CAS 3240-34-4, Cat. No EN300-43675
Reagent for sulfonyl fluoride synthesis, promoter of Hoffman rearrangement
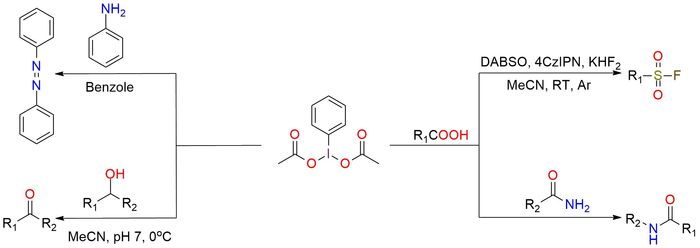
(Diacetoxyiodo)benzene is a useful hypervalent iodine reagent, used in various transformations. It is a stable white solid with good solubility in AcOH, MeCN, and CH2Cl21. The reagent can provide diverse oxidation reactions, such as alcohol oxidation (with a catalytic amount of TEMPO)1. Additionally, it can be used in the oxidation of anilines to facilitate intramolecular azo group formation. Recently, innovative protocols have emerged2, enabling the use of (diacetoxyiodo)benzene in Hoffmann rearrangement reactions and the synthesis of aliphatic sulfonyl fluorides. The Hoffmann rearrangement protocol stands out for its metal-free, acid/base-free, and additive-free nature. It exhibits a broad substrate scope and excellent compatibility with various functional groups. This protocol can yield satisfactory results even when working with sterically hindered alkyl groups, such as isopropyl or adamantyl. The sulfonyl fluoride synthesis procedure offers a convenient one-pot reaction that can be executed either through a photocatalytic process or with moderate heating.
Synonyms: (diacetoxyiodo)benzene; DIB; iodobenzene diacetate; IBD; (acetyloxy)(phenyl)-lambda3-iodanyl acetate; iodosobenzene I,I-diacetate
Selected publication
-
(Diacetoxyiodo)Benzene.
Moriarty R.; Chany C.; Kosmeder J.; Bois J. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2006. DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rd005m.pub2
-
Hypervalent Iodine Reagent-Promoted Hofmann-Type Rearrangement/Carboxylation of Primary Amides.
Wang X.; Yang P.; Hu B.; Zhang Q.; Li D. J Org Chem 2021, 86 (3), 2820–2826. DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c02767