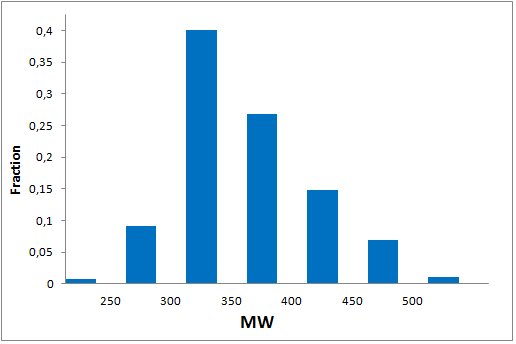
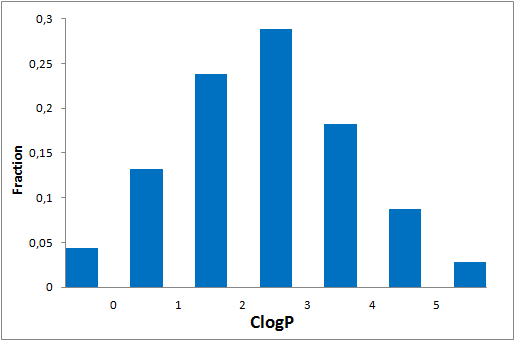
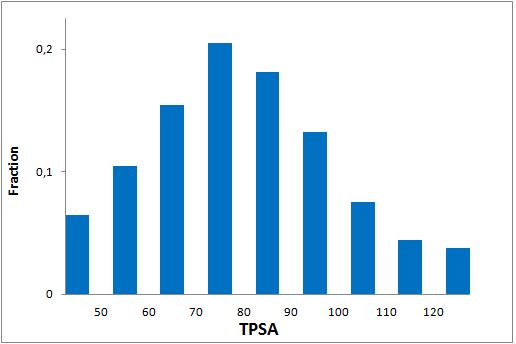
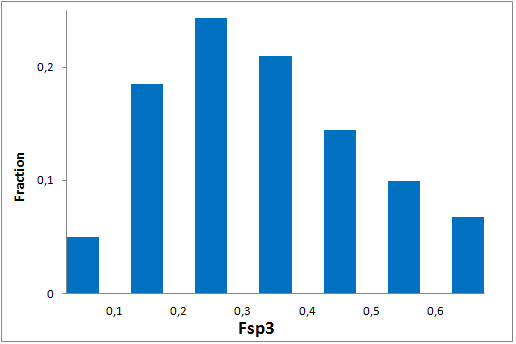
Since 2016 Enamine synthesize over 15 000 new covalent compounds each year. This greatly contributes to the constant updating of our libraries in line with the latest trends in covalent warheads.
Product catalog
CSL-11760
Size
11 760
compounds
Description
Diverse covalent library with most demanded warhead types
Download file
Covalent Serine Hydrolase Library
CSHL-12160
Size
12 160
compounds
Description
Designed for discovery of mild electrophilic inhibitors of the largest enzyme class
Download file
Coronavirus Mpro covalent Library
MPC-2640
Size
2 640
compounds
Description
Designed for the discovery of new SARS-CoV-2 and pan-Coronavirus antivirals
Download file
CFL-8480
Size
8 480
compounds
Description
Diverse covalent warheads with balanced reactivity
Download file
Cysteine-Focused Covalent Library
CYS-3200
Size
3 200
compounds
Description
Library of Cys-specific covalent electrophilic binders
Download file
Serine-Focused Covalent Library
SER-1600
Size
1 600
compounds
Description
Special selection of Serine focused irreversible binders
Download file
Lysine-Focused Covalent Library
LYS-1600
Size
1 600
compounds
Description
The ultimate selection of Lys-specific binders
Download file
Electrophilic Covalent Probe Library
ECPL-960
Size
960
compounds
Description
Characterized by a new HTS thiol-reactivity assay
Download file
sACR-4080
Size
4 080
compounds
Descriptions
Diverse screening Acrylamides pre-plated at 10 mM concentration
Download file
fACR-2240
Size
2 240
compounds
Descriptions
Representative selection of fragment Acrylamides pre-plated at 100 mM stock concentration
Download file
sCLA-1200
Size
1 200
compounds
Descriptions
Library of diverse HTS-size chloroacetamides pre-plated at 10 mM concentration
Download file
Chloroacetamide Fragment Library
fCLA-1360
Size
1 360
compounds
Descriptions
Diverse strict Ro3 compliant chloroacetamides plated at 100 mM stock concentartion
Download file
SFF-640
Size
1 120
compounds
Descriptions
Representative selection of N-, O-linked and Aryl sulfonyl fluorides within fragment space
Download file
Size
960
compounds
Description
Enantiomeric pairs of covalent electrophilic fragments
Download file
CMF‑141
Size
141
compounds
Description
Covalent Heterocyclic Fragment Library for identification of Cryptic and Allosteric Pocket
Download file
Support
- Hit Confirmation: QC check, HPLC repurification, resynthesis
- Hit follow-up: analogs search from stock or REAL Database
- Fast hit exploration libraries synthesis
We offer comprehensive support in developing your hit compounds. Naturally such programs are realised most efficiently when biological actives originate from our screening collection. However, even if the hit compounds are from the collections of other vendors lead identification and optimization projects can proceed most productively in our hands. Sometimes for this we only need to synthesize first examples of the given chemical series and validate synthesis route.
Enamine Fragment Collection currently contains 259 380 fragments being the largest and most reliable source of quality fragments. A number of focused fragment libraries were designed to perfectly meet needs of our clients. We collaborate with the leading experts in FBDD field on design and supply of top fragment libraries.
ESS-320
Size
320
compounds
Description
Elaborated tool for initial screen
Download file
High Fidelity Fragment Library
HFF-1920
Size
1 920
compounds
Description
Fragments of high MedChem tractability
Download file
DSI-860
Size
860
compounds
Description
Designed for easy and rapid follow-up synthesis
Download file
MiniFrags-80
Size
80
compounds
Description
Guiding optimisation of fragment-derived lead compounds
Download file
CFL-8480
Size
8 480
compounds
Description
Diverse covalent warheads with balanced reactivity
Download file
FDS-1000
Size
1 000
compounds
Description
Specially designed for 19F NMR ligand-based screening
Download file
Size
800
compounds
Description
Designed for easy and efficient exploration of novel protein targets
Download file
Natural Product-like Fragments
NPL-4160
Size
4 160
compounds
Description
Source of biologically validated starting points
Download file
3D Shape Diverse Fragment Library
3DF-1200
Size
1 200
compounds
Description
Unique 3D diversity among shaped molecules
Download file
PPIF-3600
Size
3 600
compounds
Description
Fragments able to mimic protein structural motifs and hot-spot residues
Download file
Single Pharmacophore Fragments
SPF-1500
Size
1 500
compounds
Description
Fragments for easy-to-analyse protein-ligand interaction
Download file
Carboxylic Acid Fragment Library
CAF-4000
Size
4 000
compounds
Description
Designed for specific protein targets and sensible onset
Download file
Size
1 280
compounds
Description
The most medchem reliable source of carboxylic acids replacement
Download file
Halogen-enriched Fragment Library
HEF-1920
Size
1 920
compounds
Description
Library of high diversity of halogen bonding motifs
Download file
Electrophilic Covalent Probe Library
ECPL-960
Size
960
compounds
Description
Characterized by a new HTS thiol-reactivity assay
Download file
Covalent Heterocyclic Fragment Library
CovHetLib‑141
Size
141
compounds
Description
Covalent Heterocyclic Fragment Library for identification of Cryptic and Allosteric Pocket
Download file
CNSF-1
Size
1 280
compounds
Description
CNS-friendly molecules capable of BBB penetration
Download file
Size
960
compounds
Description
Enantiomeric pairs of covalent electrophilic fragments
Download file
Size
372
compounds
Description
Size-optimized fragment library efficiently covering pharmacophore space, developed using ChemPass's Universal Fragment Library (UFL) Design Platform.
Download file
Size
2 301
compounds
Description
General fragment library developed with ChemPass's Universal Fragment Library (UFL) Design Platform.
Download file
Support
- Hit Confirmation: QC check, HPLC repurification, resynthesis
- Hit follow-up: analogs search from stock or REAL Database
- Fast hit exploration libraries synthesis
- Fragment growing and linking within Enamine REAL and Chemspace Freedom spaces
We offer comprehensive support in developing your hit compounds. Naturally such programs are realised most efficiently when biological actives originate from our screening collection. However, even if the hit compounds are from the collections of other vendors lead identification and optimization projects can proceed most productively in our hands. Sometimes for this we only need to synthesize first examples of the given chemical series and validate synthesis route.
Modern drug discovery requires contemporary compound libraries. We synthesize 300,000 new compounds annually and select the best candidates for our compound libraries. We offer over 100 fast-to-deliver pre-plated compound libraries for various research needs, from large-scale HTS screens to assay-specific and proteomics studies.
- Positive screening outcome. We conduct in-depth analysis of the research field and collaborate with leading industry experts to design our libraries.
- Premium quality. We produce compound libraries using only over 90%-pure compounds with analytics (LCMS and/or NMR) not older than one year. We filter compounds that are unstable in DMSO, have poor solubility, and undesirable salts. We also track the number of freeze-thaw cycles to determine pre-plated libraries shelf life based on their nature (cf. covalent vs non-covalent and other sensitive classes). When resupplying the hits, we follow our defined procedure, tracking the compound batches and their analytics. We purify or even resynthesize samples free of charge if they are of poor quality.
- Resupply from dry powders. For the library preparation, we use compounds available at 10+ mg in our stock so that they can be resupplied from the same batch. We have a program in place to maintain the dry sample stock levels through resynthesis for compounds present in REAL Space. For the best and fastest results, we encourage integrated lead discovery projects involving our biological screening, computational chemistry, efficient Hit-to-Lead using our REAL Space, ADMET/PK, and MedChem support.
Designed for the discovery of new SARS-CoV-2 and pan-Coronavirus antivirals
16 800 compounds
In spite of the previously known coronavirus outbreaks in 2002 and 2003 followed later in 2012 with MERS-CoV spread in middle-Asia, no effective treatment has been developed. Shortage of financial support and attention in R&D area resulted in a desperate outcome. The world appeared to be largely unprepared for the new outbreak, caused by SARS-CoV-2, which began in December 2019 and quickly grew into a global pandemic. The past research on SARS/MERS-CoV family of viruses has not produce any lead series which can be quickly progressed into marketed drugs.
An unprecedented biotech race is now on to design cures for COVID-19 and to curb the crisis until a reliable vaccine is available and widely adopted. While most of the efforts are focused on drug repurposing strategies, de-novo drug discovery is essential for achieving sufficient specificity and efficacy towards the new SARS-CoV-2 virus.
To meet the urgent need for potent new antivirals against COVID-19, Enamine has designed and preplated for quick delivery a small-molecule compound library focusing on SARS-CoV most promising targets. This library incarnates Enamine’s rich experience in design and synthesis of antiviral compounds. We take an active part in the global open science initiative COVID Moonshot project, providing synthesis, ADME-Tox profiling, medicinal chemistry and logistic services.
The Coronavirus Library consists of 7 sublibraries which can be also acquired separately.
Typical Formats
Coronavirus Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
COV-16800-0-Z-10
Target
3CLpro, ACE2, TRPMSS11E and all below
Compounds
16 800
14 plates
Amount
up to 300 nL of 10 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well plates, 1280 compounds per plate, 1-4 and 44-48 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
MPR-3440-10-Y-10
Target
Main protease Mpro, non-covalent compounds
Compounds
3 440
11 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates Greiner Cat. No. 781280, 320 compounds per plate, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
MPC-2640-50-X-20
Target
Main protease Mpro, covalent compounds
Compounds
2 640
33 plates
Amount
50 µL of 20 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner Cat. No. 650201, 80 compounds per plate, 1 and 12 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
TMP-3200-25-Y-10
Target
Type-II and 11e transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2)
Compounds
3 200
10 plates
Amount
25 µL of 10 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates Greiner Cat. No. 781280, 320 compounds per plate, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
PLP-3200-50-Y-10
Target
Papain-like protease (PLpro)
Compounds
3 200
10 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates Greiner Cat. No. 781270, 320 compounds per plate, 1, 2 and 23, 24 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
RDR-2880-50-X-10
Catalog No.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP)
Compounds
2 880
36 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner Cat. No. 650201, 80 compounds per plate, 1 and 12 columns empty
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Library design
To design our library we carefully collected all available structural information of most promising SARS-CoV protein targets. The protein structures were scrutinized and docking models were created. The docking models were validated by short MD simulations and verified then by ability to form complexes with reported active molecules. We have focused on the following 5 targets and NSP, reported to be most important for virus transmission and essential for viral replication:
- SARS-CoV-2 main protease Mpro (also called 3CLpro)
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
- Papain-like protease (PLpro)
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor
- Type-II transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2)
- Non-structual proteins (NSP) of SARS-CoV-2, with reported 3D-struture.
For cysteine and serine proteases (Mpro and TMPRSS2) covalent docking has been carried out to identify promising covalent binders, which can elongate inhibition action. The databases of screening compounds were preliminary filtered to contain only compounds with specific warheads that are selective to each amino acid:
sublibrary1
2 640 compounds (acrylamides, chloroacetamides, vinyl sulfones and beta-lactams)
sublibrary2
560 compounds (sulfonyl fluorides, N-nitriles, chloroacetamides, epoxides, boronics)
All other target-focused sublibraries passed stringent MedChem filters, including PAINS and Molecular Parameters restrictions to represent mainly lead-like space. The hits derived from our library can be easily followed with analogs and growing strategy to maximize MedChem variability within the structure.
Examples of the docking results
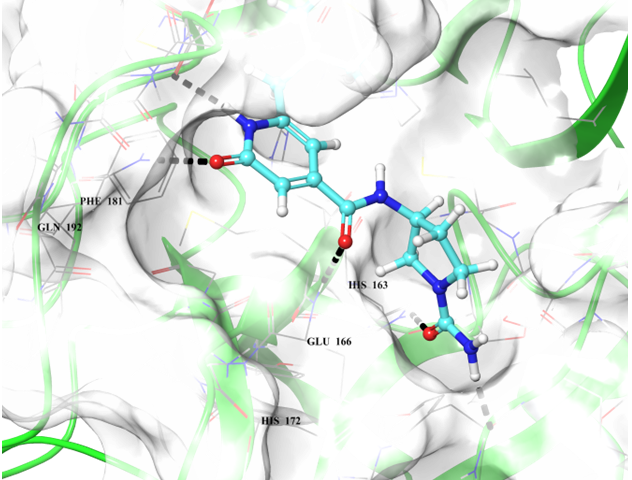
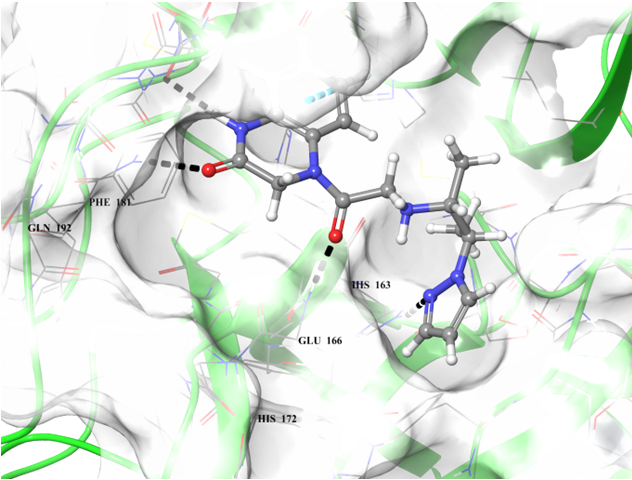
Binding poses of two predicted hit molecules after docking calculation on Mpro protease Z1609752806 (light blue ligand on the left side) and Z1143050660 (grey ligand on the right side).
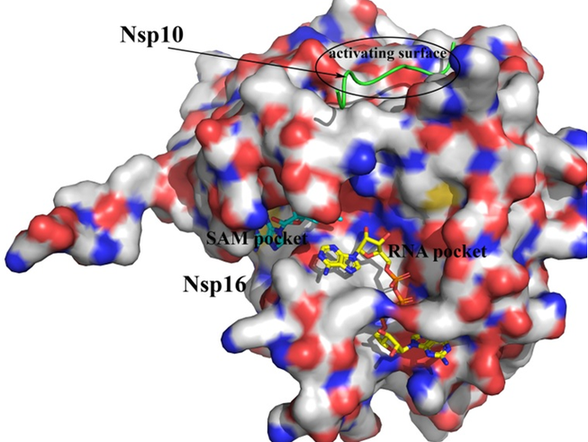
SARS-CoV-2 NSP16 protein bound to NSP10. All 3 binding pockets were used for molecular docking calculations.
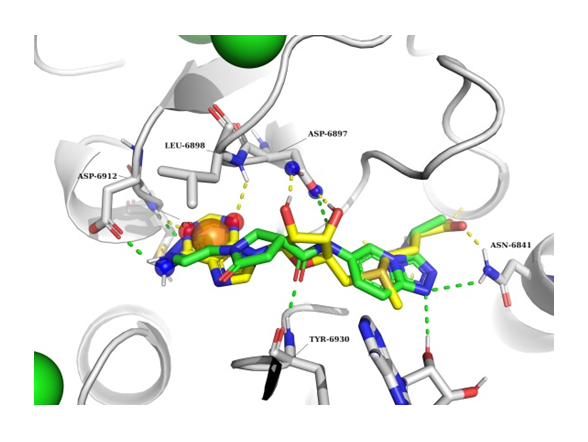
The example of NSP16 SAM binding pocket docking result. NSP16 in grey, docked ligand in green, SAM molecule in yellow.
Guiding optimisation of fragment-derived lead compounds
80 compounds
Reliable structural data of a target protein is the key to a successful drug discovery program. This knowledge is extremely important for the efficient development of selective and potent small molecule drugs. Recent achievements in the field of protein structure investigation are impressive and have enabled development of new approaches and screening techniques. Combination of modern, elaborated crystallographic methods with smart-design of chemical libraries can make a breakthrough in our understanding of protein structure changes and behavior.
Novel crystallographic screening methodology reported by O’Reilly et al. in Drug Discovery Today 2019 was developed at Astex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, UK. The high-concentration aqueous soaks were made with a chemically diverse and ultra-low-molecular-weight fragment library “MiniFrags” (heavy atom count 5–7). This allowed identification of hot and warm spots on proteins. High screening hit rates reflect enhanced sampling of chemical space. MiniFrag screening can represent thus a highly effective method for guiding optimisation of fragment-derived lead compounds.
We have collaborated with the Astex’ scientists on making MiniFrag library available to the research community in the most convenient format. Screening at 1M suggests that the fragments would be provided dry, ready for dissolution prior to protein soaking.
Typical Formats
Catalog No.
MiniFrag-80
Compounds
80
Amount
10 mg
Plates and formats
Dry samples formatted in individual sealed glass vials suitable for dissolution
Price
Download SD file
Library design
The compounds in the MiniFrag Library offered by Enamine are identical to those proposed by Astex. Their structures and selection principles are described in O’Reilly et al. in Drug Discovery Today, Volume 24, Issue 5, May 2019, Pages 1081-1086. DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2019.03.009.