Molecules 2019, 24 (3), 572
DOI: 10.3390/molecules24030572
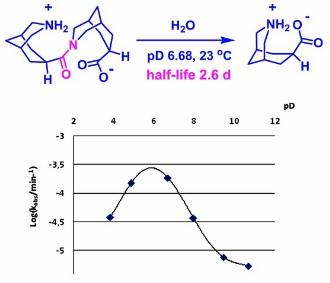
Unconstrained amides that undergo fast hydrolysis under mild conditions are valuable sources of information about how amide bonds may be activated in enzymatic transformations. We report a compound possessing an unconstrained amide bond surrounded by an amino and a carboxyl group, each mounted in close proximity on a bicyclic scaffold. Fast amide hydrolysis of this model compound was found to depend on the presence of both the amino and carboxyl functions, and to involve a proton transfer in the rate-limiting step. Possible mechanisms for the hydrolytic cleavage and their relevance to peptide bond cleavage catalyzed by natural enzymes are discussed. Experimental observations suggest that the most probable mechanisms of the model compound hydrolysis might include a twisted amide intermediate and a rate-determining proton transfer.