CAS 32133-82-7, Cat. No EN300-19626639
Reagent for dehydration of alcohols, epoxide synthesis, cleavage of amides, sulfur ylides formation
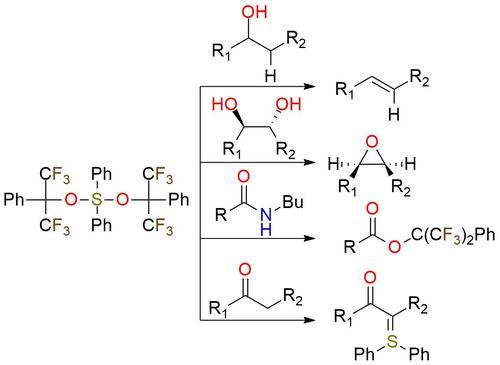
Martin sulfurane is a useful organic reagent with good physical properties and is reliable in cases of alcohol dehydration1. It is a bench-stable, but moisture-sensitive, white crystalline solid. The reagent is well soluble in ether, benzene, acetone, and alcohol but it decomposes slowly in solution. Martin sulfurane is more suited for tertiary alcohol dehydration — the process starts instantaneously at ambient temperature. Secondary alcohols can also be dehydrated, as well as primary alcohols if the β-proton is sufficiently acidic. Besides its primary use, Martin sulfurane can be used for the conversion of vicinal diols to epoxides, if they can attain an antiperiplanar relationship. Cleavage of amides with the reagent affords their conversion to esters under mild conditions and provides a simple method for the deprotection of N-acylated amines. Moreover, the reagent is known to participate in ylide transfer with the carbonyl derivatives and heteroaromatic compounds yielding carbonyl-stabilized sulfur ylides2,3.
Synonyms: (T-4)-bis[α,α-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzenemethanolato-κO]diphenylsulfur (ACI); benzenemethanol, α,α-bis(trifluoromethyl)-, sulfur complex (ZCI); sulfur, bis[[α,α-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]oxy]diphenyl- (8CI); sulfur, bis[α,α-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzenemethanolato]diphenyl-, (T-4)- (ZCI); bis[bis(trifluoromethyl)phenylmethoxy]diphenylsulfurane; diphenylbis(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-phenyl-2-propoxy)sulfurane
Selected publications
-
Martin’s Sulfurane.
Roden B.; Gennaiou K.; Kourgiantaki M.; Mazaraki K.; Zografos A. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2024, 1–10. DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rd409.pub2
-
Sulfur(IV)-Mediated Transformations: From Ylide Transfer to Metal-Free Arylation of Carbonyl Compounds.
Huang X.; Patil M.; Farès C.; Thiel W.; Maulide N. Am Chem Soc 2013, 135 (19), 7312–7323. DOI: 10.1021/ja4017683
-
A Direct Ylide Transfer to Carbonyl Derivatives and Heteroaromatic Compounds.
Huang X.; Goddard R.; Maulide N. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2010, 49 (47), 8979–8983. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201002919