this intrinsically unstable amino acid into the polypeptide backbone was achieved using a dipeptide strategy. The stable dipeptide building block with the N-acylated 4,5-difluoromethano-proline fragment was obtained by direct difluorocyclopropanation of an unsaturated precursor. The influence of the unnatural amino acid on the conformation and function of gramicidin S was evaluated using circular dichroism and biological assays. The application of trans-4,5-difluoromethano-proline as a new label for solid state 19F NMR structure analysis of membrane-active peptides was tested on gramicidin S and compared with previous labeling schemes.
Kubyshkin V. S.; Mykhailiuk P. K.; Afonin S.; Grage S. L.; Komarov I. V.; Ulrich A. S.
J. Fluorine Chem. 2013, 152 136-143
DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2013.03.002
