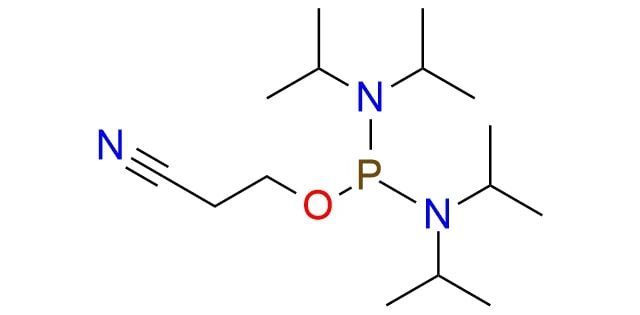
CAS 102691-36-1, Cat. No EN300-239576
Reagent for phosphitylation of DNA or RNA fragments
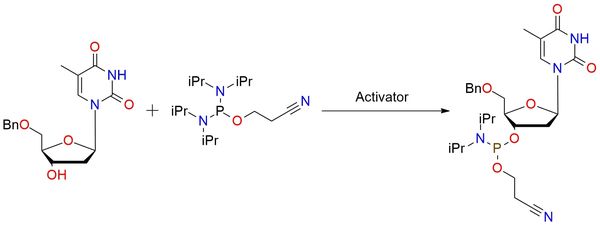
2-Cyanoethyl tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite is a phosphinylation reagent for DNA and RNA fragment synthesis that became very important in this field of study1. It is a colorless liquid that is shelf-stable and well-soluble in most organic solvents2. The reagent is stable for hydrolysis and offers an easy procedure that requires only an activator, such as EN300-77565, and no heating. After the reaction, which usually takes one night, the product can be easily purified by chromatography.
Synonyms: bis(N,N-diisopropylamino)-2-cyanoethoxyphosphine; (2-cyanoethoxy) bis(N,N-diisopropylamino)- phosphine, 2-cyanoethyl N,N,N,N -tetraisopropylphosphordiamidite
Selected publication
-
Highly Efficient Chemical Synthesis of 2′-O-Methyloligoribonucleotides and Tetrabiotinylated Derivatives; Novel Probes That Are Resistant to Degradation by RNA or DNA Specific Nucleases.
Sproat B.; Lamond A.; Beijer B.; Neuner P.; Ryder U. Nucleic Acids Res 1989, 17 (9), 3373–3386. DOI: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3373
-
2-Cyanoethyl Tetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite.
Beaucage S. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2003. DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rn00312