CAS 87413-09-0, Cat. No EN300-66581
Oxidizing reagent
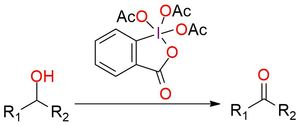
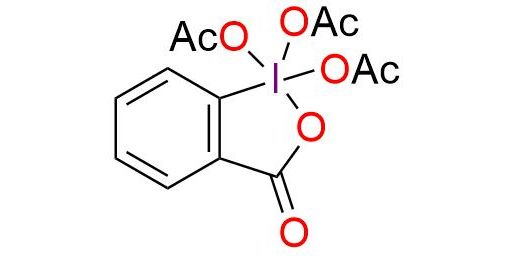
The Dess-Martin reagent is a widely utilized oxidant, effectively transforming 1° and 2° alcohols into aldehydes and ketones. Presenting as a stable white powder, it exhibits a melting point ranging from 103 to 133 °C1. The Dess-Martin reagent offers key advantages over chromium- and DMSO-based oxidants. These benefits encompass milder reaction conditions (at room temperature and neutral pH), abbreviated reaction times, elevated yields, simplified purification steps, exceptional chemoselectivity, and compatibility with sensitive functional groups2. Usually, the reaction is conducted in DCM or chloroform but can be performed in DMSO, DMF, and EtOAc. Using the standard Dess–Martin periodinane conditions, alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes/ketones without affecting furan rings, sulfides, vinyl ethers, and secondary amides1,2. Allylic alcohols, which are typically difficult to convert to their respective carbonyls using the typical oxidants, are easily oxidized using DMP. Also, it can oxidize N-protected amino alcohols without epimerization (unlike most other oxidants, including Swern oxidation).
Synonyms: Dess-Martin reagent; Dess-Martin periodinane reagent; Dess-Martin oxidant; 1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one, 1,1,1-tris(acetyloxy)-1,1-dihydro- (9CI); (1,1-diacetoxy-3-oxo-1,2-benziodoxol-1-yl) acetate; 1,1,1-Triacetoxy-1,1-dihydro-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one; 1,1,1-tris(acetyloxy)-1,1-dihydro-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-on; 3-oxo-1λ5,2-benziodoxole-1,1,1(3H)-triyl triacetate
Selected publication
-
1,1,1-Triacetoxy-1,1-Dihydro-1,2-Benziodoxol-3(1H)-One.
Boeckman R.; George K. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2009. DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rt157m.pub2
-
Dess-Martin reagent.
Wang Z. Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents 2010. DOI: 10.1002/9780470638859