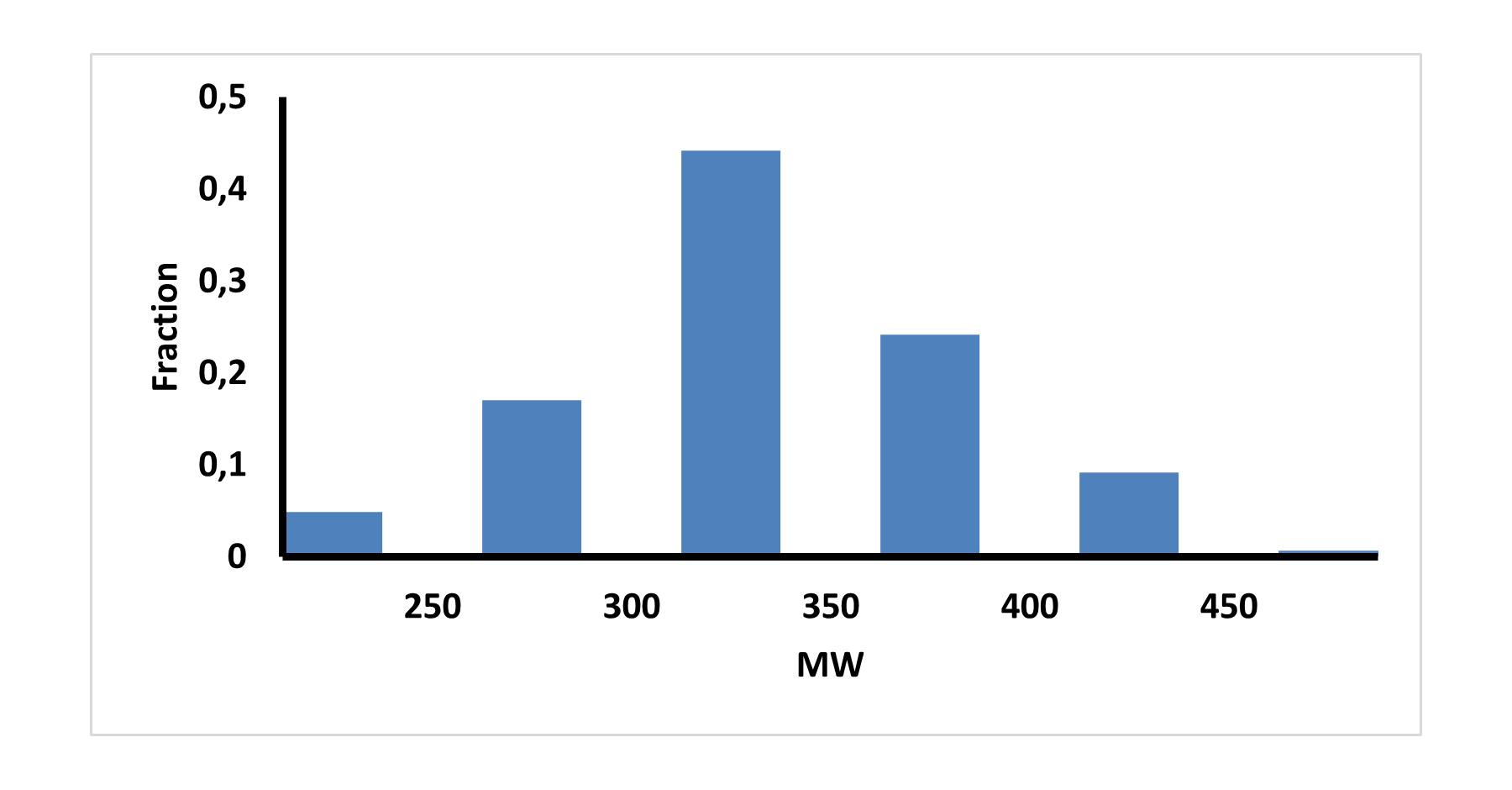
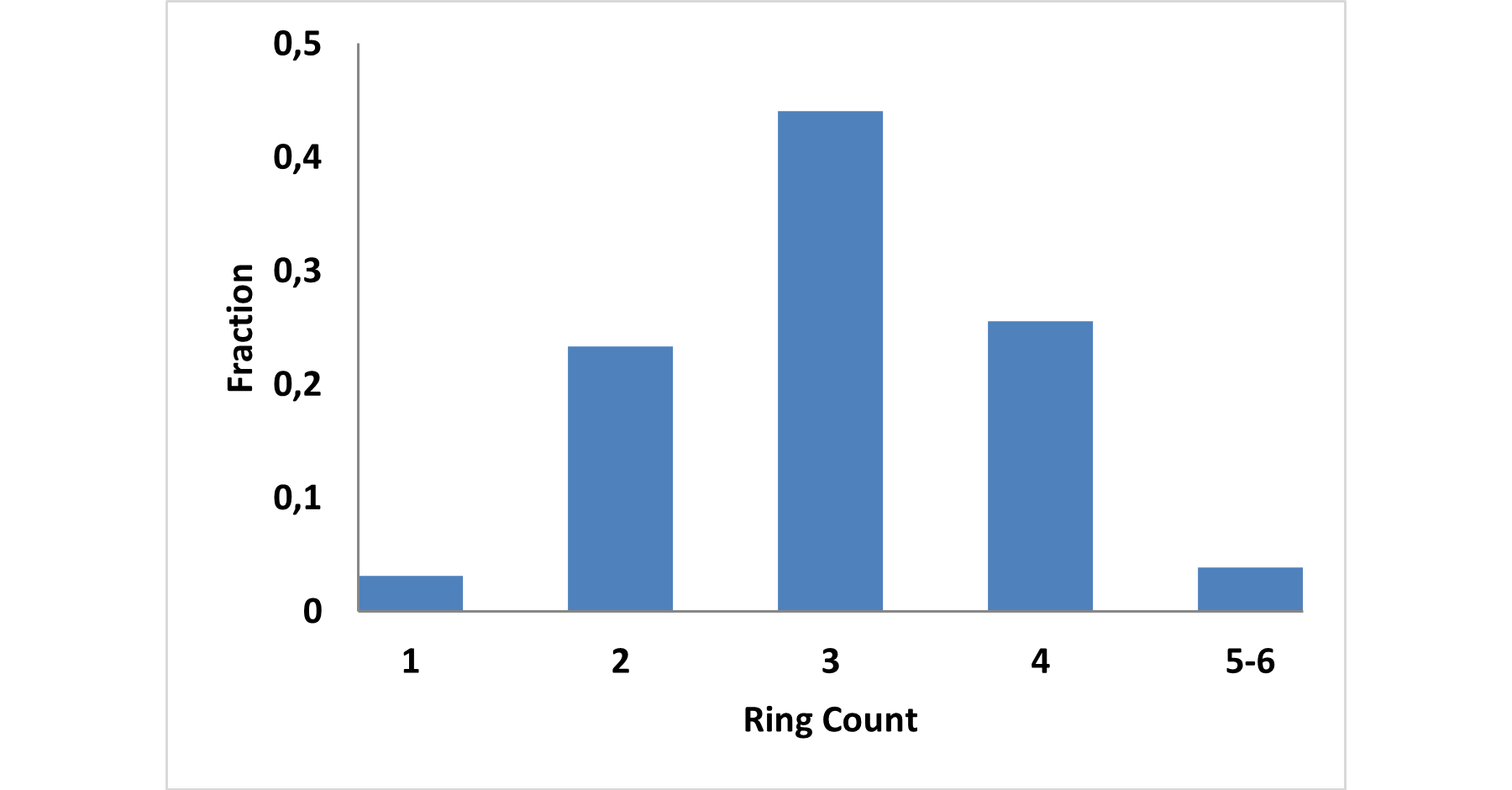
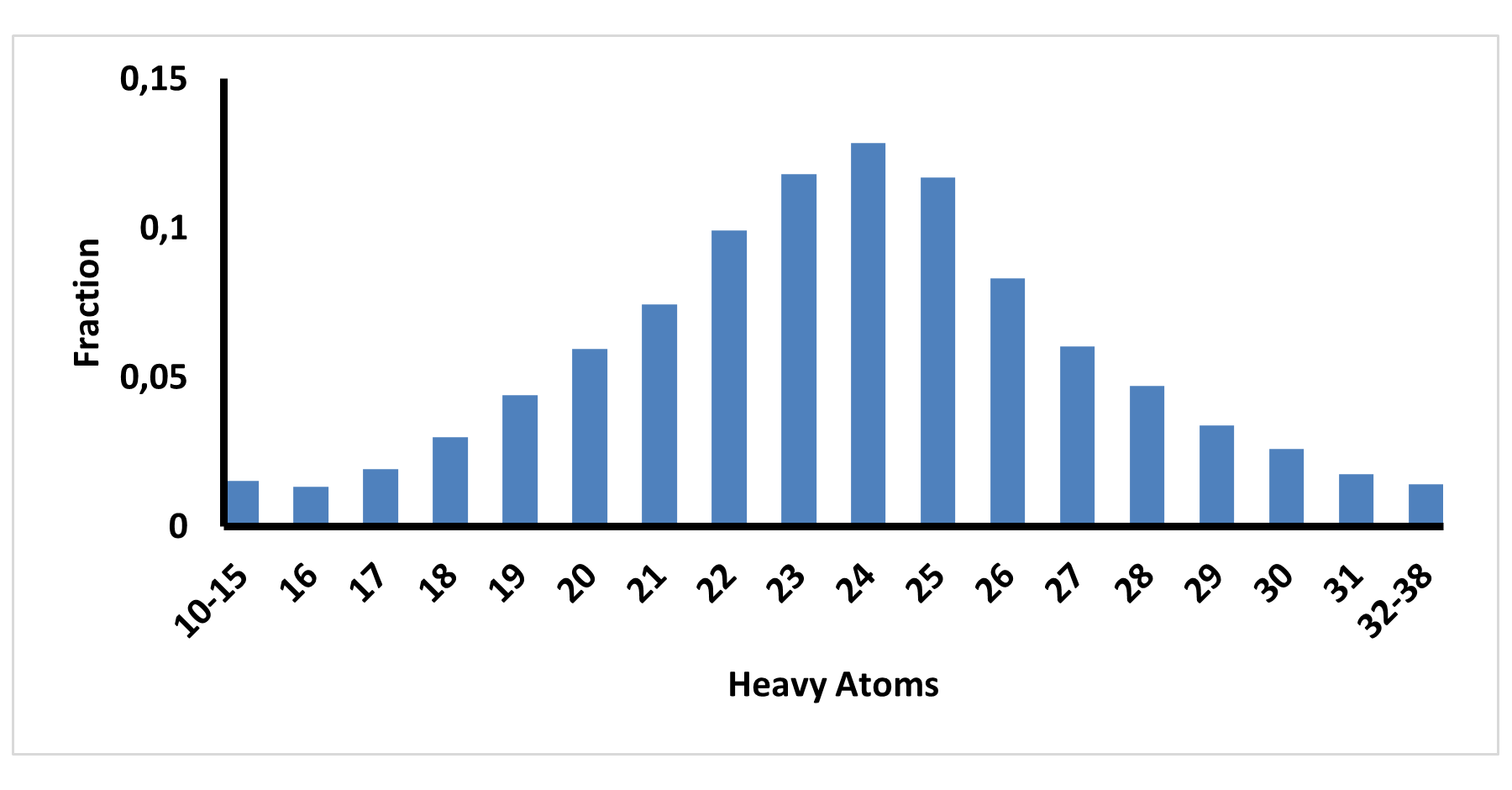
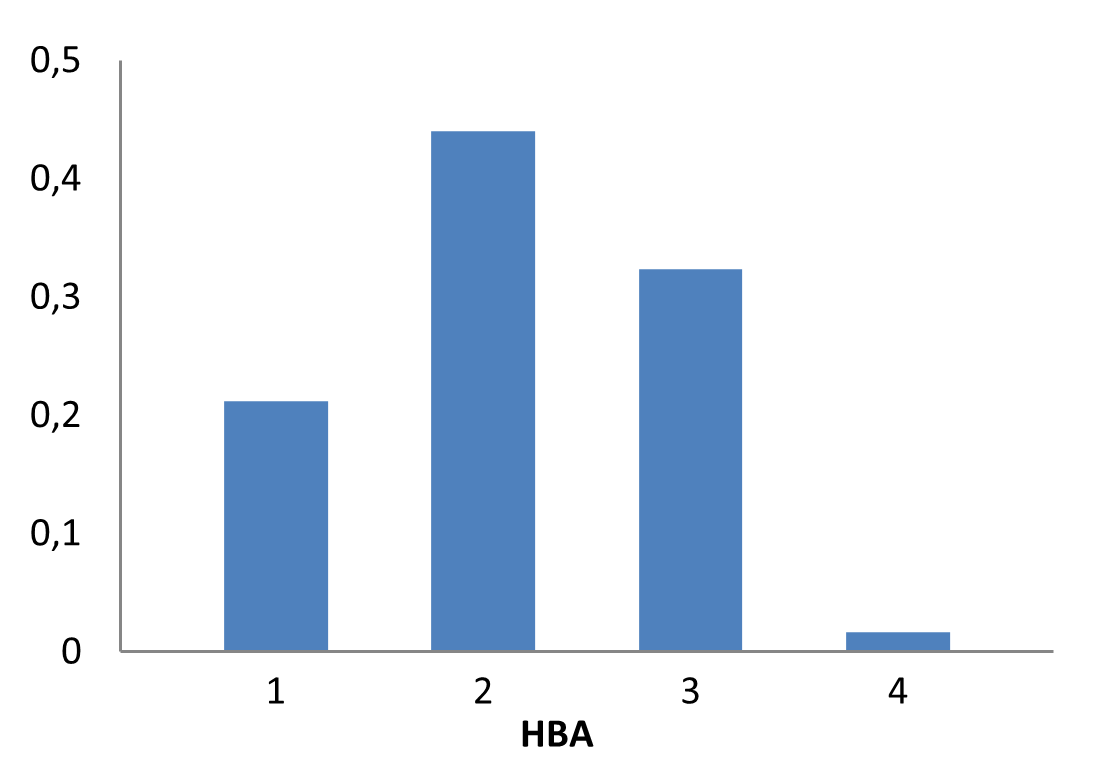
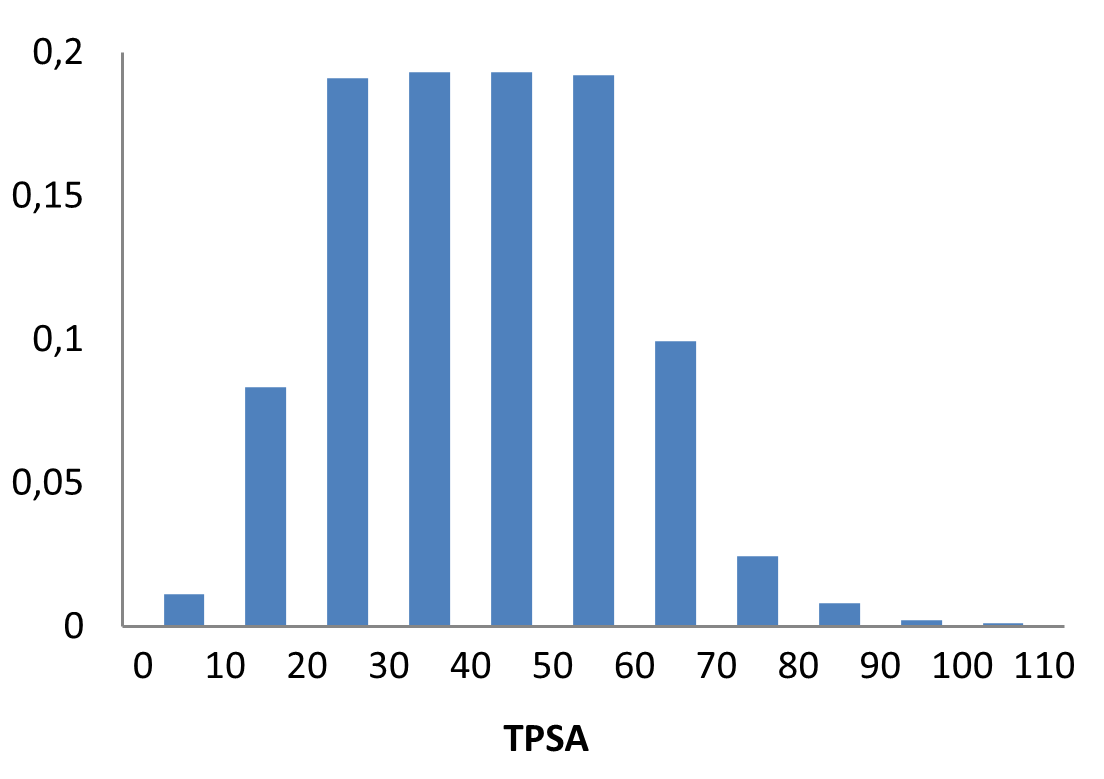
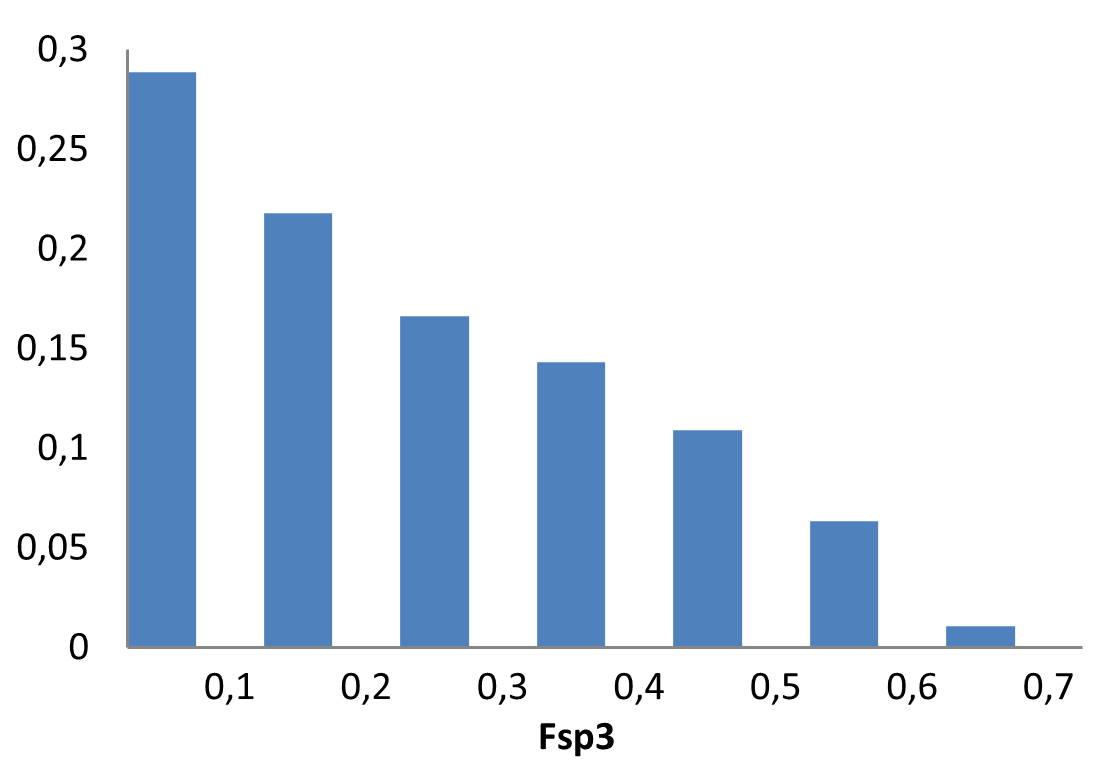
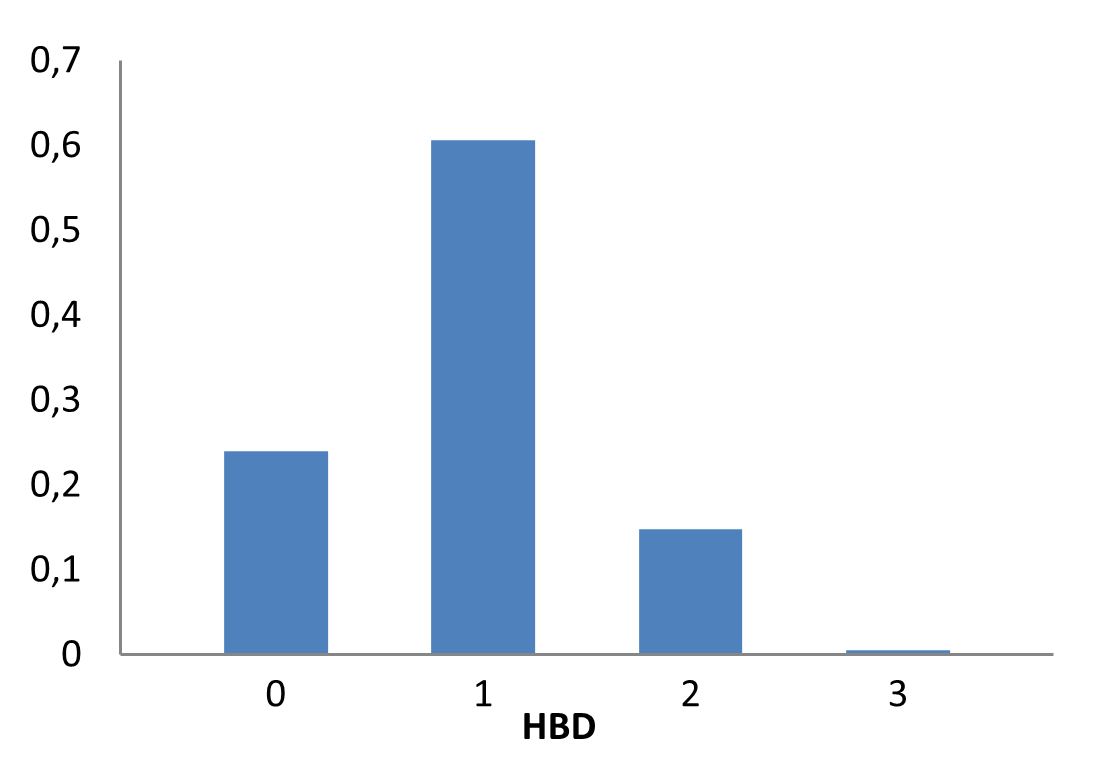Innovatively designed and experimentally confirmed library for reliable enantioselective ASMS screening
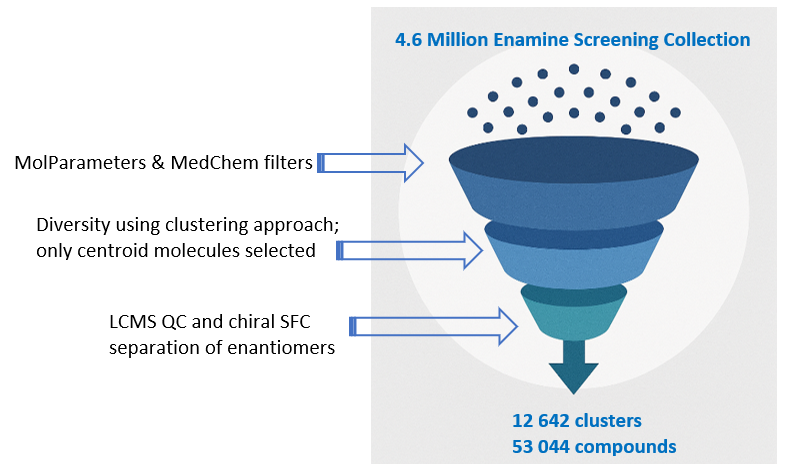
12 642 compounds
Rapid progress in drug discovery depends on the continuous development of innovative technologies and advanced screening approaches. Tackling challenging targets and so‑called “undruggable” proteins requires not only novel techniques and screening methods but also access to high‑quality, well‑characterized compound libraries.
The recently introduced enantioselective protein affinity selection mass spectrometry (E‑ASMS, Nature Comm. 2025) approach streamlines the time needed for hit identification and hit validation. This method accelerates early drug discovery by enabling the detection of weak binders, delivering critical insights into compound selectivity, and providing orthogonal confirmation of binding events — all without reliance on traditional counter‑screen assays. When combined with carefully designed compound library, E‑ASMS offers a powerful platform for fast identification of promising therapeutic leads.
In collaboration with leading experts from top Pharma companies and the Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC), we carefully designed, experimentally characterized, and validated — through numerous screening campaigns — the first edition of our Enantio‑ASMS Library (E‑ASMS).
Typical Formats
E-ASMS Library is available for supply in various pre-plated, including but not limited to the following most popular ones:
Catalog No.
E-ASMS-12642-Y-10
Compounds
12 642
40 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well echo-source plates, 320 compounds per plate, first two and last two columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
E-ASMS-12642-Y-25
Compounds
12 642
40 plates
Amount
25 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates, 320 compounds per plate, first two and last two columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
E-ASMS-12642-X-25
Compounds
12 642
158 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, 80 compounds per plate, 1 and 12 columns empty
Price
*Please select among the following standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400), C52621 or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Plated librarie in stock:
Library Design
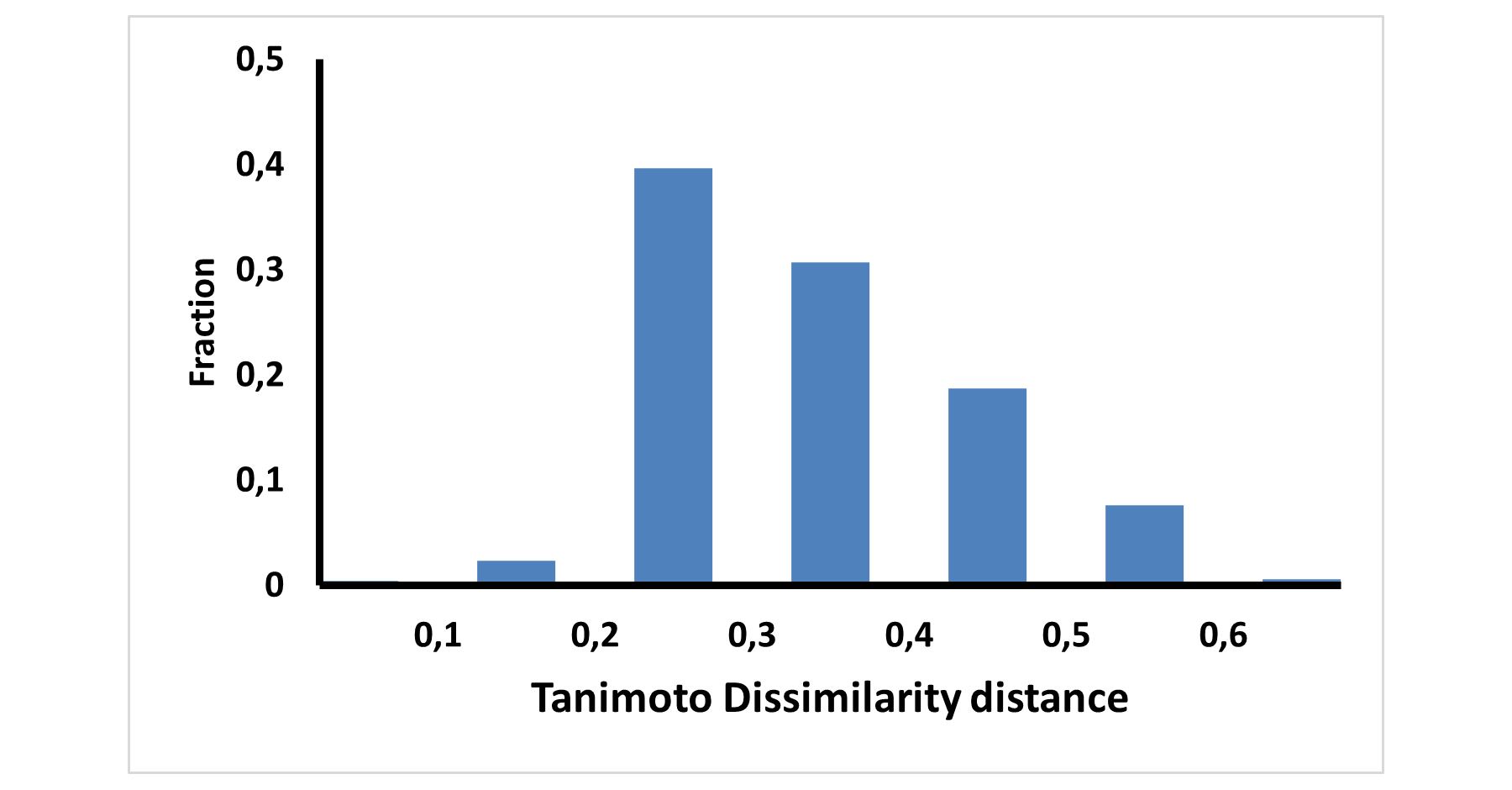
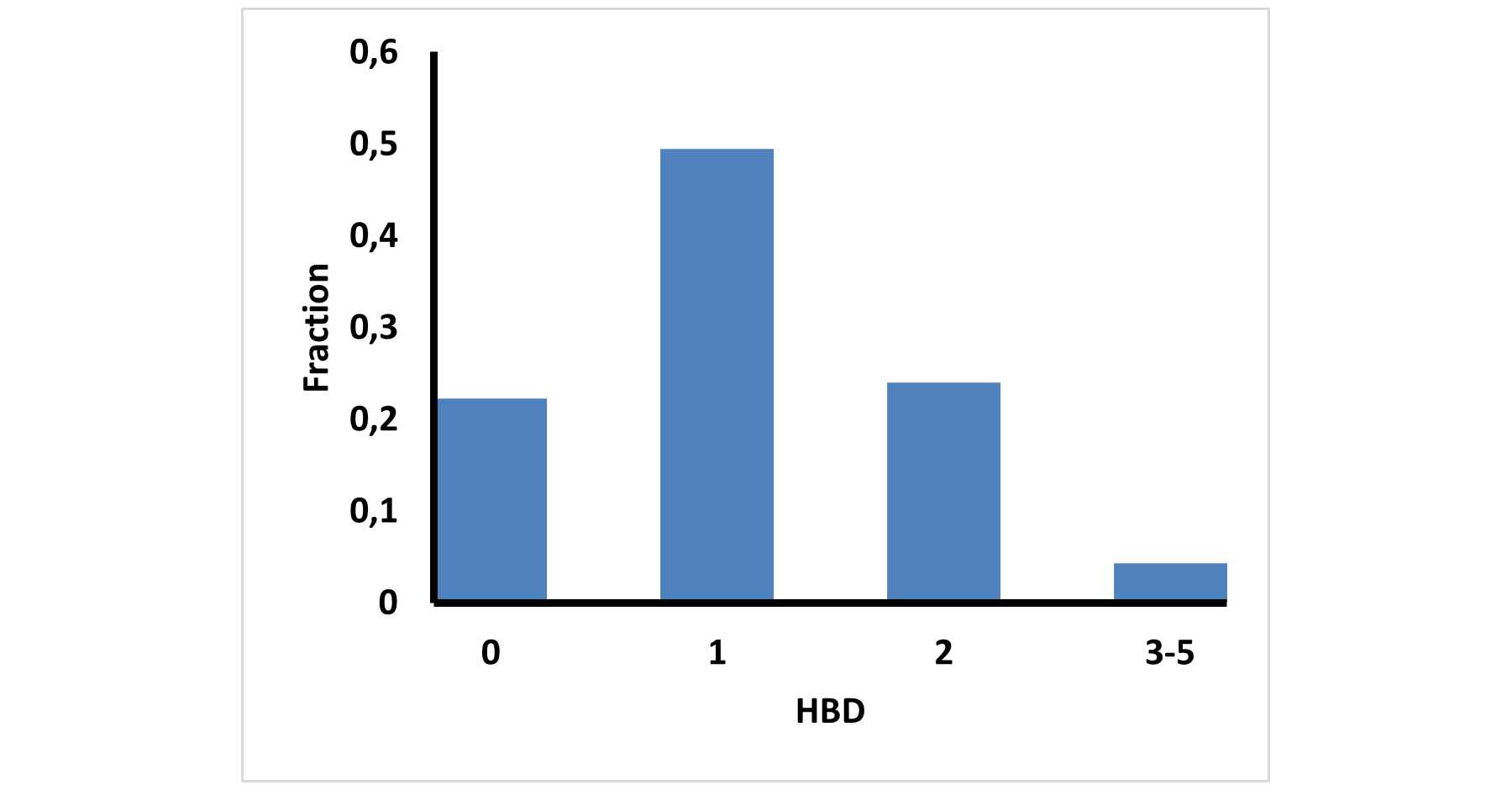
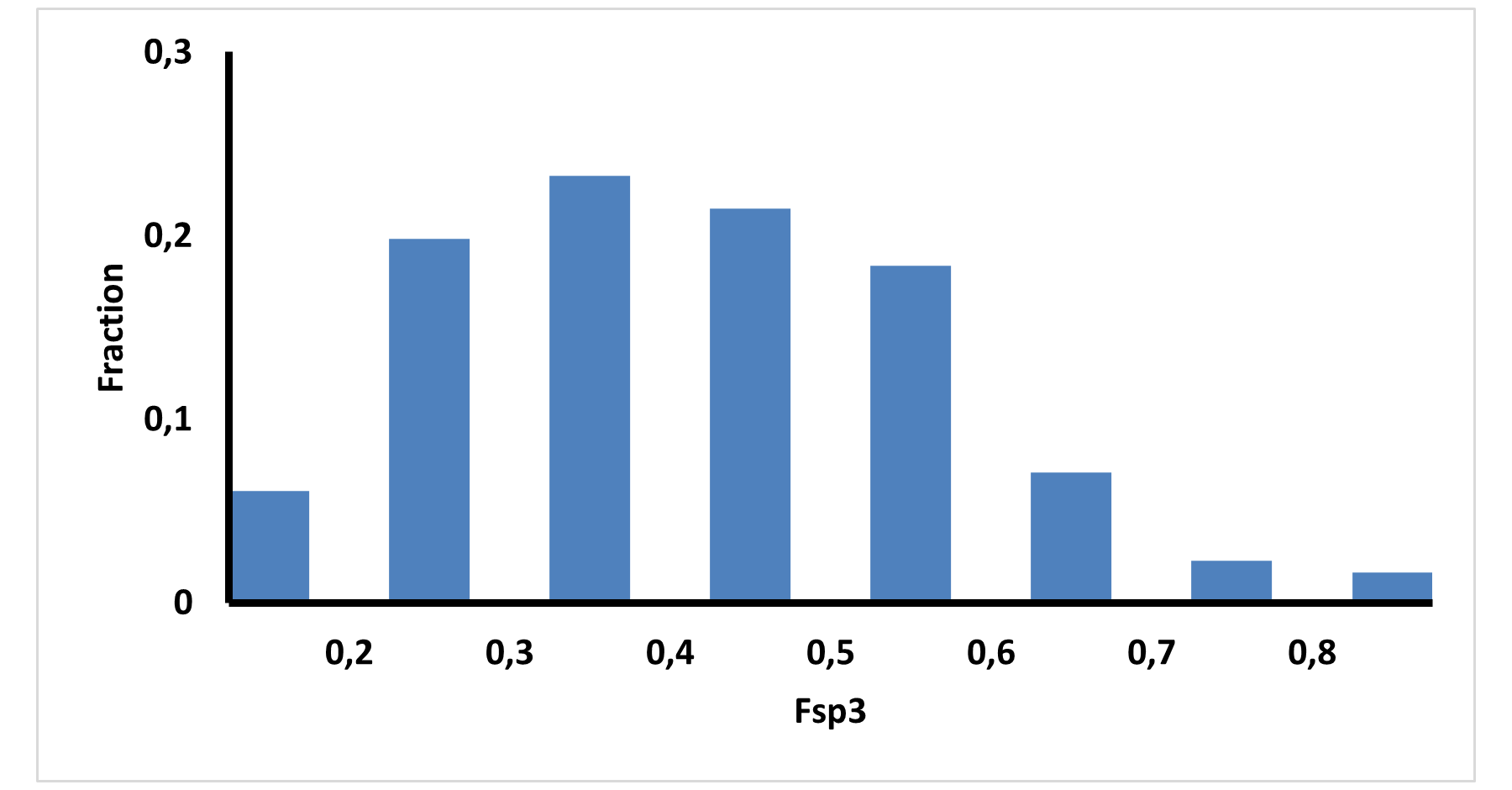
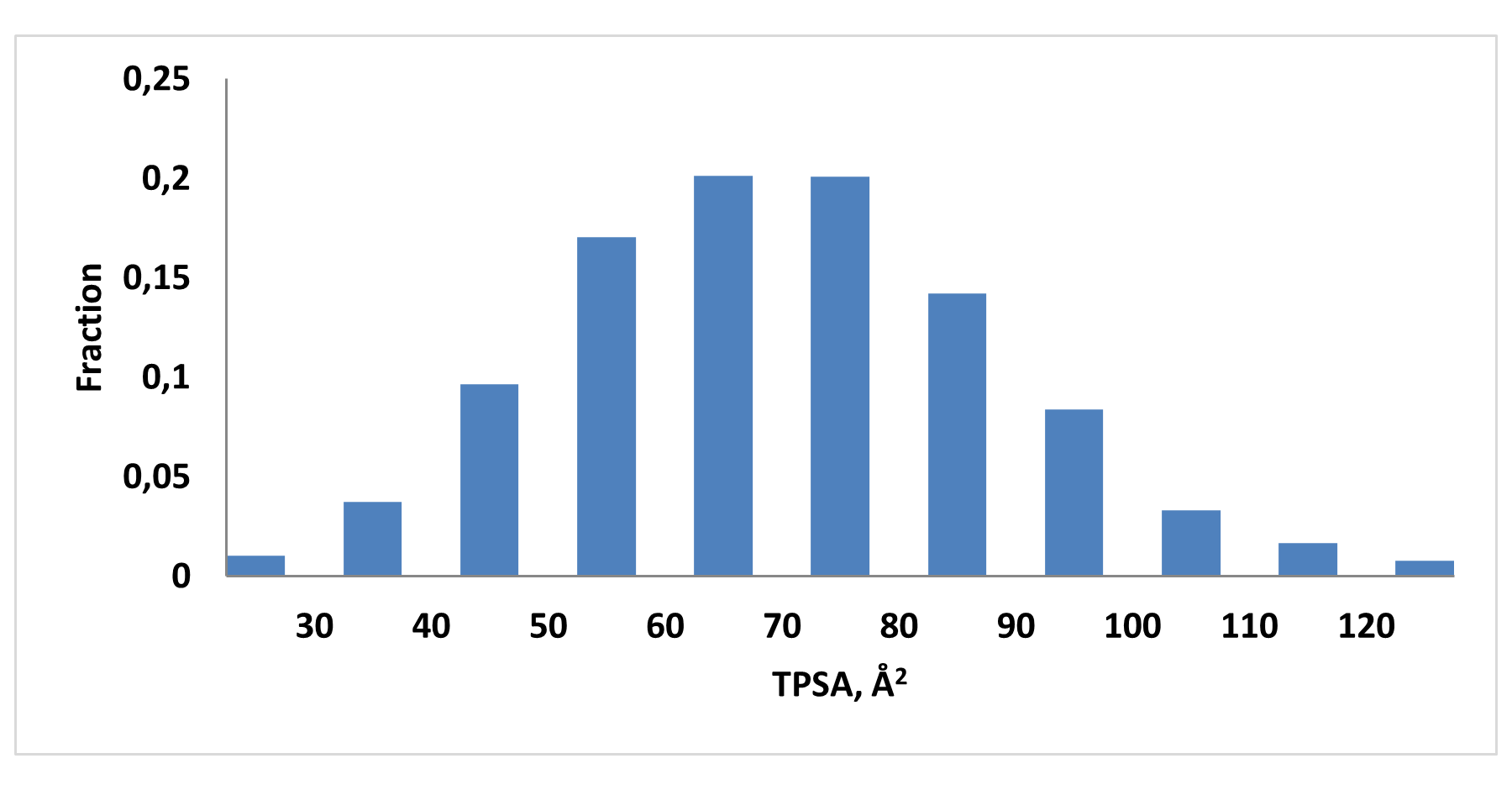
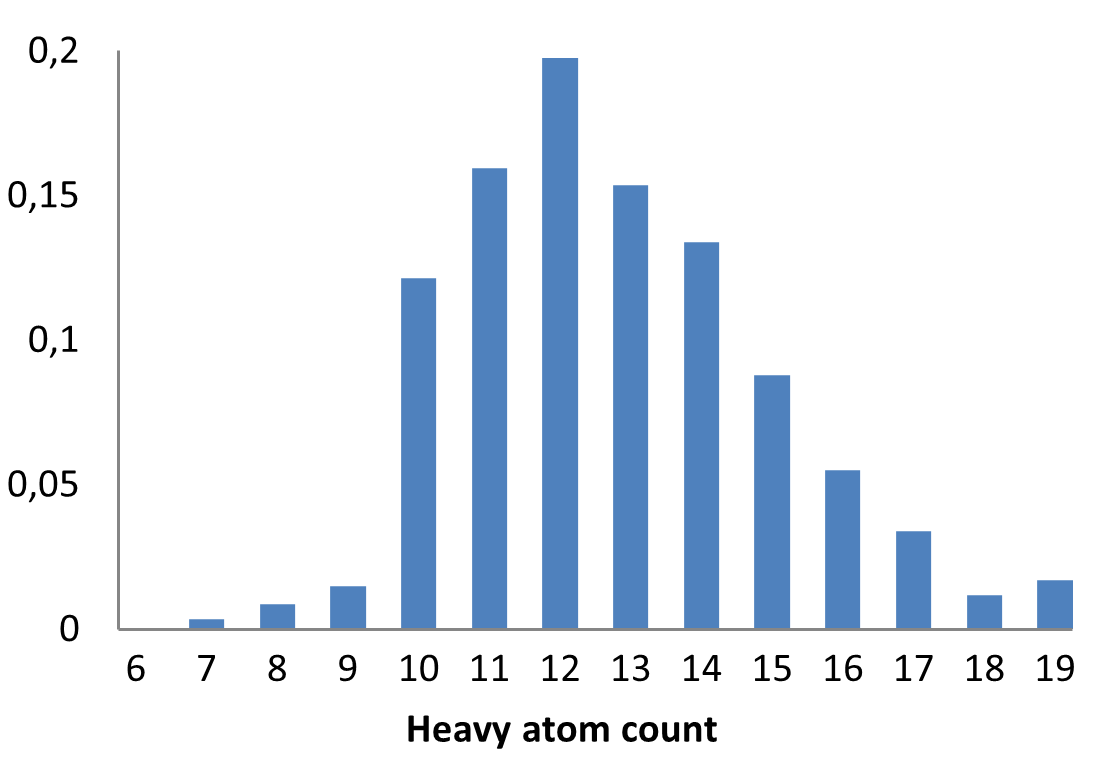
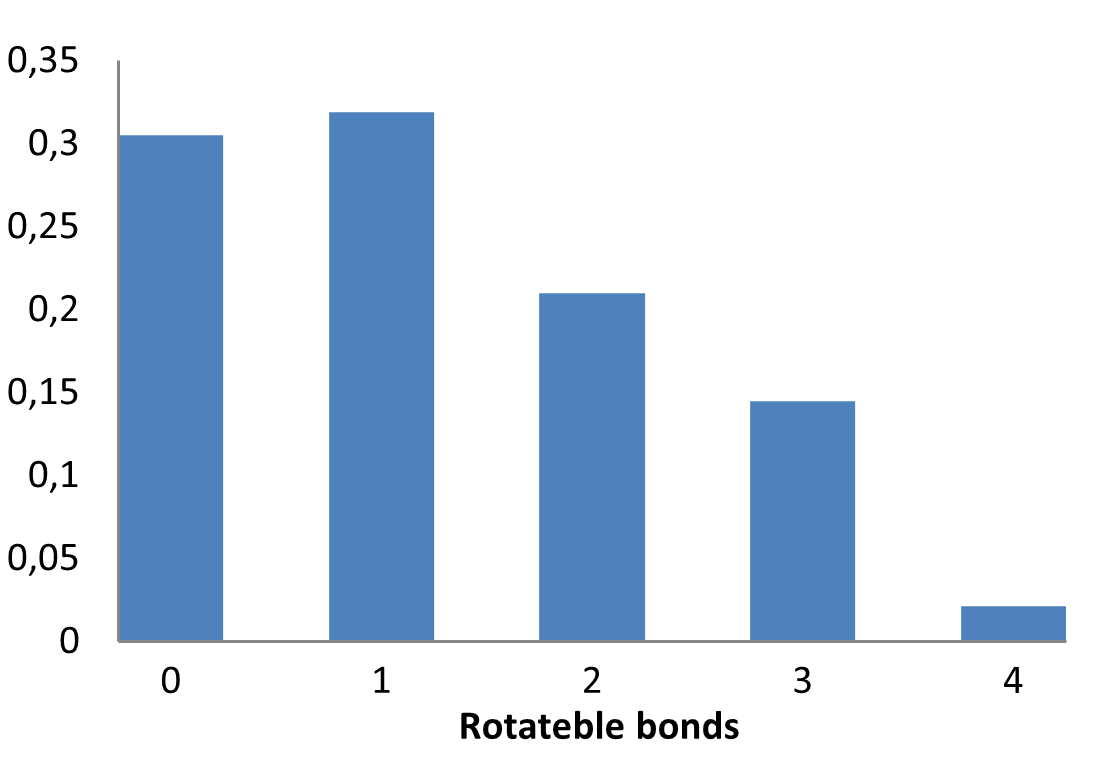
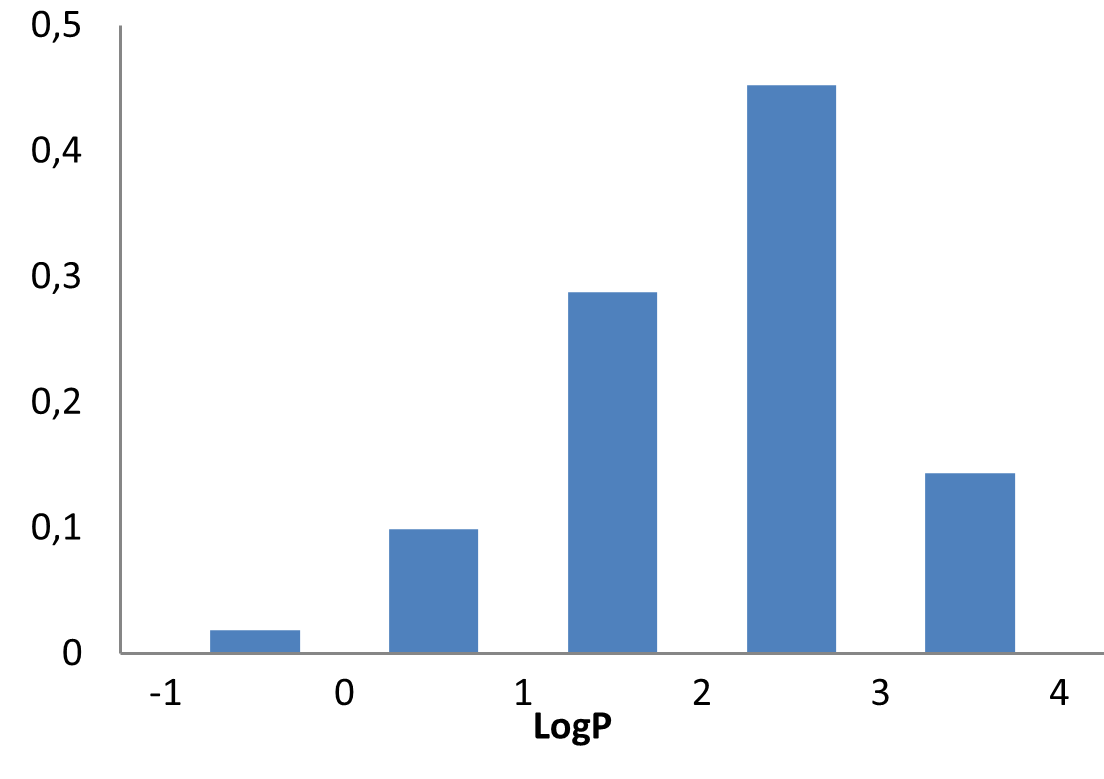
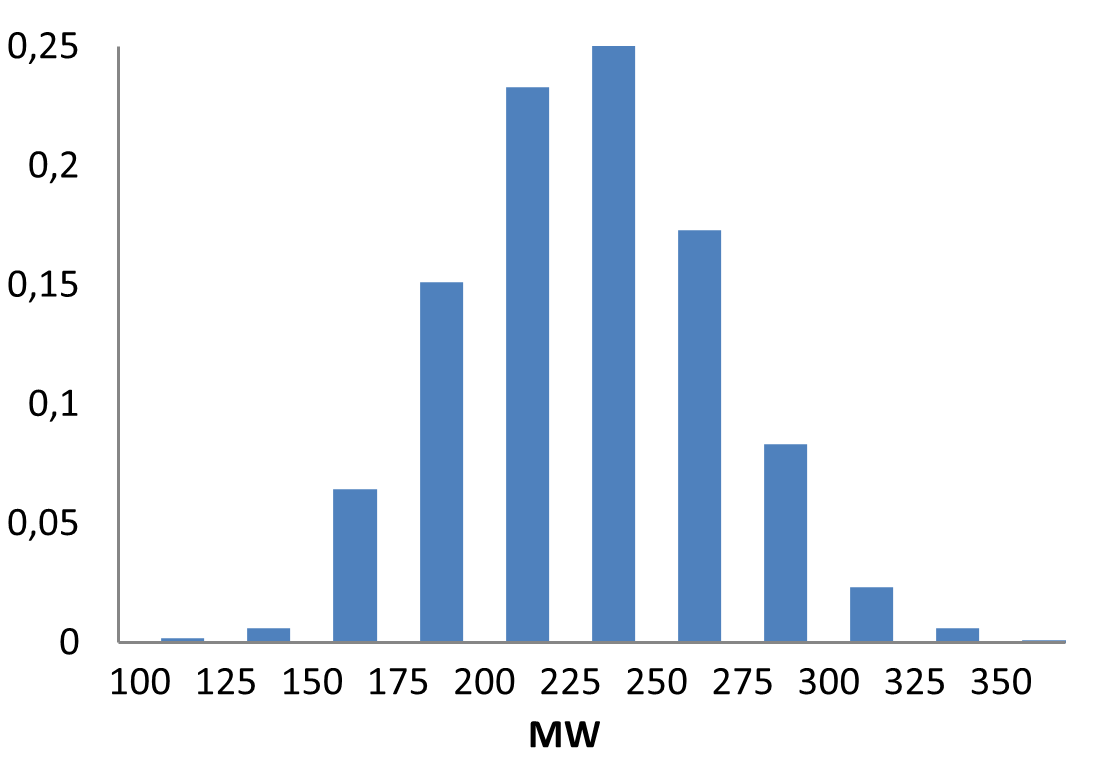
E-ASMS Library has been developed to accelerate the early stages of drug discovery by providing a diverse and well-characterized set of small molecules. Each compound has been selected to have only one chiral atom and be a mixture of only two enantiomers, which can be easily separated by using one of four standard and described in the paper conditions.
Additionally, the library is designed to maximize chemical space coverage, maintain drug‑like properties, and support efficient hit identification across diverse therapeutic areas. Rigorous quality control and SFC chiral separation of each compound ensures reproducibility and reliability, making this library a robust resource for screening campaigns.
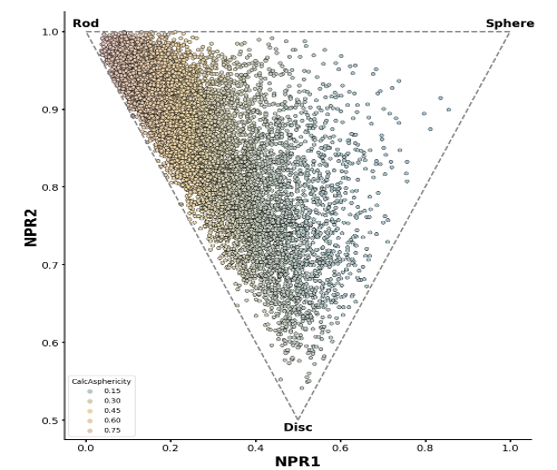
UMap projection to the entire enamine stock collection of 4.6 million compounds and PMI plot.

Each compound in the library is supported with pre-calculated analogs from stock and from REAL Space. Links to the files with calculated analogs are available from SD file in a separate column.
Analogs calculation and search in REAL Space
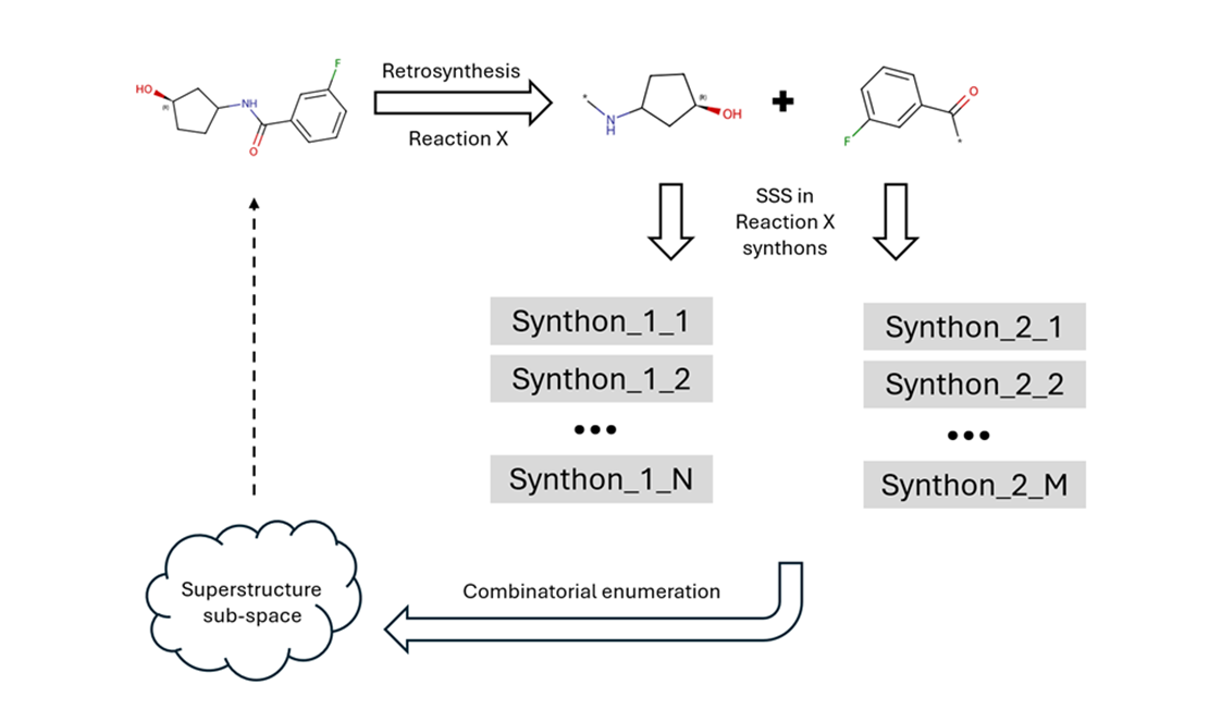
1. Reaction guided search of analogs
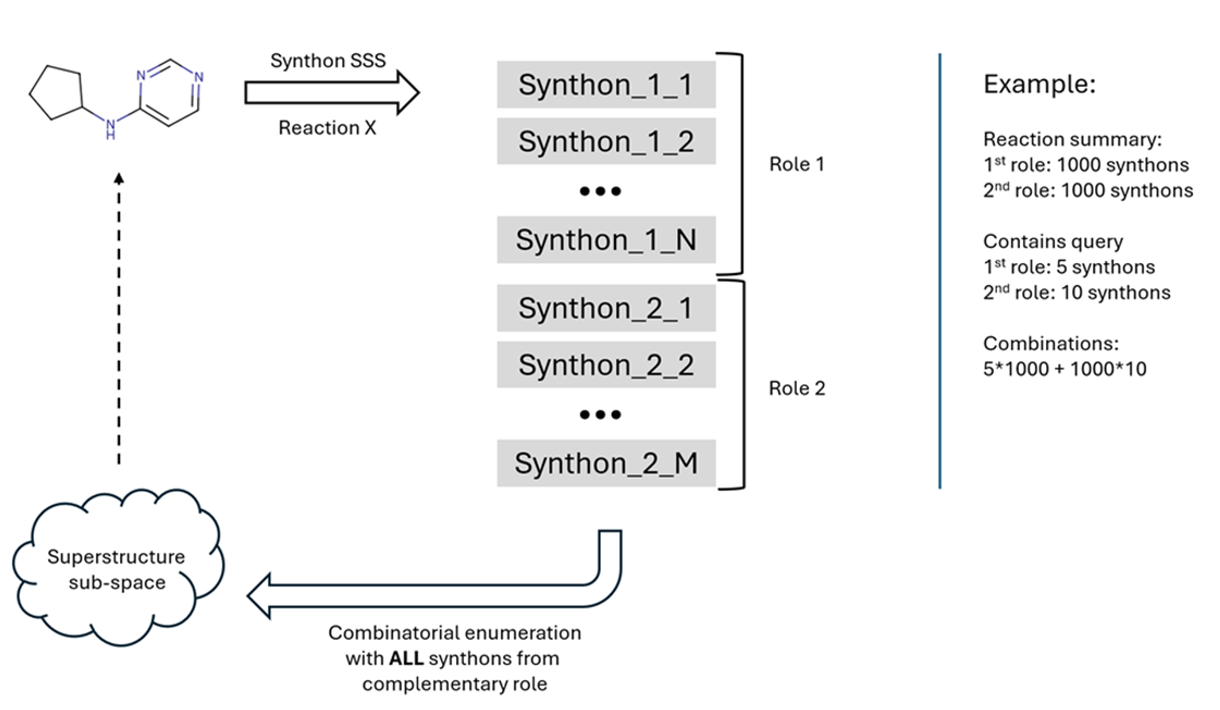
2. Synthon-based sub-structure search
We invite medicinal chemists, biologists, and drug hunters to integrate the E-ASMS Library into their discovery pipelines. By leveraging this curated library, researchers can rapidly identify novel scaffolds, explore structure activity relationships, and generate data that informs lead optimization process. Contact us today to access the library and accelerate your next breakthrough.
Support
We offer comprehensive support in developing your hit compounds. Naturally such programs are realised most efficiently when biological actives originate from our screening collection. However, even if the hit compounds are from the collections of other vendors lead identification and optimization projects can proceed most productively in our hands. Sometimes for this we only need to synthesize first examples of the given chemical series and validate synthesis route.
Most diverse halogen-enriched fragments
1 920 compounds
The concept of Halogen-Enriched Fragment Libraries (HEF) has gained significant traction in medicinal chemistry, supported by multiple successful screening campaigns.[1,2] These libraries are designed to explore halogen-mediated interactions, which can play a critical role in molecular recognition and binding affinity. Halogen bonding, the key interaction exploited by HEF, has been extensively studied since its initial discovery via X-ray crystallography.[3] Its electrostatic nature is now well understood, and it has been shown to significantly influence both selectivity and efficacy in drug-target interactions.[4,5,6]
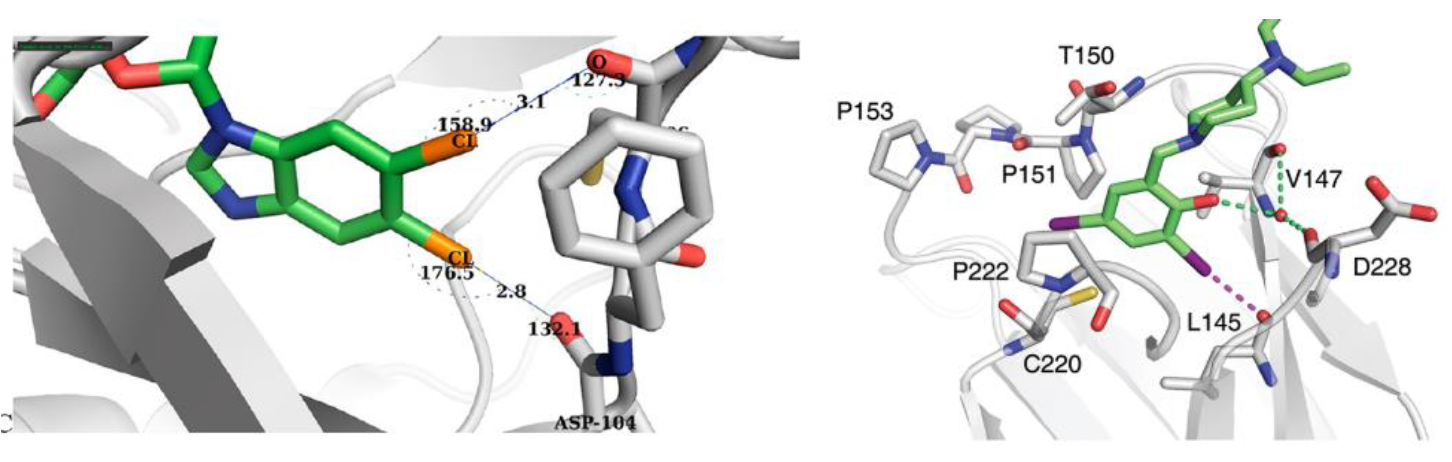
Halogen bonding through σ-hole interactions
A major factor in halogen bonding is the σ-hole, whose characteristics can be “tuned” by varying (hetero)aromatic ring systems and their substitution patterns. This tunability allows for precise control over interaction strength and directionality.
Enamine, a global leader in heterocyclic chemistry, has synthesized thousands of novel halogenated scaffolds, creating the most diverse collection of halogenated core heterocycles available. Our carefully designed Halogen-Enriched Fragment Library comprises the most relevant fragments for exploring affinity towards binding via these non-covalent halogen-mediated interactions.
Typical Formats
Catalog No.
HEF-1920-10-Y-100
Compounds
1 920
6 plates
Amount
10 µL of 100 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
384-well microplates, Echo qualified Labcyte, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
HEF-1920-25-X-100
Compounds
1 920
24 plates
Amount
25 µL of 100 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner Cat. No 650201, round (U) bottom, 1 & 12 columns empty, 80 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
HEF-1920-50-X-100
Compounds
1 920
24 plates
Amount
50 µL of 100 mM DMSO stock solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner Cat. No 650201, round (U) bottom, 1 & 12 columns empty, 80 compounds per plate
Price
Download SD files
Key features
- Diverse (hetero)aromatic fragments set for probing halogen bonds
- All compounds include at least one non-fluorine halogen atom
- No PAINS, only MedChem friendly compounds
- Express follow-up from stock and from Enamine REAL
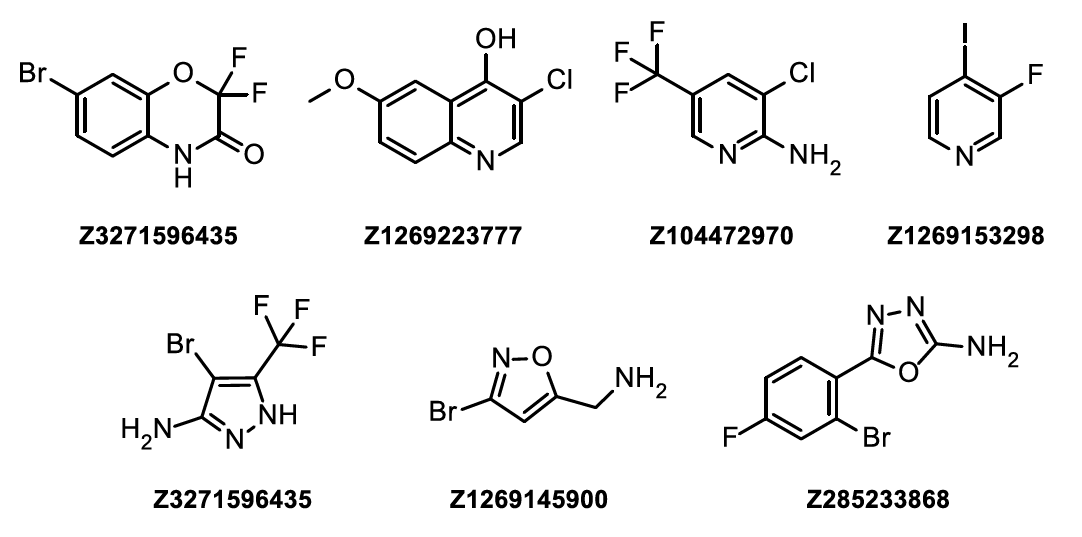
Examples of compounds from HEF Library
Library design
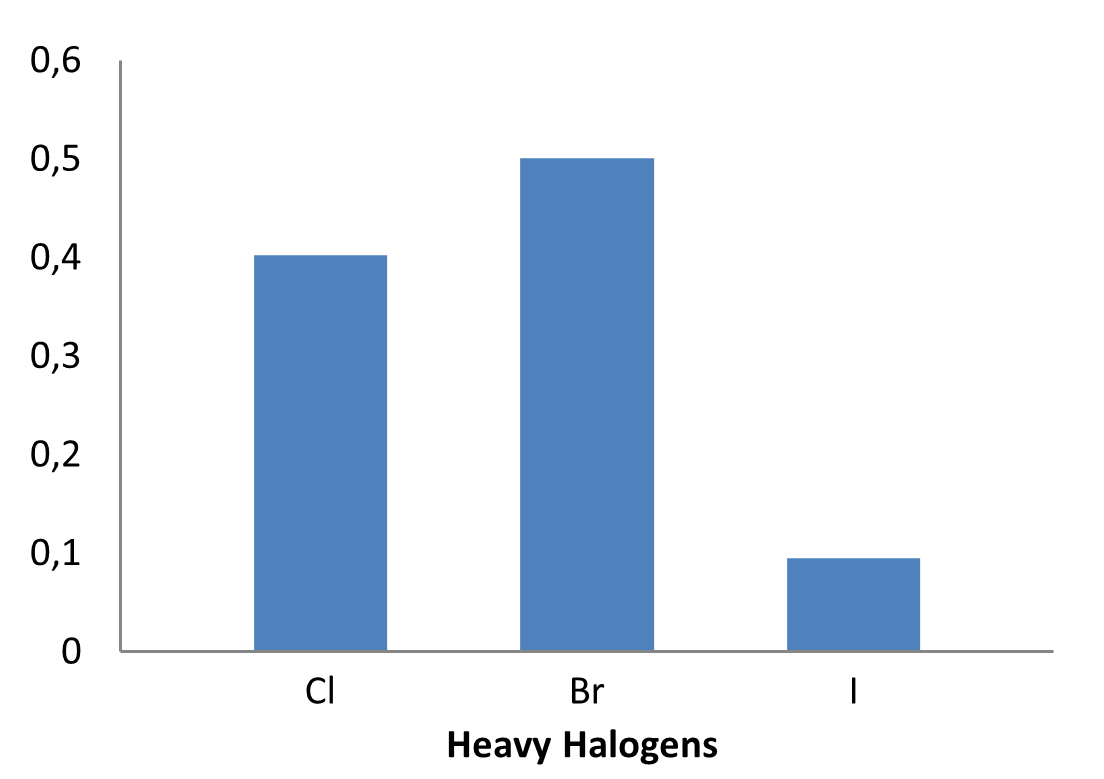
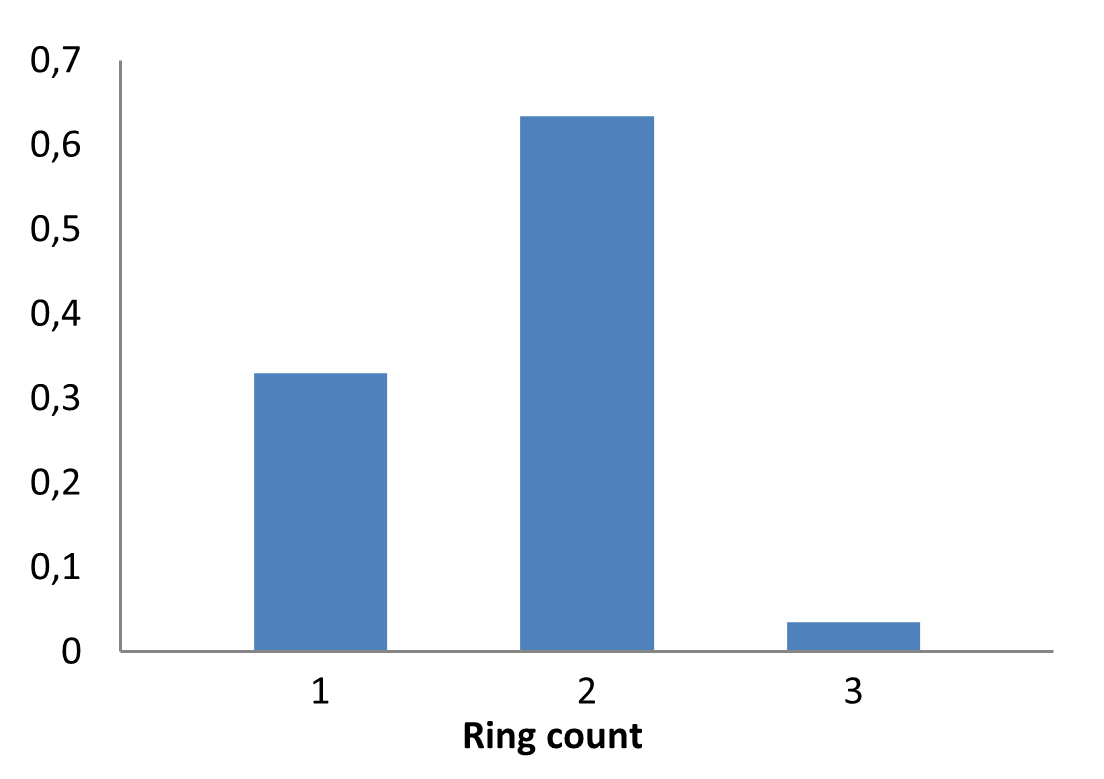
The fragment library was constructed from a curated database of over 250,000 compounds, all strictly compliant with the Rule of Three (Ro3) and filtered using medicinal chemistry criteria. Each compound includes at least one heavy halogen atom (Cl, Br, or I), with 95% containing only one. The distribution is as follows: 183 iodides (9.5%), 963 bromides (50.1%), and 684 chlorides (35.6%). The remaining 4.8% are dichloro derivatives. Additionally, the library includes 194 fluorinated compounds (10.1%). Fragments were selected with heavy atom counts (HA) ranging from 6 to 19, with a majority (1,206 fragments) falling within the 12–16 HA range. Each fragment contains between one and three rings, with 97% featuring one or two. We also included 154 fragments from 200 originally described as HEFLib by Frank M. Boeckler. Scaffold analysis revealed the most frequently occurring (hetero)aromatic ring systems.
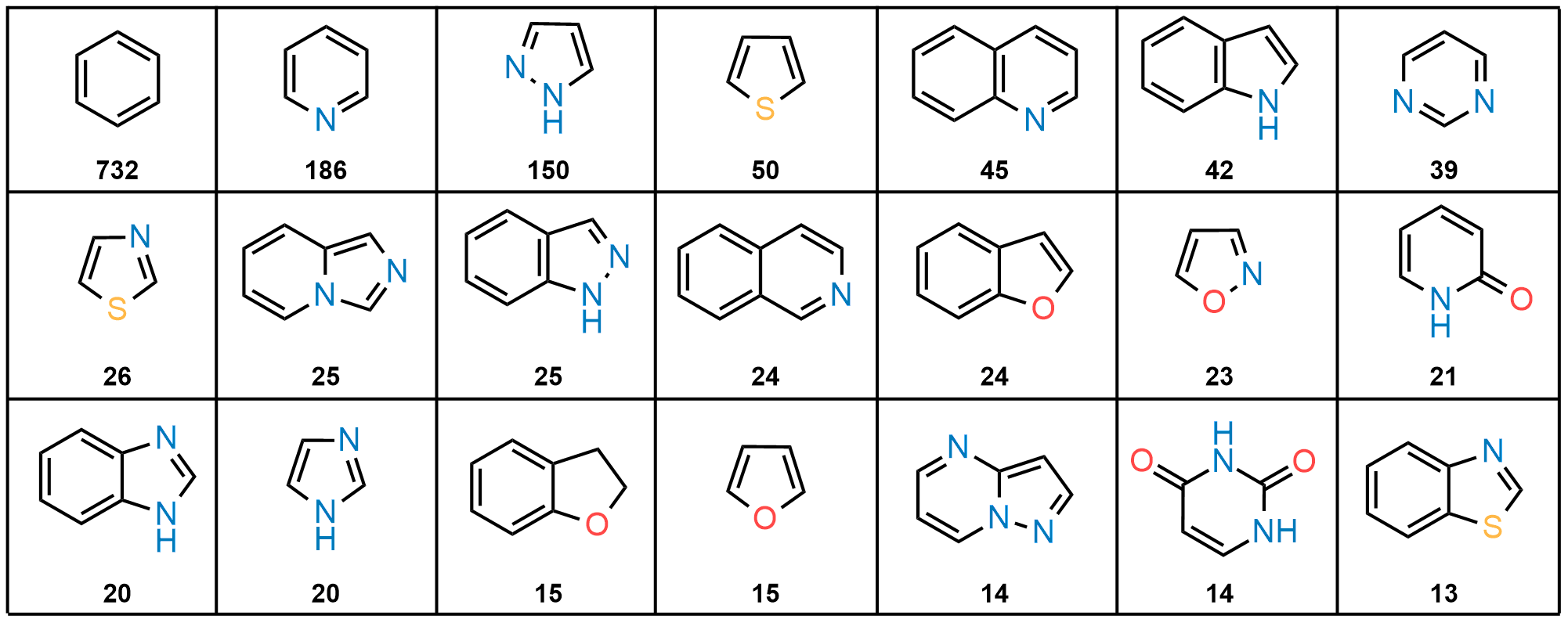
Most Frequently Used Heteroaromatic Ring Systems in the HEF Library
Selected publications
-
Embracing the Diversity of Halogen Bonding Motifs in Fragment-Based Drug Discovery—Construction of a Diversity-Optimized Halogen-Enriched Fragment Library.
J. Heidrich, L. E. Sperl, F. M. Boeckler Front. Chem. 2019, 7. DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00009 -
Halogen interactions in protein-ligand complexes: implications of halogen bonding for rational drug design.
S. Sirimulla, J. B. Bailey, R. Vegesna, M. Narayan J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2781–2791. DOI: 10.1021/ci400257k -
Ultrahigh resolution drug design I: Details of interactions in human aldose reductase-inhibitor complex at 0.66 Å.
E. I. Howard, R. Sanishvili, R. E. Cachau, A. Mitschler, B. Chevrier, P. Barth, V. Lamour, M. Van Zandt, E. Sibley, C. Bon, D. Moras, T. R. Schneider, A. Joachimiak, A. Podjarny Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2004, 55, 792–804. DOI: 10.1002/prot.20015 -
Halogen bonding: an electrostatically-driven highly directional noncovalent interaction.
P. Politzer, J. S. Murray, T. Clark Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7748–7757. DOI: 10.1039/C004189K -
Halogen bonding: the sigma-hole.
T. Clark, M. Hennemann, J. S. Murray, P. Politzer J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 291–296. DOI: 10.1007/s00894-006-0130-2 -
Halogen-Enriched Fragment Libraries as Leads for Drug Rescue of Mutant p53.
R. Wilcken, X. Liu, M. O. Zimmermann, T. J. Rutherford, A. R. Fersht, A. C. Joerger, F. M. Boeckler J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6810–6818. DOI: 10.1021/ja301056a
Curated selection of frequent hitters
83 compounds
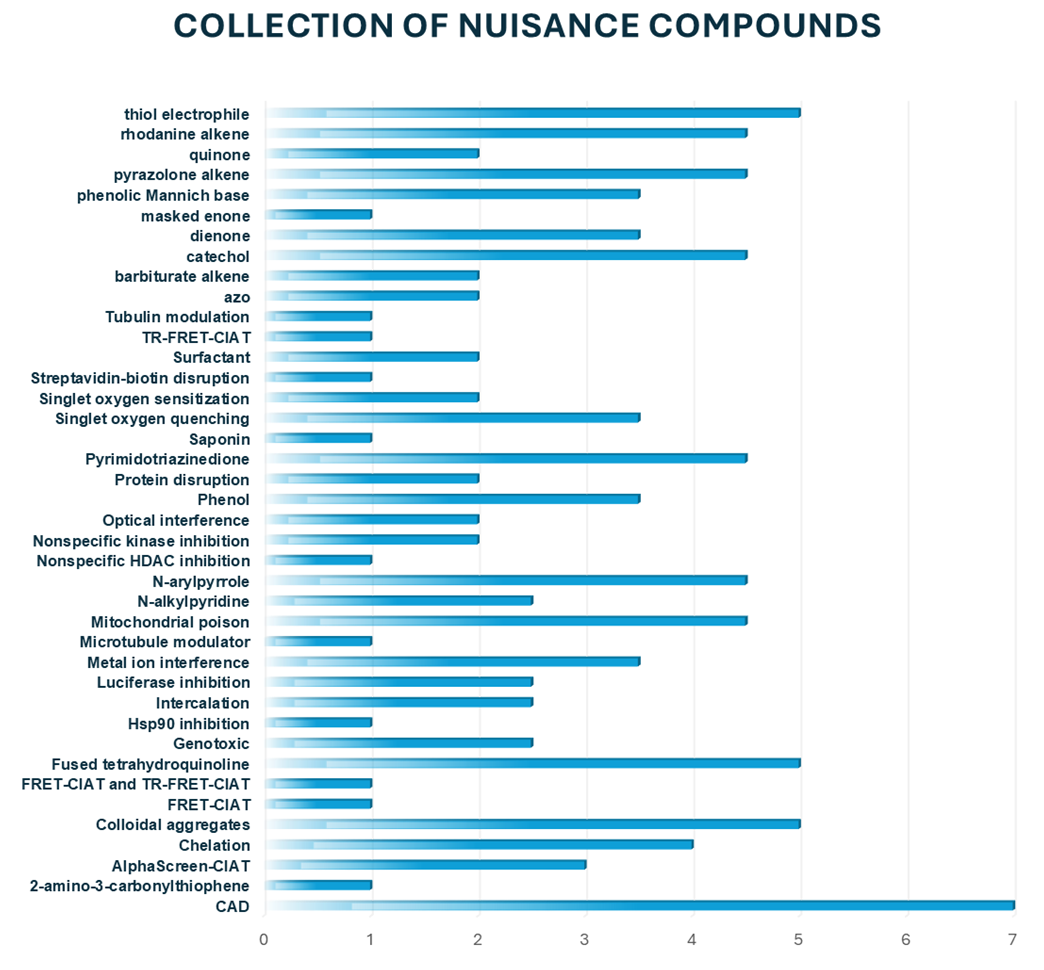
Nuisance compounds are commonly known for their interference with bioassay readouts in high-throughput screening (HTS), causing false positives that are inapplicable to the hit-finding process. Recently, Jonathan Baell provided a description of nuisance compound classes, including colloidal aggregates, PAINS (Pan-Assay Interference Compounds), electrophiles and redox cyclers, chelators, as well as optical and phenotypic assay interference compounds.
We provide a curated list of more than 80 nuisance chemicals known to obstruct assay readouts in target-based and phenotypic screenings. Conveniently available in an assay-ready screening plate, this nuisance compound set is expected to be of great interest to the research community, helping to develop high-quality HTS assays that yield promising, optimizable hits. Hits arising from this small set of nuisance compounds would be highly informative in screening campaigns, assisting target-owners in identifying the types of interference compounds that their assays might be susceptible to.
Most popular library formats available for immediate supply
Catalog No.
CONS-0-Z-10
Compounds
83
1 plate
Amount
≤ 300 nL of 10 mM of DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
1536 well, Echo Qualified 001-6969 (LP-0400), first four and last four columns empty, 1280 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
CONS-10-Y-10
Compounds
83
1 plate
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384 well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates 001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
Catalog No.
CONS-50-Y-10
Compounds
83
1 plate
Amount
50 μL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384 well, Echo Qualified LDV microplates 001-12782 (LP-0200), first and last two columns empty, 320 compounds per plate
Price
*We will be happy to provide our library in any other most convenient for your project format. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400) or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD files
Key features
- Enhances HTS assay reliability by addressing potential interference
- Over 40 different modes of action
- Readily accessible in an assay-ready screening plate
- References for compounds are available
Library design
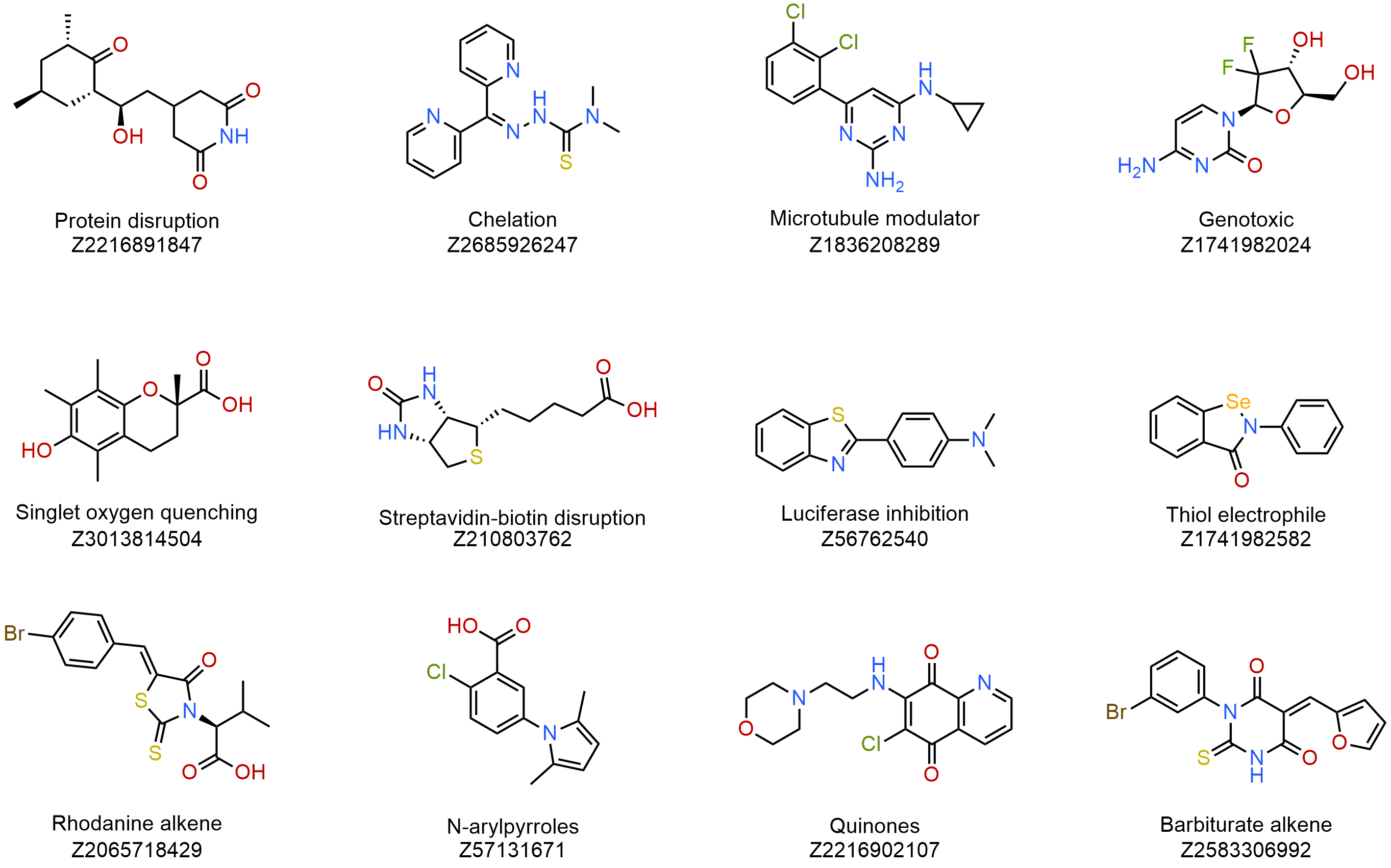
The global literature overview and data analysis served as the foundation for the design. Over 80 compounds are categorized based on their specific targets, structural elements, and types of interactions. The collection includes compounds widely recognized and validated as promiscuous across a range of independent and distinct screening methodologies.
Example of structures
Modulating protein function through small-molecule binding is a key therapeutic strategy for numerous diseases. Molecular Glues are a class of small molecules that induce proximity between a target protein and an E3 ubiquitin ligase, resulting in selective degradation of the target protein. Recent advances in the discovery of Molecular Glues have greatly expanded the potential of targeted protein degradation, opening new avenues in drug discovery—particularly for proteins previously considered “undruggable.”
Leveraging global expertise in drug discovery and the powerful capabilities of Enamine’s REAL Space, we have assembled focused libraries of Molecular Glues designed to engage multiple E3 ligases.
Product catalog
DCAF-5440
Size
5 440
compounds
Descriptions
Designed to target DCAF family of E3 ligases
Download file
IMiD Library
IMiD-4900
Size
4 900
compounds
Descriptions
Designed and specially synthesized for the discovery of Immunomodulatory Imide Drugs
Download file
CRBN-MG-4560
Size
4 560
compounds
Description
Designed to capture the widest possible range of novel chemotypes of CRBN binders, providing a foundation for the discovery of next-generation Molecular Glues
Download file
PAG-640
Size
640
compounds
Description
Built upon novel Phenyl Amino Glutarimide (PAG) analogs, these compounds combine structural innovation with potent activity — offering a fresh perspective in Molecular Glue design
Download file
PD-880
Size
880
compounds
Description
Chemical stability, cellular potency, and permeability are just a few of the advantages that make Phenyl Dihydrouracil (PD)-based CRBN ligands promising candidates for optimal Molecular Glue discovery
Download file
PG-800
Size
800
compounds
Description
Phenyl Glutarimide (PG)-based library was purposefully developed to expand the structural diversity space of Molecular Glues
Download file
Len Library
Len-640
Size
640
compounds
Description
Lenalidomide- and Pomalidomide-scaffold based — a time-tested backbone, reimagined for modern Molecular Glue design
Download file
AAG Library
AAG-1600
Size
1 600
compounds
Description
Acylated Amino Glutarimide (AAG) featuring 5- and 6-membered heterocyclic systems: a promising platform for the discovery of next-generation Molecular Glues
Download file
Avadomide library
AVD-560
Size
560
compounds
Descriptions
A special selection of new Avadomide analogs
Download file
Diverse CRBN Library
CRBN-960
Size
960
compounds
Descriptions
Designed to cover all structural diversity of CRBN binders, a key component of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex
Download file
CRBN Covalent Library
CCRBN-160
Size
160
compounds
Descriptions
A small selection of diverse covalent binders capable of interacting with CRBN
Download file
VHL ligands and intermediates
VHL-80
Size
80
compounds
Descriptions
A versatile tool for discovering new VHL-based degraders
Download file
Selected publications
-
Molecular Glues Begin to Stick.
Vitale G. C&EN Global Enterp. 2022, 100 (29), 20– 24. DOI: 10.1021/cen-10029-cover -
Big Pharma eyes a slew of molecular glues.
Braner S. C&EN Global Enterp. 2024, 102 (36), 10. DOI: 10.1021/cen-10236-buscon2
Support
We offer comprehensive support in developing your hit compounds. Naturally such programs are realised most efficiently when biological actives originate from our screening collection. However, even if the hit compounds are from the collections of other vendors lead identification and optimization projects can proceed most productively in our hands. Sometimes for this we only need to synthesize first examples of the given chemical series and validate synthesis route.
Designed for the discovery of new effective and safe treatment
2 500 compounds
Tuberculosis (TB) is among the most threatening diseases that can cause the next pandemic across the world. It is one of the most rampant infectious diseases owing largely to the methods of transmission and high death ratio. The absence of efficient treatment and the rapid appearance of drug resistance make TB one of the most emerging tasks to resolve in public health. Continuously mutated, Mtb remains one of the most dangerous and difficult-to-treat bacterial diseases. Lack of early diagnosis and the prevalence of resistant strains make TB extremely difficult for timely detection and treatment. Antituberculosis drug development is a high priority to prevent future pandemics. It needs further investment in scientific research and rational drug design to combat the high death rate caused by this disease.
The library is available in pre-plated formats for quick access and is supported with multiple benefits on hit follow-up studies:
- Analogs and hit samples resupply from dry stock of over 4.4 M compounds with immediate QC check.
- MedChem support in hit follow-up and optimization to lead series.
- Same-day ADME tests for design and synthesis prioritization.
Typical Formats
Catalog No.
ATB-2500-10-Y-10
Compounds
2 500
14 plates
Amount
10 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
384-well plates Greiner #781280, 320 compounds per plate, first two and last two columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
ATB-2500-50-X-10
Compounds
2 500
53 plates
Amount
50 µL of 10 mM DMSO solutions
Plates and formats
96-well plates, Greiner #650160, 80 compounds per plate, 1 & 12 columns empty
Price
Catalog No.
Library & follow-up package
Plates and formats
ATB-2500-10-Y-10 library, hit resupply from dry stock and fresh DMSO solutions plus 240+ analogs from stock and follow-up synthesis from REAL Space
Price
*We will happily provide our library in any other most convenient format for your project. Please select among the following our standard microplates: Greiner Bio-One 781270, 784201, 781280, 651201 or, Echo Qualified 001-12782 (LP-0200), 001-14555 (PP-0200), 001-6969 (LP-0400) or send your preferred labware. Compounds pooling can be provided upon request.
Download SD file
Library Design
To design the library and select the most promising molecules, we pay attention to the complexity of Mtb cell-wall and the difficulties of membrane penetration. Despite the absence of certain ruleless and defined filters, we tried to remove all compounds that could have issues with penetration based on the reported data and structure analysis of cell active vs inactive compounds.
Having studied some special features related to the biochemical pathways and morphological properties inherent to Mtb, a group of protein targets has been selected and prioritized to perform in silico screening (vHTS) and select compounds with the alleged activity. Generally, the protein targets in this library can be divided into two subsets: Cell Wall Synthesis-associated proteins and Mtb-specific Essential protein targets distinct from those present in eukaryotic organisms.
Alanine racemase (Alr), which catalyzes the interconversion of L-alanine and D-alanine. Which in turn plays a key role in peptidoglycan cross-linking.
dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase (RmlC) is involved in the biosynthesis of the dTDP-L-rhamnose which is required for connection of the galactan region of arabinogalactan to peptidoglycan molecule.
Enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase [NADH] (InhA) is involved in the biosynthesis of mycolic acids playing a key role in the fatty acid elongation process.
Decaprenylphosphoryl-beta-D-ribose oxidase (Dpre1) is a component of the complex that catalyzes the formation of decaprenyl-phospho-arabinose (DPA), a key precursor required for the synthesis of cell-wall arabinans.
N-Acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GLMU) is an enzyme that catalyzes the final two steps in the biosynthesis of UDP-GlcNAc and is essential for the synthesis of the lipid A of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Shikimate kinase (AroK) is necessary for the synthesis of the common precursor of aromatic amino acids and secondary metabolites by phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP. The amino acids biosynthesis is also a very attractive direction for drug design, particularly as it is represented with a broad family of enzymes.
Beta-lactamase responsible for resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Isocitrate lyase is in charge of the first step of the glyoxylate shunt, namely the synthesis of C4 dicarboxylic acids from C2 compounds.
ATPases (ClpC, ClpX) – chaperon proteins that induce degradation of proteins by bacterial proteasome. Play an essential role in bacterial proteostasis.
Mtb regulatory Serine Proteases (ClpP1P2) – serine proteases that form bacterial proteasomes and are responsible for protein homeostasis and degradation in bacteria.
Peptidyl tRNA hydrolase (Pth) is an essential Mtb-specific RNA hydrolase that participte in bacteria homeostasis and protein synthesis control.
The vHTS procedure assumes the application of grid-based representation of the binding site and designation of constraints based on literature data (mutation experiments) or ligand-protein interaction map with subsequent partial or full matching. Besides the rating of compounds by empirical docking score, the result conformations were also visually checked for the reliability of the binding mode. At the same time, the number of reference compounds against selected targets is relatively small and possesses a low degree of diversity inside each target-based reference set.
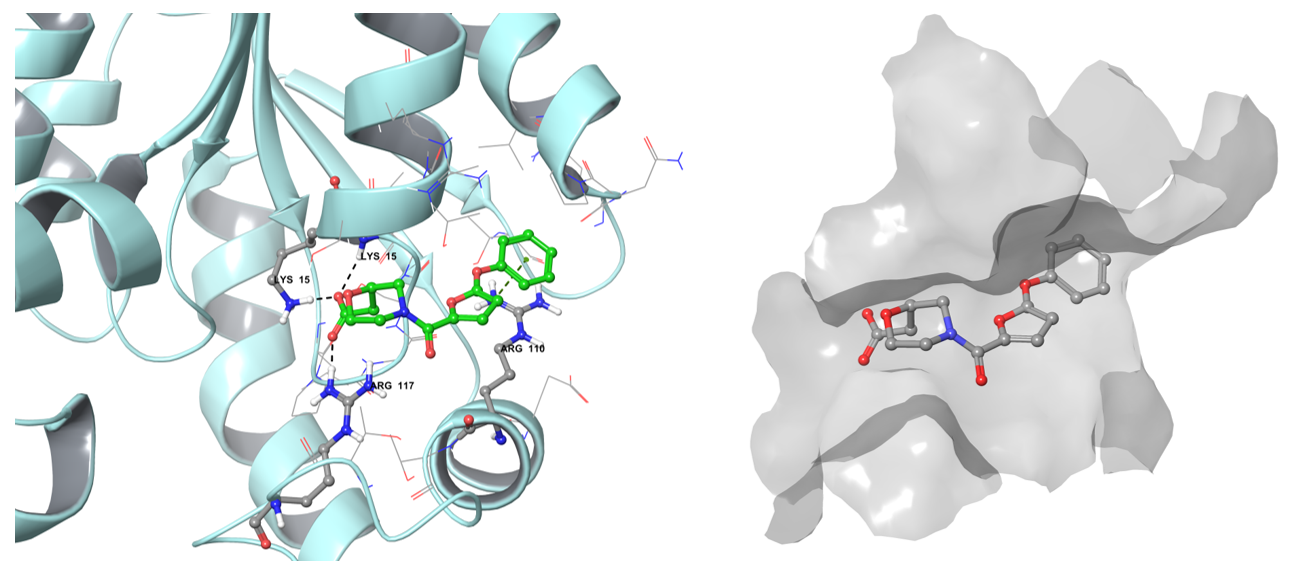
The example of the binding pose of Z1603549506 in the Shikimate kinase binding site.
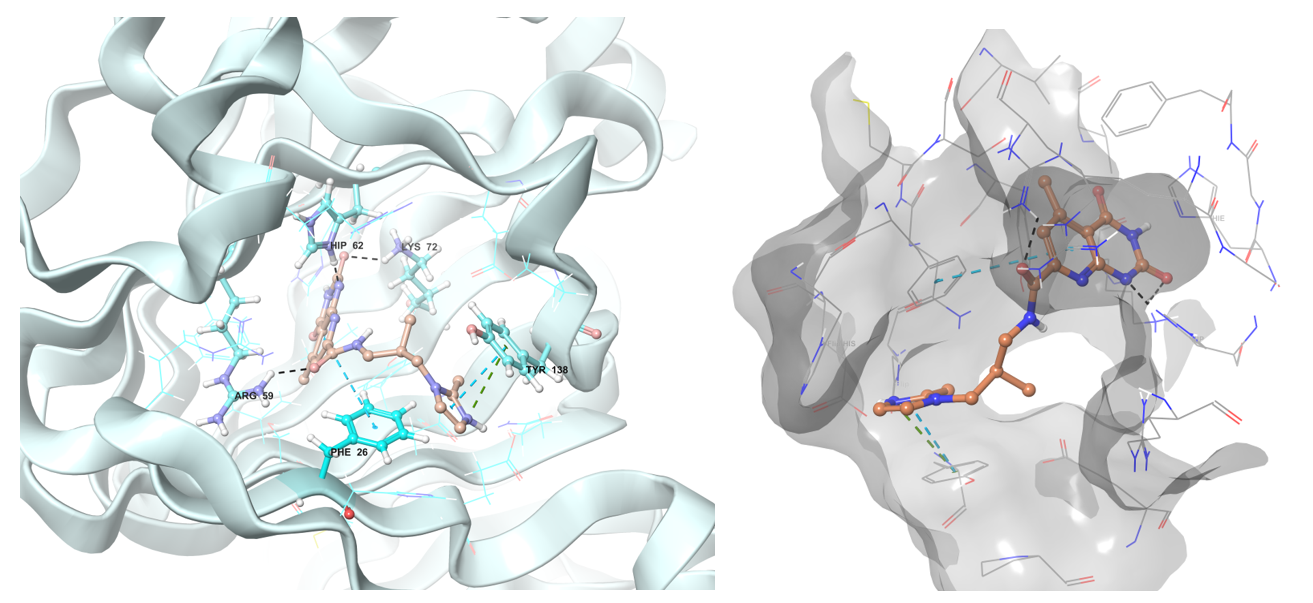
Predicted binding conformation in ribbon and shape protein representation of Z1313265676 to RmlC reductase.
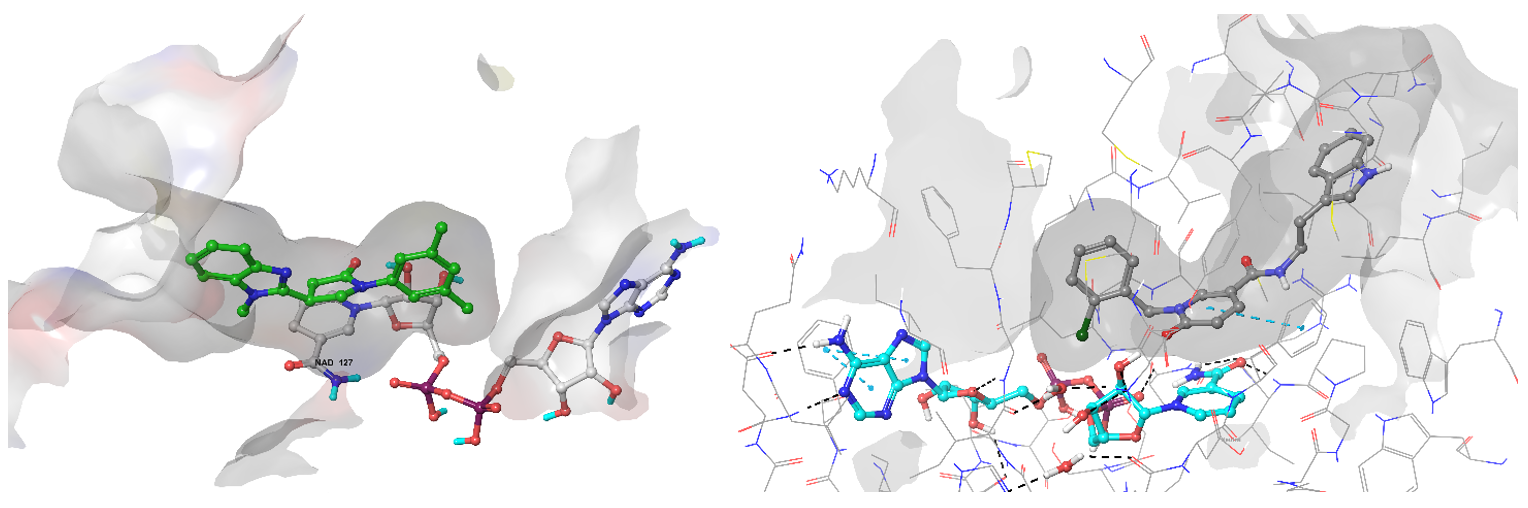
Examples of predicted hits Z111780734 (left) and Z189105794 binding conformation in the active site of InhA enzyme.
References
-
Consolidated Guidelines on Drug-resistant Tuberculosis Treatment
World Health Organization, 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/2019/consolidated-guidelines-drug-resistant-TB-treatment/en/ -
In Silico Strategies in Tuberculosis Drug Discovery
Macalino, S. J. Y.; Billones, J. B.; Organo, V. G.; Carrillo, M. C. O. Molecules2020, 25(3), 665. doi:10.3390/molecules25030665 -
Drug Resistance Characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates From Patients With Tuberculosis to 12 Antituberculous Drugs in China
Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Tan, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Gao, R.; Wan, B.; Yu, F. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.2019, 9, 345. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2019.00345 -
Mycobacterium enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase (InhA): A key target for antitubercular drug discovery
Prasad, M. S.; Bhole, R. P.; Khedekar, P. B.; Chikhale, R. V. Bioorg. Chem.2021, 115, 105242. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105242 -
Structural Basis for Inhibition of Enoyl-[Acyl Carrier Protein] Reductase (InhA) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
de Ávila, M. B.; Bitencourt-Ferreira, G.; de Azevedo, W. F. Curr. Med. Chem.2020, 27(5), 745-759. doi:10.2174/0929867326666181203125229 -
Discovery of New and Potent InhA Inhibitors as Anti-tuberculosis Agents: Structure Based Virtual Screening Validated by Biological Assays and X-ray Crystallography
Kamsri, P.; Hanwarinroj, C.; Phusi, N.; Punkvang, A. J. Chem. Inf. Model.2019, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00918 -
New InhA Inhibitors Based on Expanded Triclosan and Di-Triclosan Analogues to Develop a New Treatment for Tuberculosis
Chetty, S.; Armstrong, T.; Sharma Kharkwal, S. Pharmaceuticals2021, 14(4), 361. doi:10.3390/ph14040361 -
Drug discovery in tuberculosis. New drug targets and antimycobacterial agents
Campaniço, A.; Moreira, R.; Lopes, F. Eur. J. Med. Chem.2018, 150, 525-545. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.020 -
Recent Progress in the Development of Novel Mycobacterium Cell Wall Inhibitor to Combat Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Belete, T. M. Microbiol. Insights2022. doi:10.1177/11786361221099878 -
Virtual screening for identifying a putative inhibitor of rmlc, a major target protein in tuberculosis disease
Sunilkumar, B.; Basheera, S. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci.2015, 6, 616-628. -
Spinning sugars in antigen biosynthesis: characterization of the Coxiella burnetii and Streptomyces griseus TDP-sugar epimerases
Cross, A.; Roy, S. J. Biol. Chem.2022, 298(5), 101903. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101903 -
High-resolution structures of RmlC from Streptococcus suis in complex with substrate analogs locate the active site of this class of enzyme
Dong, C.; Major, L. L.; Allen, A.; Blankenfeldt, W. Structure2003, 11(6), 715-723. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00098-4 -
Synthetic molecules as DprE1 inhibitors: A patent review
Imran, M.; A S, A.; Thabet, H. K.; Abida; Bakht, M. A. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat.2021, 31(8), 759-772. doi:10.1080/13543776.2021.1902990 -
Inhibiting Mycobacterium tuberculosis within and without
Cole, S. T. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B2016, 371, 20150506. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0506 -
Advances in Key Drug Target Identification and New Drug Development for Tuberculosis
Mi, J.; Gong, W.; Wu, X. Biomed. Res. Int.2022, Article ID 5099312. doi:10.1155/2022/5099312 -
Genome-wide requirements for Mycobacterium tuberculosis adaptation and survival in macrophages
Rengarajan, J.; Bloom, B. R.; Rubin, E. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.2005, 102(23), 8327-8332. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503272102 -
Identification of cell wall synthesis inhibitors active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by competitive activity-based protein profiling
Li, M.; Patel, H. V.; Cognetta, A. B. 3rd; et al. Cell Chem. Biol.2022, 29(5), 883-896.e5. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.09.002 -
Characterization of M. tuberculosis SerB2, an essential HAD-family phosphatase, reveals novel properties
Yadav, G. P.; Shree, S.; Maurya, R.; et al. PLoS One2014, 9(12), e115409. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115409 -
High throughput screen identifies small molecule inhibitors specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoserine phosphatase
Arora, G.; Tiwari, P.; Mandal, R. S.; et al. J. Biol. Chem.2014, 289(36), 25149-25165. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.597682 -
Regulatory Mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Phosphoserine Phosphatase SerB2
Grant, G. A. Biochemistry2017, 56(49), 6481-6490. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01082 -
Targeting the Serine Pathway: A Promising Approach against Tuberculosis?
Haufroid, M.; Wouters, J. Pharmaceuticals2019, 12(2), 66. doi:10.3390/ph12020066 -
Characterization of M. tuberculosis SerB2, an essential HAD-family phosphatase, reveals novel properties
Yadav, G. P.; Shree, S.; Maurya, R.; et al. PLoS One2014, 9(12), e115409. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115409 -
Identification of cell wall synthesis inhibitors active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by competitive activity-based protein profiling
Li, M.; Patel, H. V.; Cognetta, A. B. 3rd; et al. Cell Chem. Biol.2022, 29(5), 883-896.e5. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.09.002