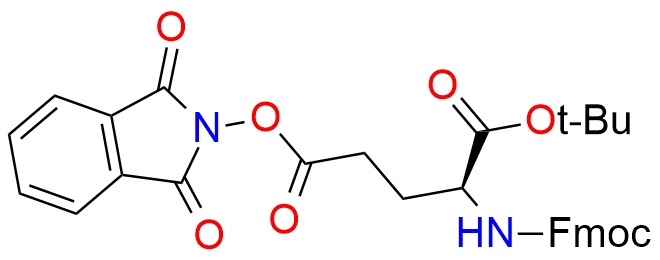
CAS 2244699-96-3, Cat. No EN300-6522359
Reagent for synthesis of unnatural amino acids
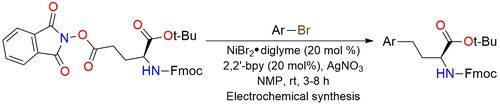
Redox-active ester (RAE)-modified t-Bu-Fmoc-glutamic acid is a reagent used for radical site-selective electrochemical decarboxylative arylation1. The process selectively forms carbon-carbon bonds with electron-deficient aryl bromides and heterocycles. The reagent is essential for incorporating heteroaryl groups into glutamic acid scaffolds, expanding the chemical space of unnatural amino acids. It offers high enantioselectivity and stability under electrochemical conditions.
Synonyms: 5-(1,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl) 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl) N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-L-glutamate (ACI); 1-(tert-butyl) 5-(1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl) N-[[(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy]carbonyl]-L-glutamate; 1-tert-butyl 1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-2-yl (2S)-2-([[(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methoxy]carbonyl]amino)pentanedioate
Selected publication
-
Electrochemical Synthesis of Unnatural Amino Acids Embedding 5- and 6-Membered Heteroaromatics.
Bombonato E.; Fasano V.; Pecorari D.; Fornasari L.; Castagnini F.; Marcaccio M.; Ronchi P. ACS Omega 2024. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09357