Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858 (9), 2019‑2027
DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.06.002
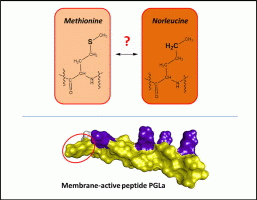
Yes. To understand the molecular mechanisms of amphiphilic membrane-active peptides, it is essential to study their interactions with lipid bilayers under near-native conditions. Amino acid composition largely determines the non-specific properties of peptides, on the basis of the physicochemical properties of the side chains. The resultant effects on peptides' functional properties include influences on the conformation, structural dynamics and binding affinities within the peptide interactome. Here, we studied the effect of substituting oxidation-prone methionine (Met) with non-oxidizable norleucine (Nle) in the model α-helical antimicrobial peptide PGLa, through systematic comparison of PGLa with the 2Met/2Nle mutant. Both peptides were evaluated for their bacteriostatic and hemolytic activities (using in situ assays), for their conformational preferences in isotropic solutions (using circular dichroism spectropolarimetry) and for their abilities to modulate membrane curvature (using a solid-state 31P NMR assay). We determined the membrane-bound states in detail and characterized the orientational dynamics of both peptides in oriented phospholipid membranes by solid-state 19F NMR spectroscopy. On the one hand, the bioactivity results, the structure in the diluted membrane-mimicking environments and the strong inhibition of the negative membrane curvature were comparable between PGLa and the mutant. On the other hand, the alignments in DMPC bilayer were qualitatively the same but differed in absolute values – the more hydrophobic Nle residue inserted deeper in the membrane core. Furthermore, the mutant peptide displayed a significantly reduced ability to re-orient from the monomeric, surficial to the putative dimeric, tilted state. Overall, these results confirm the functional isosterism of Nle and Met in the helical membrane-active peptides but highlight differences in the ways in which the two residues affect non-specific binding to the lipid bilayer and homomeric peptide-peptide interactions.