Designed for the discovery of novel antibacterials
32 000 compounds
Despite extensive research in the antibacterial field, the need for new effective, and safe treatment remains one of the most important tasks in modern drug discovery. During the last decades, many investigations on antibacterials led to systematic research and the emergence of special rules in molecular parameters and structural features. Molecules with antibacterial activity are typically larger and more polar compared to the general drugs. Carefully collected and analyzed available data on active agents was used for the construction of our new Antibacterial library.
To provide a good outcome from HTS screening campaigns in this field we designed a dedicated library that might ensure high quality of derived hits and easy tractability of follow-up chemistry. Hits identified from our libraries can be easily followed with in-stock analogs or analog synthesis through REAL Database technology with up to 80% synthetic success rate. Using our screening libraries you can save on time and cost in hit follow-up:
- Hit Confirmation support – QC check, resupply from dry powders and freshly prepared DMSO solutions, HPLC repurification samples if needed, and enantiomers separation.
- Fast and affordable library synthesis of analogs from over 300k in-stock building blocks.
- Computational and MedChem support enhanced with on-site ADME/T panel.
You have also an option to screen the library directly at Enamine. We will be happy to offer you a discount on library costs depending on the collaboration scope.
Antibacterial library and gram-negative sub-library are now available for supply in the following most popular pre-plated formats.
Typical Formats
Antibacterial Library is available for supply in various pre-plated formats, including the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
ABAC-32-0-Z-10
Compounds
32 000
25 plates
Amount
≤ 150 nL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536-well Echo LDV microplates, first and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
ABAC-32-10-Y-10
Compounds
32 000
100 plates
Amount
≤ 10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates #001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
ABAC-32-50-Y-10
Compounds
32 000
100 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well, Greiner Bio-One plates #781280, 1,2 and 23,24 columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
GNB-6400-50-X-10
Compounds
6 400
80 plates
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
96-well Greiner bio-one plates, 1 and 12 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
ABAC-32-10-Y-10 screening library 32 000 cmpds, hit resupply, analogs from 4.7M+ stock and synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD file
Library Design
The knowledge-based approach was mainly used in the construction of our antibacterial library. Strict refinement with the right molecular parameters profile was the first and basic stage in library design. Then the substructure and shape-based searches were used for the selection of molecules with privileged cores, motifs and natural product-like scaffolds, which are known to be essential for antibacterial activity.
Structural fragments used for the selection: beta-lactams, oxazolidinones, quinolones, nitroimidazoles, sulfa drugs, and some others. Examples of the molecules in the library with the reference antibacterials described below:
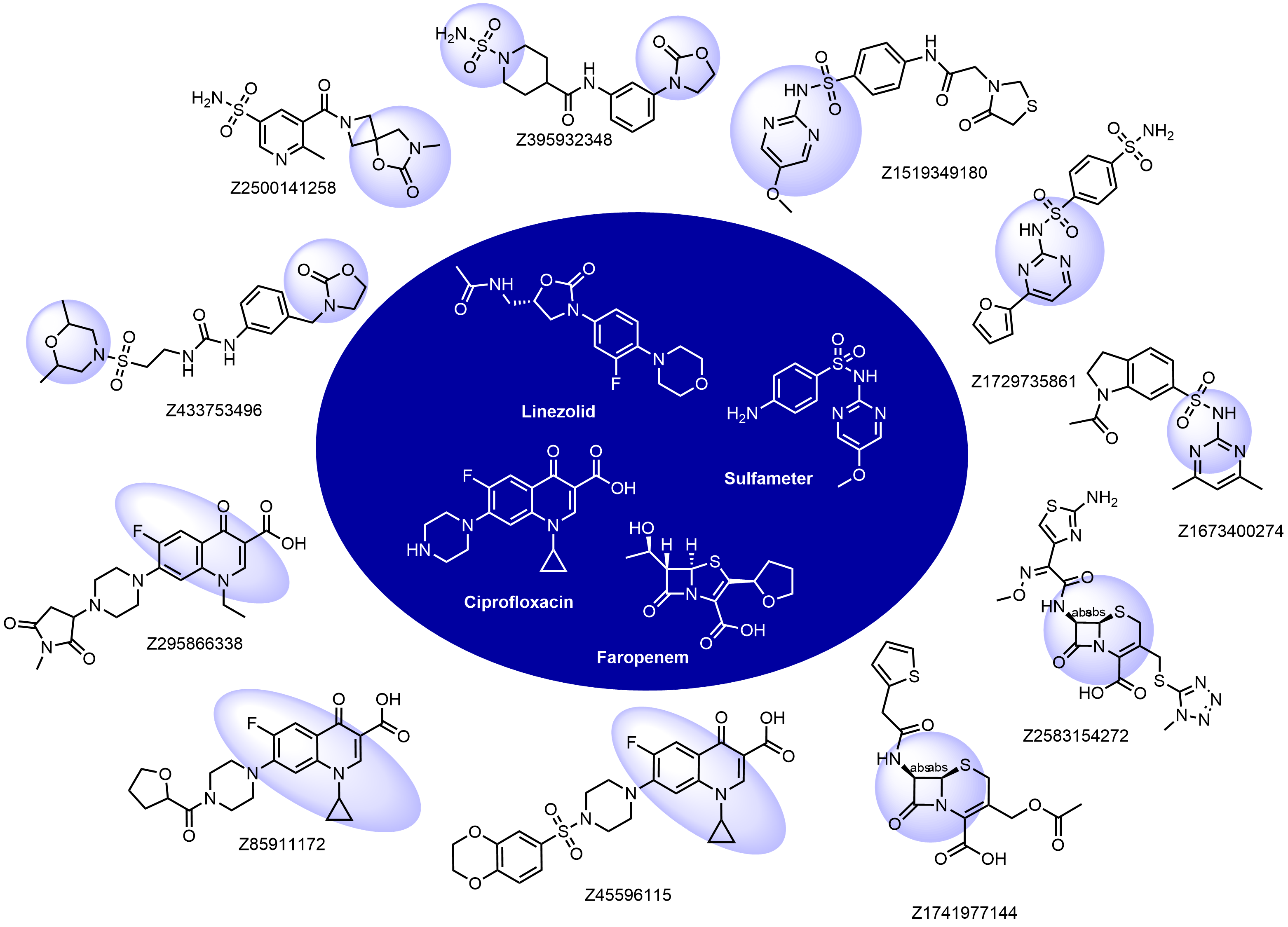
Antibacterial drugs occupy a unique property space that is remarkably different compared to drugs from other therapeutic areas. This fact has been long recognized, and general rules such as Lipinski’s rules of five do not apply to these compounds. The major differences between antibacterial and other drugs are MW and lipophilicity (ClogD7.4, ClogP, number of H-donors and -acceptors, and relative PSA).
The library perfectly matches the distribution of physicochemical properties of known antibiotics, which enhances hit finding probability in both target-directed and cell-based assays. Particular attention was paid to the problems of cell penetration for Gram-negative pathogens where the compounds with only a very narrow distribution of molecular weights, lipophilicity, and polar surface area can effectively work.
Actives against gram-negative bacteria must overcome further barriers to function, namely penetration of the outer lipid membrane and evasion of efflux pumps. To address this challenge, we applied recently developed accumulation rules, also known as “eNTRy rules”. According to these rules, a compound should possess ionizable Nitrogen (primary amines being the best choice), low 3-dimensionality (as described by the “globularity” parameter), and no more than 5 rotatable bonds. Approximately 20% of the compounds in our Antibacterial Library successfully meet these eNTRy rules. The parameters were calculated using the resource available at http://www.entry-way.org/, which was developed by authors of Richter, Drown, Riley, Garcia, Shirai, Svec, Hergenrother. Nature 545, 299–304 (2017).
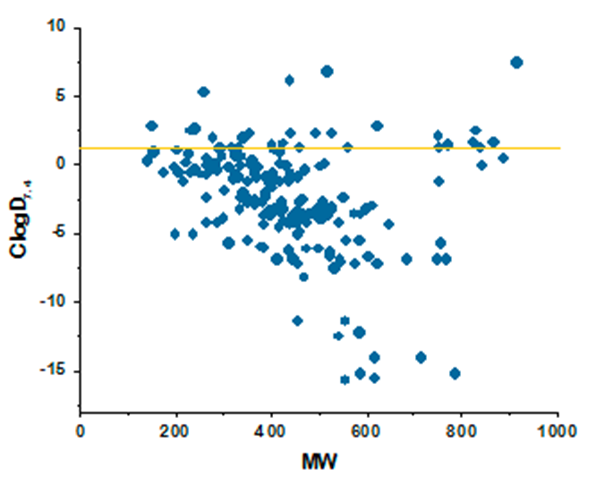
ClogD7.4 values plotted against MW for major classes of antibacterial compounds
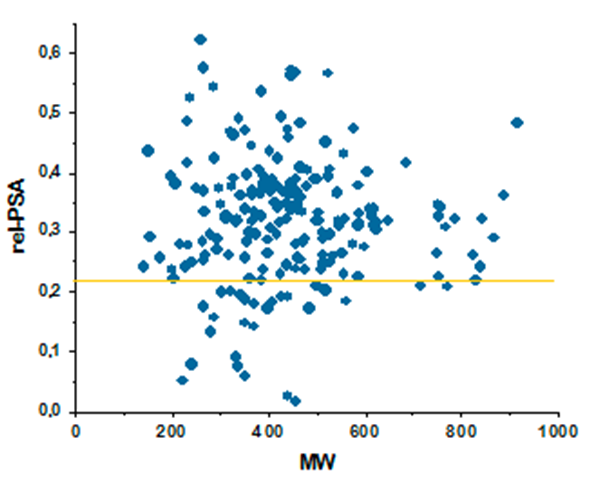
Relative PSA against MW for major antibacterial classes



