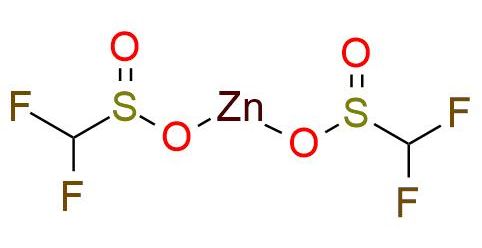
CAS 1355729-38-2, Cat. No EN300-138725
Reagent for the innate difluoromethylation of organic substrates
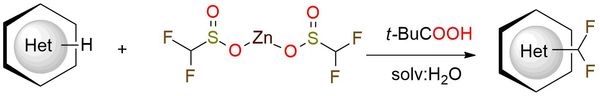
DFMS is a zinc sulphinate reagent that revolutionizes C-H difluoromethylation methods1,2. This reagent offers a rapid, scalable, and operationally simple approach under air, enabling the efficient introduction of difluoromethyl groups while maintaining excellent functional group compatibility (including COOR, COR, Hlg, CN) and substrate affinity3,4. DFMS is a source of difluoromethyl free radicals, which subsequently form new HF2C-C bonds upon addition to heteroarenes. This transformation allows for the incorporation of difluoromethyl groups into diverse target molecules. It is worth noting that commercially available DFMS may contain concomitant impurities such as ZnCl2 and H2O. While these impurities do not negatively impact the reaction, they should be considered when calculating the reaction stoichiometry4.
Synonyms: zinc difluoromethanesulfinate; zinc(II) difluoromethanesulfinate; DFMS
Selected publication
-
Practical and Innate Carbon–Hydrogen Functionalization of Heterocycles.
Fujiwara Y.; Dixon J.; O’Hara F.; Funder E.; Dixon D.; Rodriguez R.; Baxter R.; Herlé B.; Sach N.; Collins M.; Ishihara Y.; Baran P. Nature 2012, 492 (7427), 95–99. DOI: 10.1038/nature11680
-
Substitutions by Nucleophilic Free Radicals: A New General Reaction of Heteroaromatic Bases.
Minisci F.; Fontana F.; Vismara E. J Heterocycl Chem 1990, 27 (1), 79–96. DOI: 10.1002/jhet.5570270107
-
Metal‐Catalyzed Direct Difluoromethylation Reactions.
Rong J.; Ni C.; Hu J. Asian J Org Chem 2017, 6 (2), 139–152. DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201600509
-
A New Reagent for Direct Difluoromethylation.
Fujiwara Y.; Dixon J.; Rodriguez R.; Baxter R.; Dixon D.; Collins M.; Blackmond D.; Baran P. J Am Chem Soc 2012, 134 (3), 1494–1497. DOI: 10.1021/ja211422g