Br. J. Pharmacol. , 2014, 171 (22), 5059-5075
DOI: 10.1111/bph.12863
Background and Purpose
HIV-1 transcription is activated by the Tat protein which recruits the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK9/cyclin T1 to TAR RNA. Tat binds to protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) through the Q35VCF38 sequence and translocates PP1 to the nucleus. PP1 dephosphorylates CDK9 and activates HIV-1 transcription. We have synthesized a low MW compound 1H4, that targets PP1 and prevents HIV-1 Tat interaction with PP1 and inhibits HIV-1 gene transcription. Here, we report our further work with the 1H4-derived compounds and analysis of their mechanism of action.
Experimental Approach
Using the 1H4-PP1 complex as a model, we iteratively designed and synthesized follow-up libraries that were analysed for the inhibition of HIV-1 transcription and toxicity. We also confirmed the mechanism of action of the PP1-targeting molecules by determining the affinity of binding of these molecules to PP1, by analysing their effects on PP1 activity, disruption of PP1 binding to Tat and shuttling of PP1 to the nucleus.
Key Results
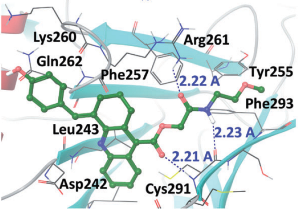
We identified a tetrahydroquinoline derivative, compound 7, which disrupted the interaction of Tat with PP1. We further optimized compound 7 and obtained compound 7c, renamed 1E7-03, which inhibited HIV-1 with low IC50 (fivefold lower than the previously reported compound, 1H4), showed no cytotoxicity and displayed a plasma half-life greater than 8 h in mice. 1E7-03 bound to PP1 in vitro and prevented shuttling of PP1 into the nucleus.
Conclusions and Implications
Our study shows that low MW compounds that functionally mimic the PP1-binding RVxF peptide can inhibit HIV-1 transcription by deregulating PP1.
Ammosova T.; Platonov M.; Ivanov A.; Kont Y. S.; Kumari N.; Kehn-Hall K.; Jerebtsova M.; Kulkarni A. A.; Üren A.; Kovalskyy D.; Nekhai S.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171 (22), 5059-5075
DOI: 10.1111/bph.12863